Configuration
5.3 Examples
1FN3 linear motors
128 Configuration Manual, 10/2018, 6SN1197-0AB86-0BP2
Peak load motor
1FN3150-4WC00-0BA1
F
1
= m
ges
· a + F
r
= 2617 N
F
2
= F
r
= 100 N
F
3
= -m
ges
· a + F
r
= - 2417 N
F
4
= 0 N
F
5
= -m
ges
· a - F
r
= - 2617 N
F
6
= F
4
- F
r
= - 100 N
F
7
= m
ges
· a - F
r
= 2417 N
F
eff
= 1246 N
The effective force therefore remains
below the permissible value of F
N
=
Travel to position s
MAX
Dwell time
Travel to position s
0
Continuous load motor
1FN3150-4NB80-0BA1
F
1
= m
ges
· a + F
r
= 2777 N
F
2
= F
r
= 100 N
F
3
= -m
ges
· a + F
r
= - 2577 N
F
4
= 0 N
F
5
= -m
ges
· a - F
r
= - 2777 N
F
6
= F
4
- F
r
= - 100 N
F
7
= m
ges
· a - F
r
= 2577 N
F
eff
= 1325 N
The effective force therefore remains
below the permissible value of F
N
Travel to position s
MAX
Dwell time
Travel to position s
0
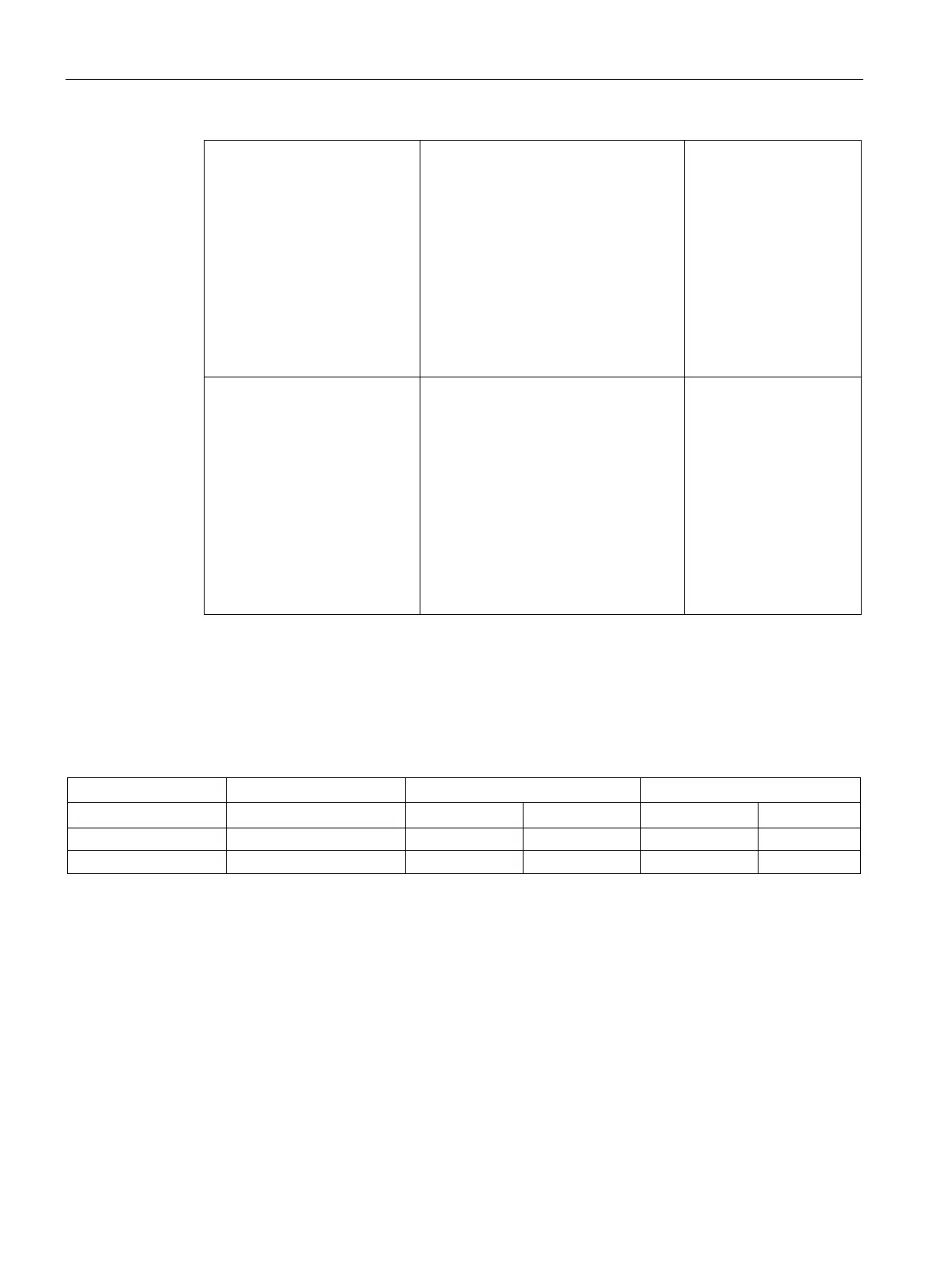
Final selection of the primary section
For the example considered here, for a peak load motor, primary section 1FN3150-4WC00-
0BA1 is suitable, and for a continuous load motors, primary section 1FN3150-4NB80-0BA1.
Which primary section is best suited to the specified duty cycle can be derived from the
following summary:
Values from the data sheet
Values from the duty cycle
Decision-making criteria for the primary section include:
● Size and installation conditions
● Thermal conditions
● Idle times
● Power reserves for peak and continuous loads
● Acceleration and velocity class
● Velocity class
● Converter power module

 Loading...
Loading...