location information in “Hard disk drive locations” on page 183. If you install a
drive in the wrong bay, you might lose data.
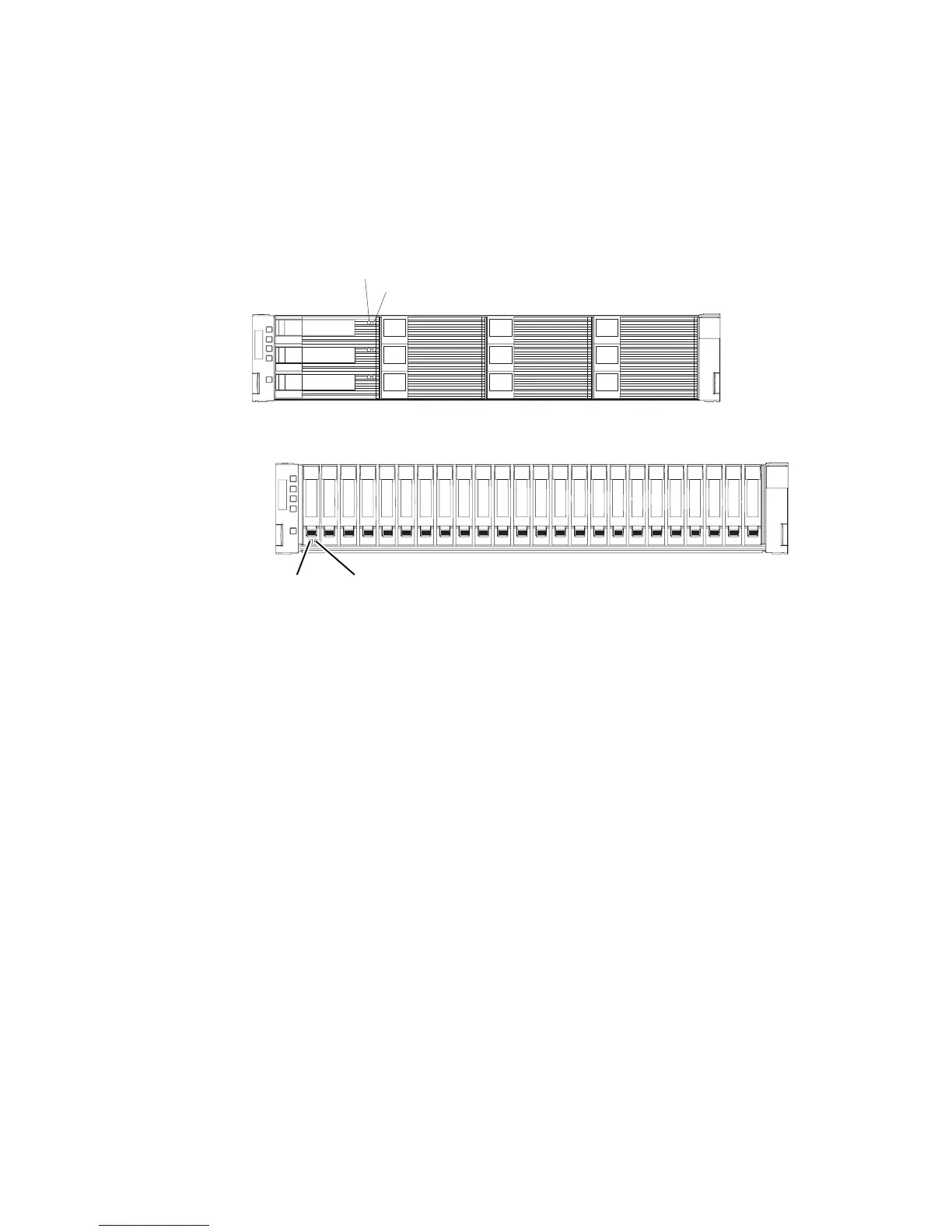
v Drive LEDs: Each drive enclosure has two associated LEDs, a green activity
LED and an amber status LED. These LEDs indicate the status for that drive.
The drive LEDs on the DS3512 storage subsystem and EXP3512 storage
enclosure are shown in Figure 98. The drive LEDs on the DS3524 storage
subsystem and EXP3524 storage enclosure are shown in Figure 99.
Drive activity LED (green)
When this LED flashes, it indicates that there is activity to the drive.
Drive status LED (amber)
When this LED flashes, it indicates that the drive has been identified by
the software. When this LED is lit and not flashing, it indicates that the
drive has failed.
v Hot-swap hardware: The storage subsystem contains hardware that enables you
to replace a failed drive without turning off the storage subsystem. You can
continue to operate the storage subsystem while a drive is being removed or
installed. These drives are known as hot-swap drives.
Removing a hard disk drive
To remove a hot-swap drive, complete the following steps.
Note: The drive comes installed in a drive enclosure. Do not attempt to detach the
drive from the enclosure.
Attention: Handle drives gently and do not stack them. Follow all precautions
for static-sensitive devices.
1. Use “Hard disk drive locations” on page 183 to record the location and identify
the drives. Record this information so that you can replace the drives in the
same bays from which you removed them.
Hard disk drive activity LED
Hard disk drive status LED
Figure 98. DS3512 storage subsystem and EXP3512 storage enclosure drive LEDs
Hard disk
drive status
LED (amber)
Hard disk
drive activity
LED (green)
dg1fy171
Figure 99. DS3524 storage subsystem and EXP3524 storage enclosure drive LEDs
122 IBM System Storage DS3500 and EXP3500 Storage Subsystem: Installation, User's, and Maintenance Guide
 Loading...
Loading...











