Page 16-46
The continuous spectrum, F(ω), is calculated with the integral:
This result can be rationalized by multiplying numerator and denominator by
the conjugate of the denominator, namely, 1-iω. The result is now:
which is a complex function.
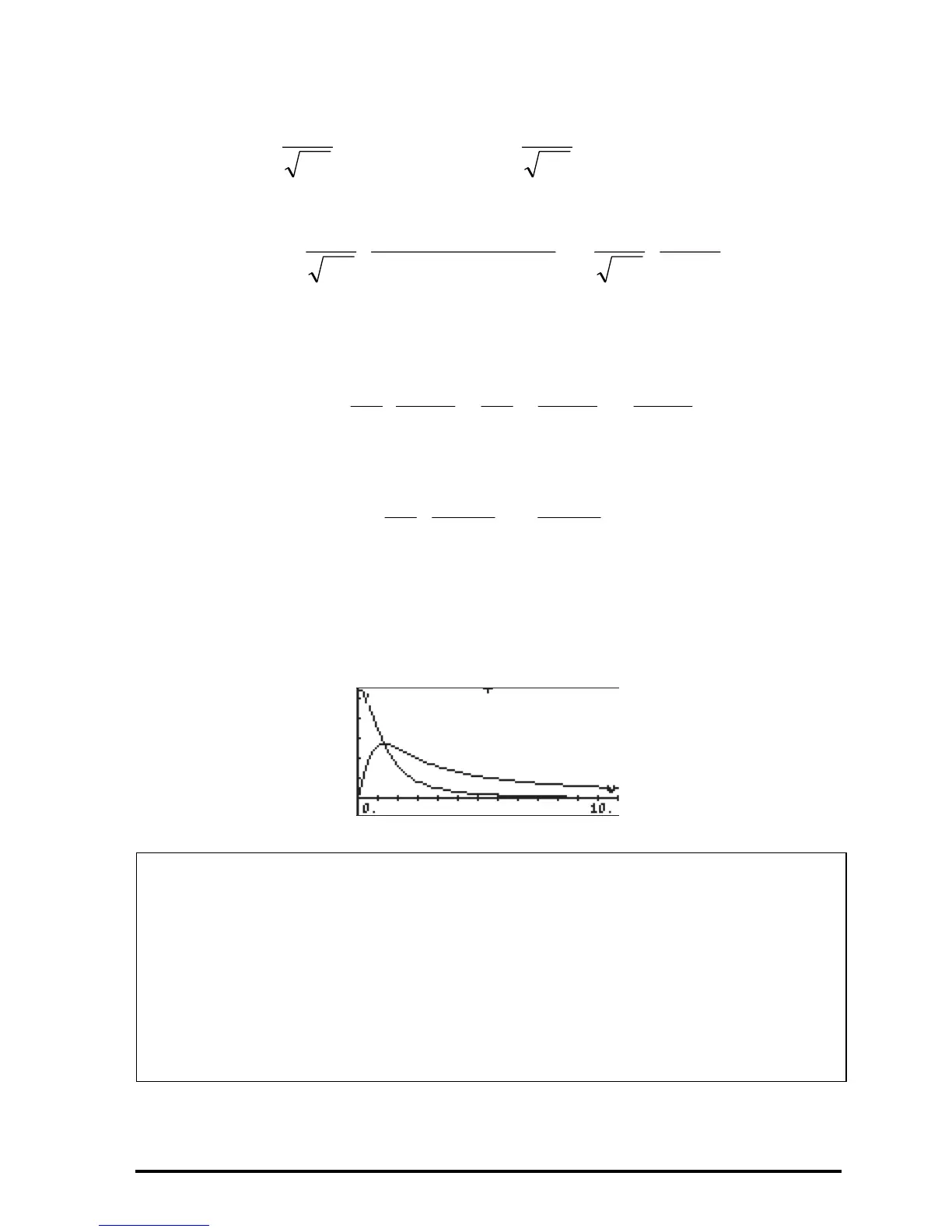
The absolute value of the real and imaginary parts of the function can be
plotted as shown below
Notes:
The magnitude, or absolute value, of the Fourier transform, |F(ω)|, is the
frequency spectrum of the original function f(t). For the example shown above,
|F(ω)| = 1/[2π(1+ω
2
)]
1/2
. The plot of |F(ω)| vs. ω was shown earlier.
Some functions, such as constant values, sin x, exp(x), x
2
, etc., do not have
Fourier transform. Functions that go to zero sufficiently fast as x goes to infinity
do have Fourier transforms.
∫∫
+−
∞
∞→
+−
=
ε
ω
ε
ω
ππ
0
)1(
0
)1(
2
1
lim
2
1
dtedte
titi
.
1
1
2
1
1
))1(exp(1
2
1
lim
ω
π
ω
ω
π
ε
ii
ti
+
⋅=
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡
+
+−−
=
∞→
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
−
−
⋅
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
+
⋅=
+
⋅=
ω
ω
ωπωπ
ω
i
i
ii
F
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
1
2
1
)(
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
+
⋅−
+
=
22
11
1
2
1
ω
ω
ω
π
i

 Loading...
Loading...




