Principles for control
2.7 Selection of the controller structure for specified controlled systems
PID control
36 Function Manual, 03/2017, A5E35300227-AC
Selection of the controller structure for specified controlled systems
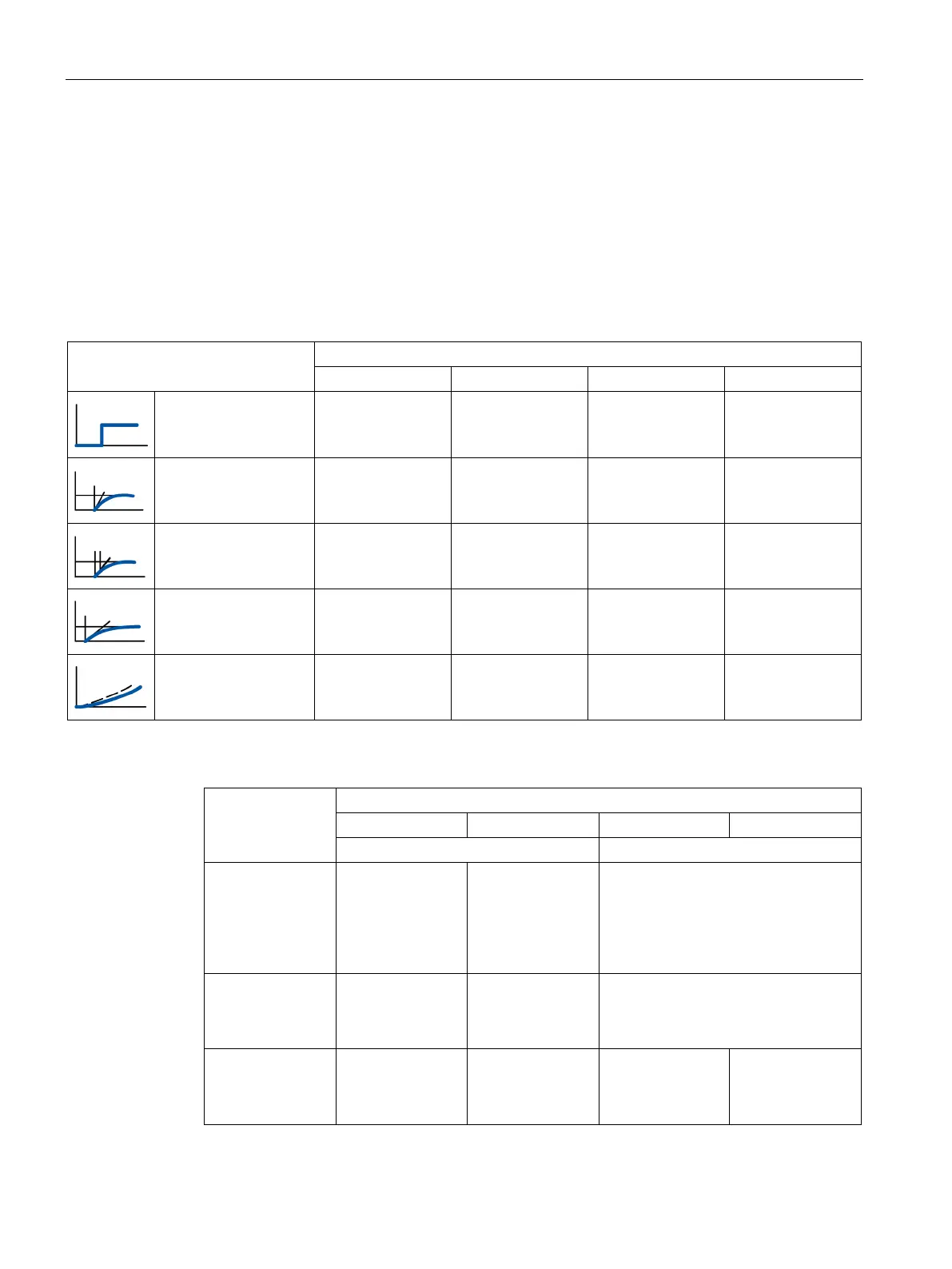
Selection of the Suitable Controller Structures
To achieve optimum control results, select a controller structure that is suitable for the
controlled system and that you can adapt to the controlled system within specific limits.
The table below provides an overview of suitable combinations of a controller structure and
controlled system.
With dead time only Unsuitable Unsuitable Suitable Unsuitable
PT1 with dead time Unsuitable Unsuitable Well suited Well suited
PT2 with dead time Unsuitable Suited conditionally Well suited Well suited
Higher order Unsuitable Unsuitable Suited conditionally Well suited
Not self-regulating Well suited Well suited Well suited Well suited
The table below provides an overview of suitable combinations of a controller structure and
physical quantity.
Sustained control deviation
No sustained control deviation
Temperature For low perfor-
mance require-
ments and
proportional action
controlled systems
u
Well suited The most suitable controller structures
for high performance requirements
(except for specially adapted special
controllers)
Pressure Suitable, if the
delay time is in-
considerable
Unsuitable The most suitable controller structures
for high performance requirements
(except for specially adapted special
controllers)
Flow rate Unsuitable, be-
cause required
GAIN range is
Unsuitable Suitable, but inte-
gral action control-
ler alone often
Hardly required

 Loading...
Loading...






















