Principles for control
2.6 Control Response at Different Feedback Structures
PID control
32 Function Manual, 03/2017, A5E35300227-AC
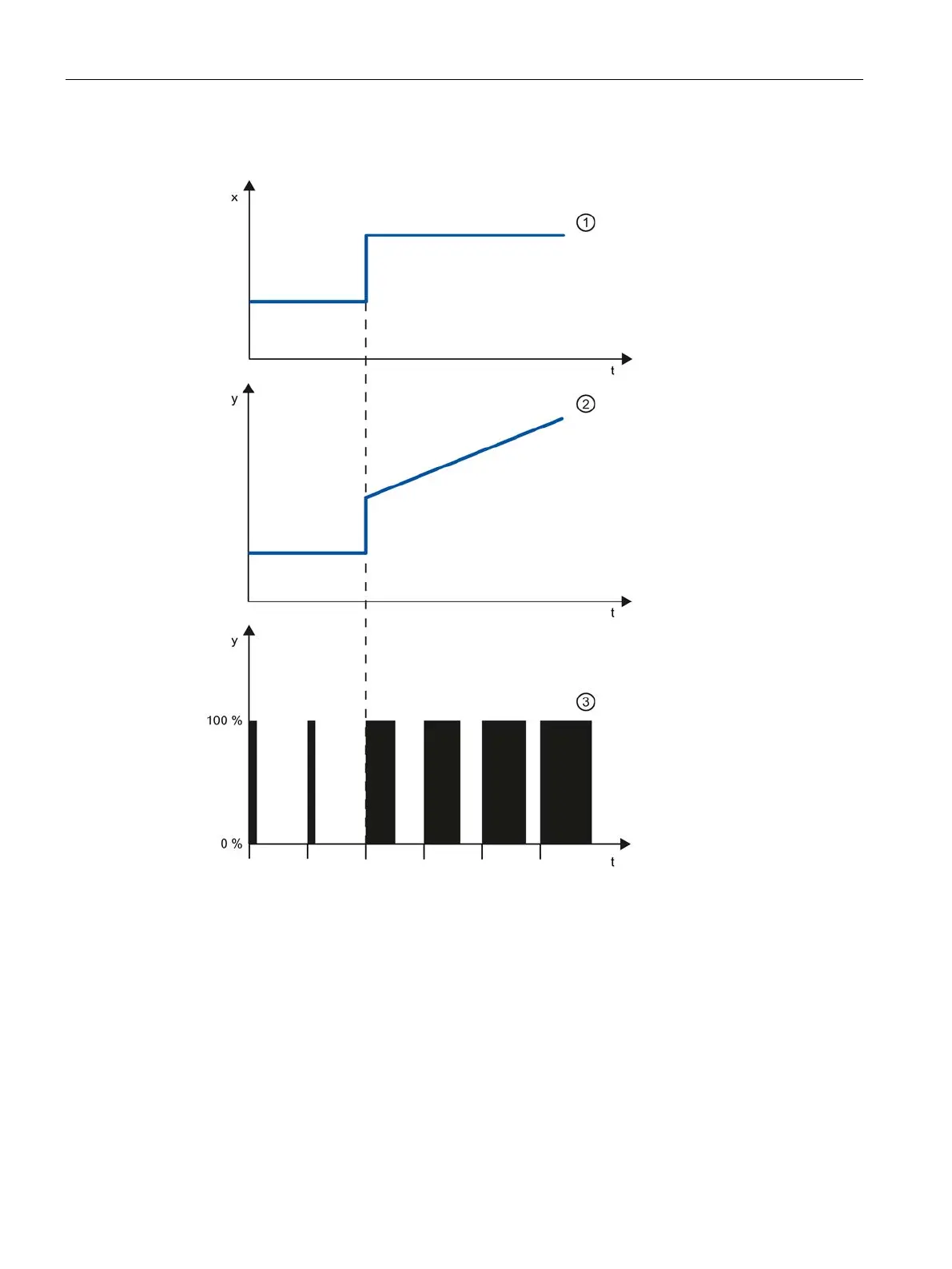
Step response of a PI-action controller
Output value of a continuous controller
Output value of a pulse controller
An integral action in the controller adds the control deviation as a function of the time. This
means that the controller corrects the system until the control deviation is eliminated. A
sustained control deviation is generated at controllers with proportional action only. This
effect can be eliminated by means of an integral action in the controller.
In practical experience, a combination of the proportional, integral and derivative actions is
ideal, depending on the requirements placed on the control response. The time response of
the individual components can be described by the controller parameters proportional gain
GAIN, integral action time TI (integral action), and derivative action time TD (derivative
action).

 Loading...
Loading...






















