RH850/F1Kx, RH850/F1K Series Hardware Design Guide
R01AN3841ED0110 Rev. 1.10 Page 30 of 108
August 8, 2019
1.4.2 Power Supply Pin Configuration of RH850/F1KH-D8
The following shows power supply pin configuration. Do not open any power and GND terminals even if those are
internally connected.
• The EVCC supply pins are internally connected
• The BVCC supply pins are internally connected.
• The EVSS pins are internally connected.
• The BVSS pins are internally connected.
• AWOVSS and ISOVSS are internally connected.
• Others are not internally connected.
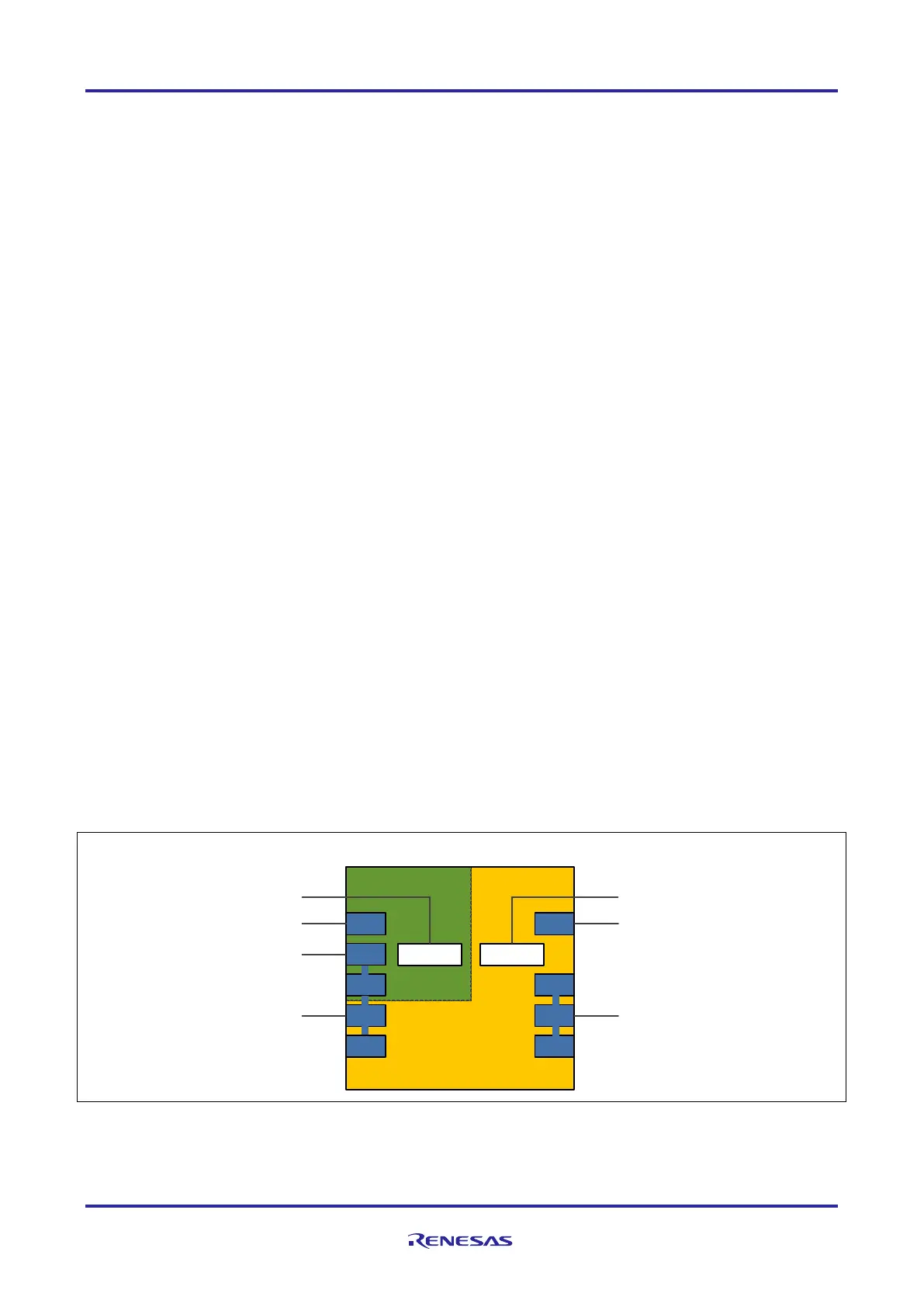
1.4.3 Power Supply Pin Architecture of RH850/F1KH-D8
The RH850/F1KH-D8 supports different power supply architectures. The power supply architecture depends on the
chosen RH850/F1KH-D8 device, application requirements and the use case.
Some common conditions apply to the supply of the RH850/F1KH-D8:
REG0VCC = EVCC = VPOC to 5.5V
REG1VCC = VPOC to 3.6V
REG1VCC ≤ REG0VCC
BVCC = VPOC to REG0VCC
A0VREF = 3.0V to 5.5V
A1VREF = 3.0V to 5.5V
AWOVSS = ISOVSS = EVSS = BVSS = A0VSS = A1VSS = 0V
The following figure and the different cases describe the impact to the ADC ports and the ports with analog/digital
function depending on the power supply architecture. In addition, it describes the limitations to these ports.
Figure 11: RH850/F1KH-D8 Power supply architecture
RH850/F1KH-D8
AWO-Are a ISO-Area
AP0
REG0VCC
A0 VRE F
EVCC
EVCC
Pn
R eg ul at or
R eg ul at or
P8
P9
Pm
AP1
A1VREF
Pr
P18
BVCC
P19
REG1VCC

 Loading...
Loading...











