IV–23
A22 Coolant Pump Error
Error detection method
Errors can be determined when coolant pump rotations and driving meet the following conditions.
• When an error is triggered once owing to the coolant pump revolutions not increasing or not being able to be
detected when the engine is started up.
• When either overcurrent, insuffi cient revolutions or excessive revolutions are detected in the coolant pump
when the engine is operating, the engine will be momentarily halted and an error fl ag set. The reason for the
engine being shut down is due to the error fl ag being triggered fi ve consecutive times in one hour.
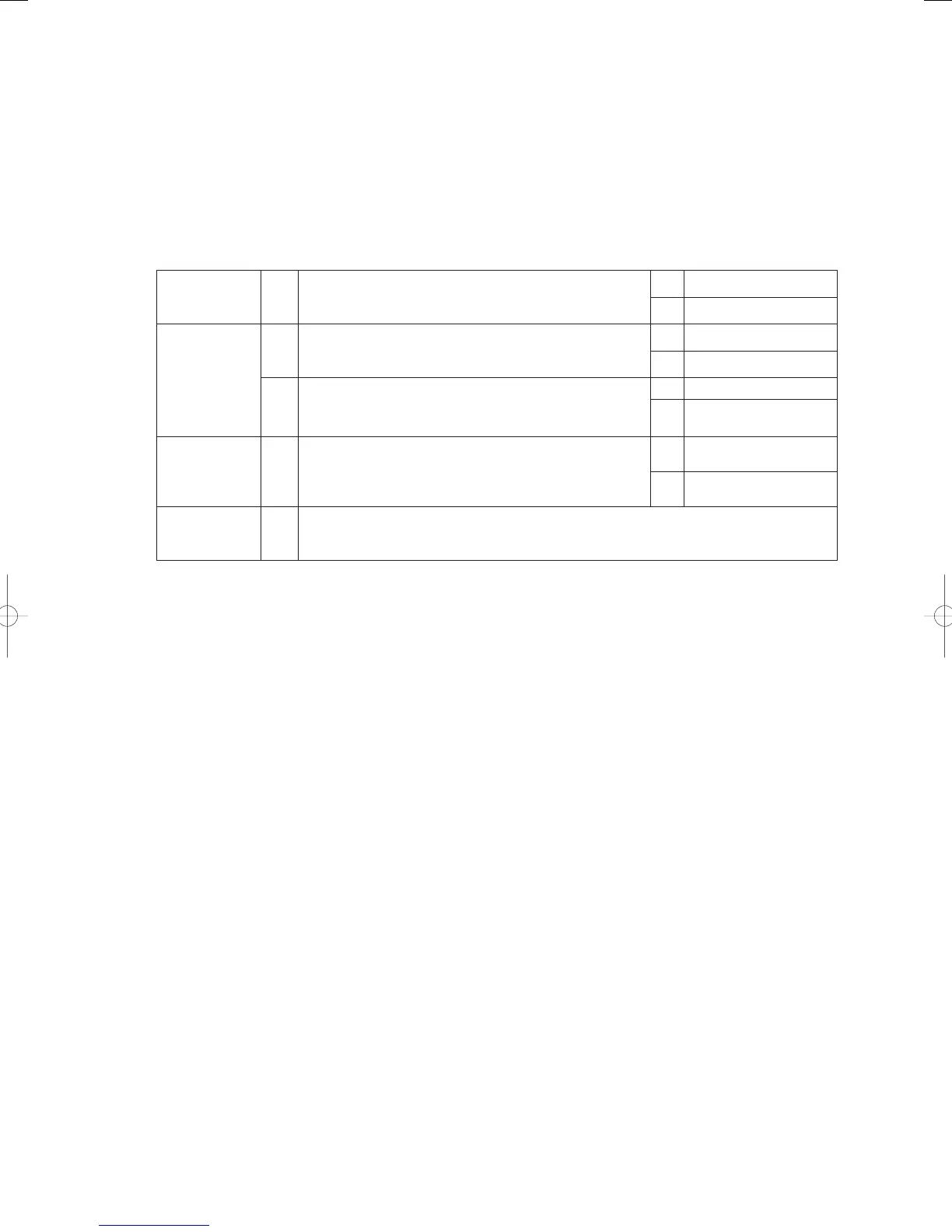
Troubleshooting
1
Power source
check
1-1
Is the voltage being supplied to the outdoor unit normal?
(Check to see whether the voltage is too low or unstable)
Yes 2-1
No Repair the power source
2
Coolant pump 2-1
Are there any bad power cable connections when 3-phase
equipment is in use? Or, is the power cable severed or the
connection faulty?
Yes 2-2
No Repair the power cable
2-2
Is the coolant pump locked or are there any severed wires,
poor contacts or short circuits?
(Coil resistance should be around 14-18Ω for each phase.)
Yes 3 -1
No
Replace the coolant
pump
3
Coolant circuit
3-1
Has air entered the coolant circuit?
(There is a chance of air having entered the circuit if
there is a slight banging noise and pump revolutions are
fl uctuating during coolant pump operations.)
Yes 4-1
No Perform an air purge
4
Outdoor unit’s
power board
4-1
Replace the outdoor unit’s power board and keep an eye on the situation.
Replace the coolant pump if the problem reoccurs.
● For board and Electrical Wiring Diagram, see Chapter 6.
• Outdoor main board: page VI-2
• Outdoor power board: page VI-3
• Converter board: VI-4
• Indoor control board for DC motor models: page VI-5
• Outdoor Unit Electrical Wiring Diagram: page VI-6 *Reference (Electrical Wiring Diagram A-B-3)
GHPtroubleshooting.indbIV‒23GHPtroubleshooting.indbIV‒23 2012/11/2611:20:072012/11/2611:20:07
 Loading...
Loading...











