4 - 4
Transpector MPH Operating Manual
Some elements have many intense isotopes (e.g., xenon is 0.096% mass 124,
0.090% mass 126, 1.92% mass 128, 26.44% mass 129, 4.08% mass 130, 21.18%
mass 131, 26.89% mass 132, 10.44% mass 134, and 8.87% mass 136).
Isotope ratios, like fragmentation patterns, are a very useful aid in recognizing
specific materials. Under normal ionization conditions, the peak height ratios for the
various isotopes of an element will be the same as the ratios of their natural
abundances. That is, the probability of ionizing, for example, the mass 35 isotope
of chlorine (
35
Cl) is the same as the probability of ionizing the mass 37 isotope
(
37
Cl). Thus, the peak height ratio of mass 35 to 37 from HCl will be 3.07 to 1
(75.4% / 24.6%).
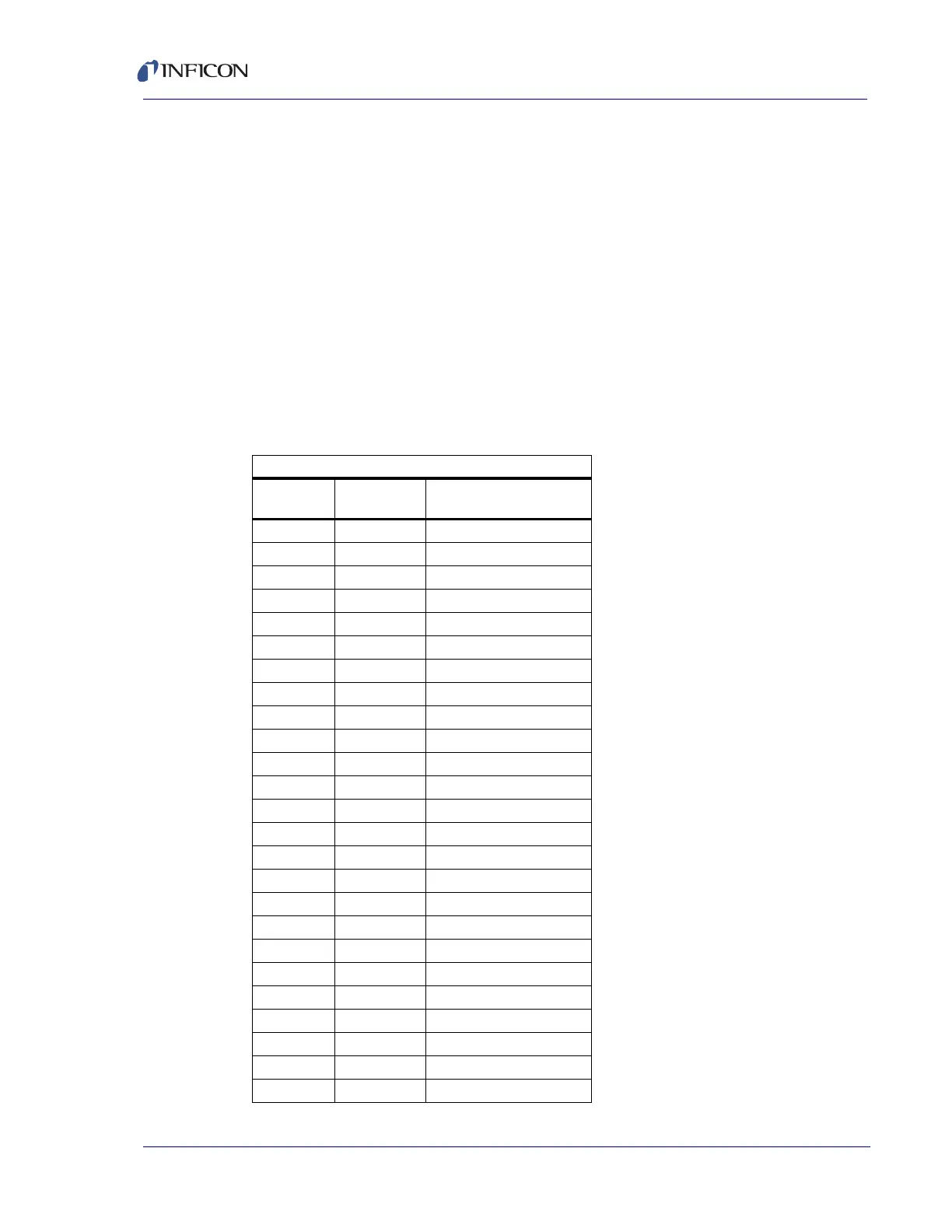
For a listing of the isotopic ratios for the lighter elements, see Table 4-2. For a
complete listing of the natural abundances for the isotopes of all the elements, see
the Handbook of Chemistry and Physics from CRC Press.
Table 4-2 Isotope ratios
Isotope Ratios
Element Mass No.
Relative
Abundance
H1 99.985
20.015
He 3 0.00013
4 ~100.0
B 10 19.78
11 80.22
C12 98.892
13 1.108
N 14 99.63
15 0.37
O16 99.759
17 0.0374
18 0.2039
F19 100.0
Ne 20 90.92
21 0.257
22 8.82
Na 23 100.0
Al 27 100.0
Si 28 92.27
29 4.68
30 3.05
P31 100.0
S 32 95.06
33 0.74
 Loading...
Loading...