Page 16-18
The result is ‘H=((X+1)*h0+a)/(X^2+(k+1)*X+k)’.
To find the solution to the ODE, h(t), we need to use the inverse Laplace
transform, as follows:
OBJ ƒ ƒ Isolates right-hand side of last expression
ILAP μ Obtains the inverse Laplace transform
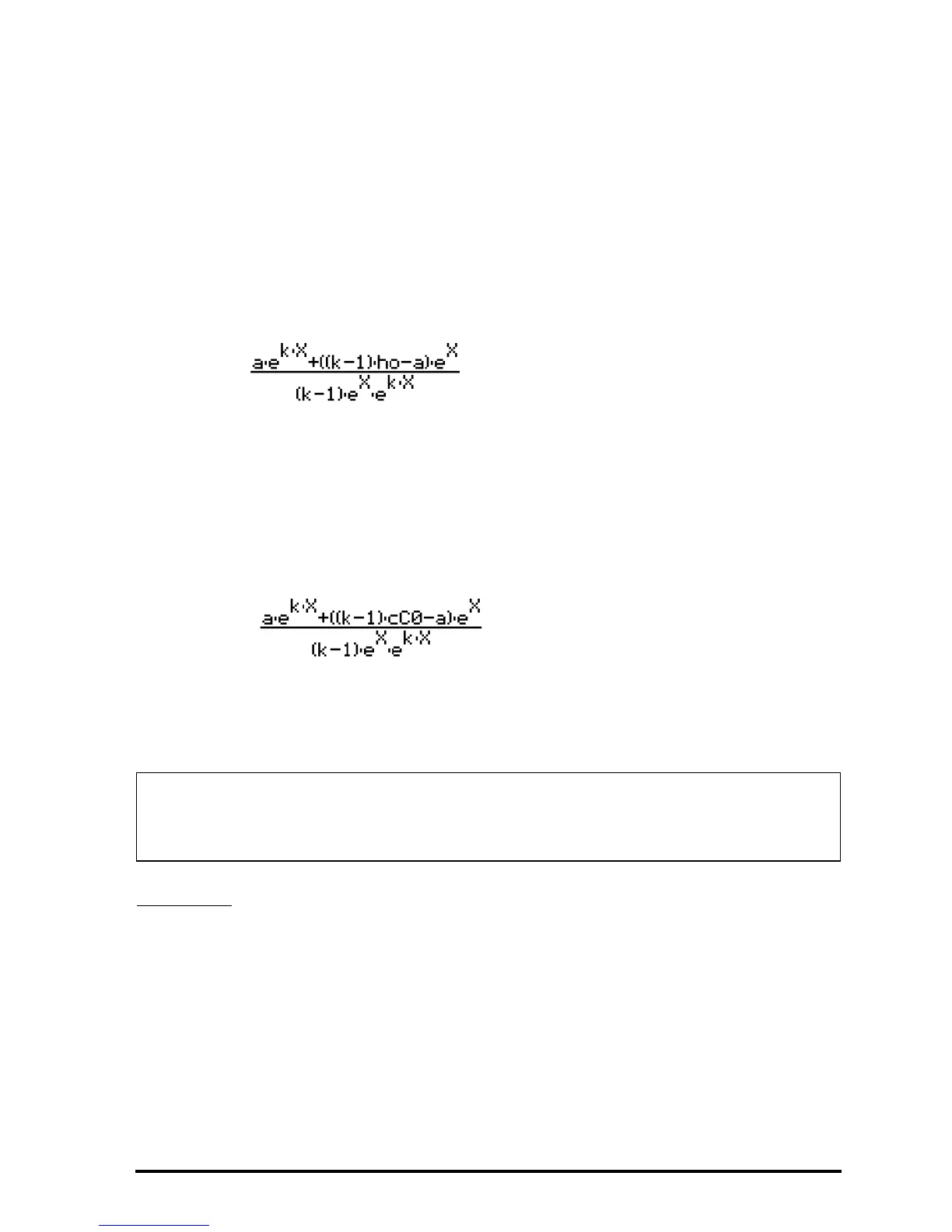
The result is . Replacing X with t in this expression and
simplifying, results in h(t) = a/(k-1)⋅e
-t
+((k-1)⋅h
o
-a)/(k-1)⋅e
-kt
.
Check what the solution to the ODE would be if you use the function LDEC:
‘a*EXP(-X)’ ` ‘X+k’ ` LDEC μ
The result is: , i.e.,
h(t) = a/(k-1)⋅e
-t
+((k-1)⋅cC
o
-a)/(k-1)⋅e
-kt
.
Thus, cC0 in the results from LDEC represents the initial condition h(0).
Example 2
– Use Laplace transforms to solve the second-order linear equation,
d
2
y/dt
2
+2y = sin 3t.
Using Laplace transforms, we can write:
L{d
2
y/dt
2
+2y} = L{sin 3t},
L{d
2
y/dt
2
} + 2⋅L{y(t)} = L{sin 3t}.
Note: When using the function LDEC to solve a linear ODE of order n in f(X),
the result will be given in terms of n constants cC0, cC1, cC2, …, cC(n-1),
representing the initial conditions f(0), f’(0), f”(0), …, f
(n-1)
(0).

 Loading...
Loading...




