Analog Interface Input and Output Options Chapter Four: Analog and Digital Interfaces
31
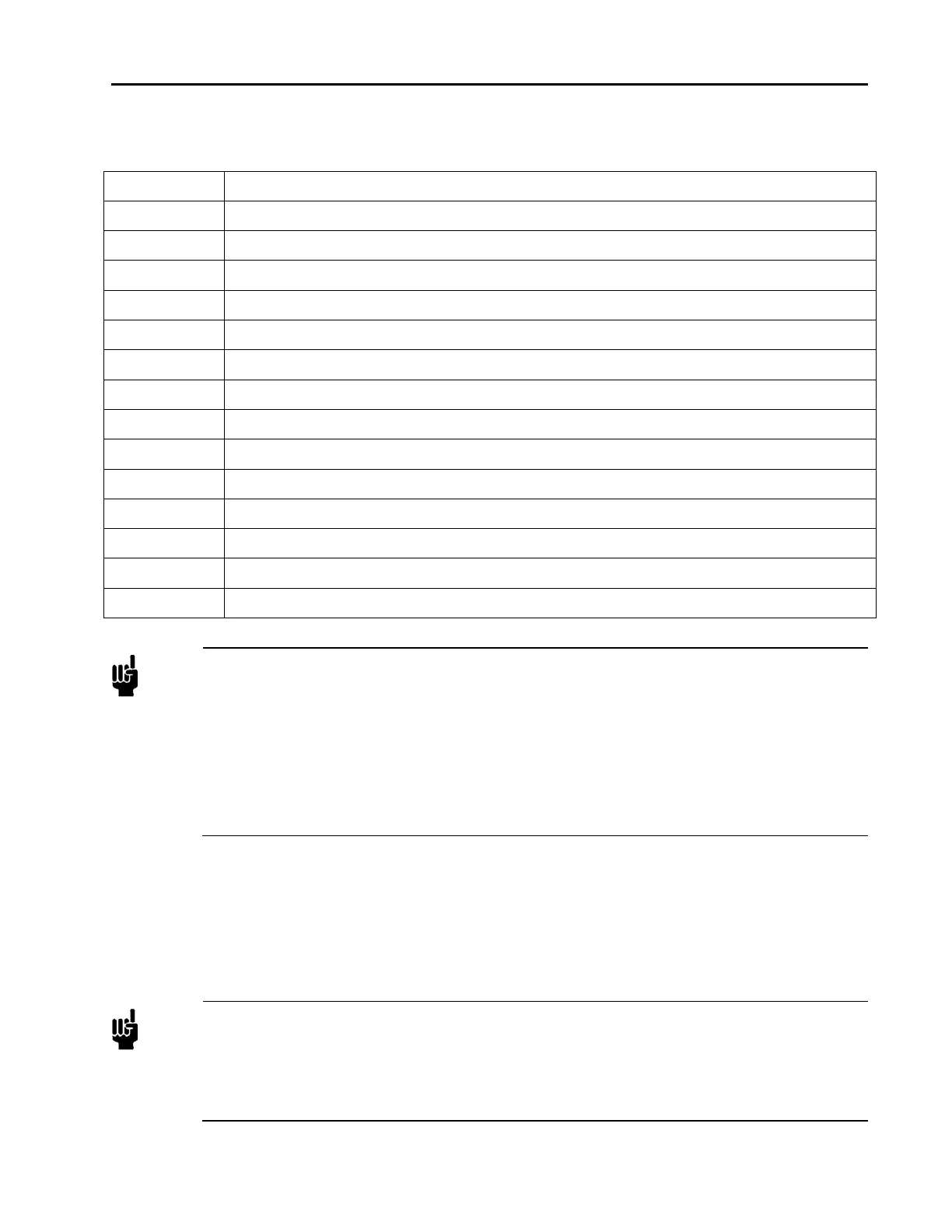
Table 9: Analog Interface Voltage I/O (0 to 5 VDC) – 15 Pin D Male Pinouts – Model Code B
Pin 1 Valve Test Point
Pin 2 Flow Signal Output, 0 to 5 VDC (into high impedance load, minimum 10K-ohm)
Pin 3 Valve Close (Pull to Ground or Pull Low – 5 to -15 VDC)
Pin 4 Valve Open (Pull High +5 to +15 VDC)
Pin 5 Power Supply Common Digital Ground (see Note 4 below)
Pin 6 No Connection
Pin 7 +15 to +25 VDC (see Note 4 below)
Pin 8 Setpoint Input (0 to +5 VDC)
Pin 9 Zero Function
Pin 10 Optional Input
Pin 11 Signal Common
Pin 12 Signal Common
Pin 13 No Connection
Pin 14 No Connection
Pin 15 Chassis Ground
Note
1. The “No Connection” pin assignment refers to a pin with no internal connection.
2. The 0 to 5 VDC flow signal output comes from pin 2 and is referenced to pin 12 (signal
common).
3. Any appropriate 0 to 5 VDC input signal of less than 1K ohm source impedance referenced
to pin 12 can be used to supply a setpoint signal to pin 8.
4. A signal common line MUST be connected to the power common line at either at the tool
end or at the MFC 15 pin D connector end of the cable to avoid setpoint/readback offsets.
DO NOT connect a signal common line and the power common line at both ends of the
cable as this will result in ground loops.
The Optional Input (15 Pin D Analog Controllers Only)
The standard 15-pin MFC can control flow based on a 0 to 5 Volt signal from an external sensing device
using the optional input feature (for a 0 to 10 Volt input range, contact the MKS Applications Department). A
common application of this feature is for pressure control using input from a pressure transducer.
To use the optional input feature, route the 0-5 Volt (or 0 to 10 VDC) output from the desired external device
to the optional input pin 10.
Note
The optional input feature is only available on the 15-pin Type D connector with standard MKS
inout assignments. The 9-pin Type D connector does not support this feature. Voltage applied
to the optional input pin overrides the signal generated by the flow sensor internal to the MFC.
The control electronics drives the valve so that the optional input signal matches the setpoint.
Use the same pin for the setpoint signal, regardless of whether you are using the optional input
or the standard flow control signal. Although controlling to the external optional input signal, the

 Loading...
Loading...