Redstone™ Optical Spectrum Analyzer Chapter 8: Operation
Rev C, January 21, 2022 Page 58
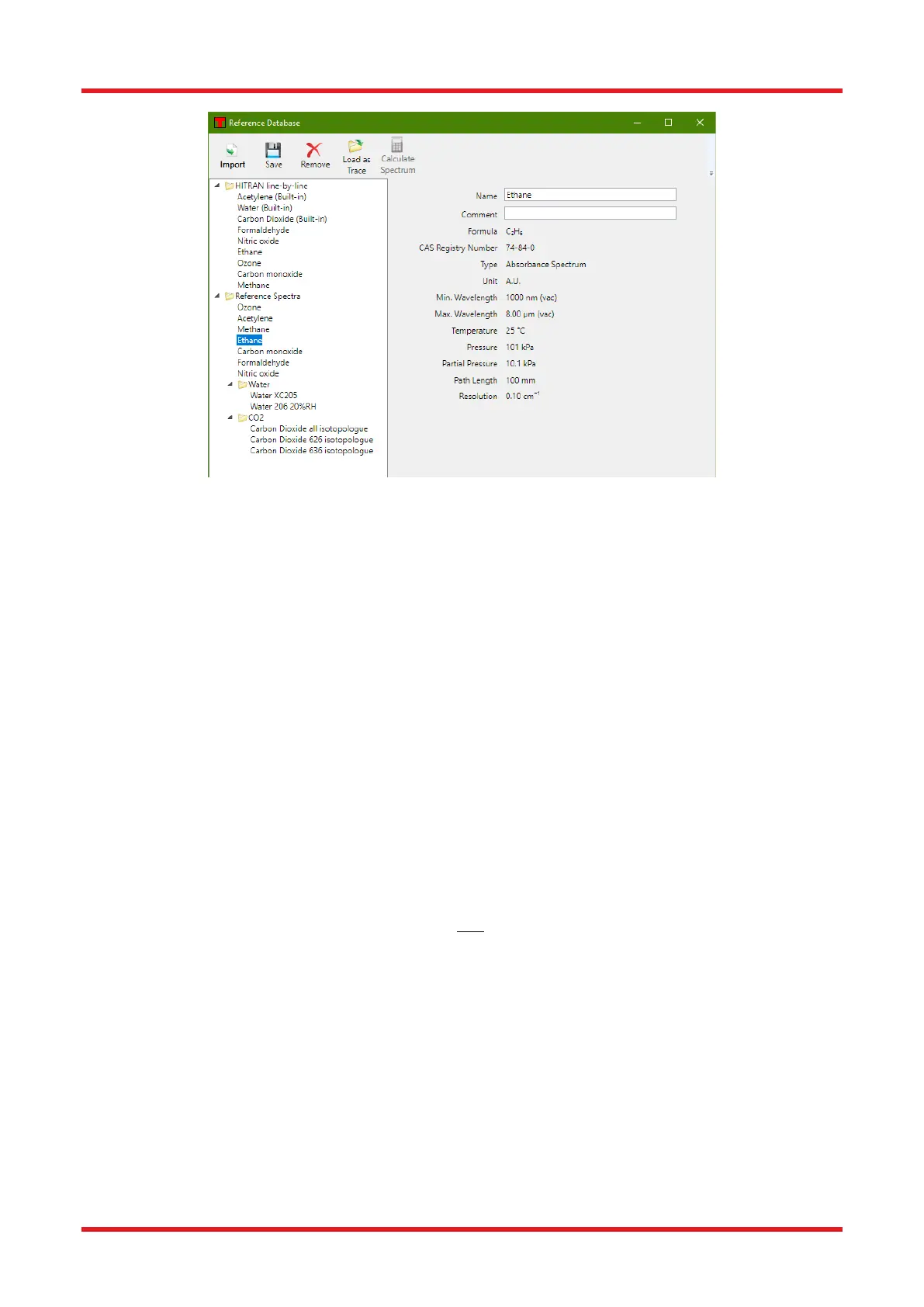
Figure 60. Reference Database Window
Converting HITRAN References into Absorption Cross Sections, Absorption Spectra, or Transmission
Spectra
A line-by-line reference must be converted into a regular spectrum before it can be used in the software. This
spectrum will be used during the Reference fitting step to help account for line-shifts, modulations in line
intensity, line broadening caused by air, and self-broadening. To obtain a regular spectrum, an absorption cross
section must first be calculated.
An absorption cross section is a physical property of a molecule that describes how strongly the molecule
absorbs light at a particular wavelength. It is denoted by in the Beer-Lambert law:
Here, is the light intensity after absorption,
the incident light intensity, is the wavelength, is the
wavelength-dependent absorption cross section, is the concentration of the gas of interest, and is the total
path length traversed by the light as it passes through the gas. The calculated absorption cross section has
units of cm
2
/molecule.
The absorption cross section is related to the absorption coefficient, denoted by . The absorption coefficient
can be calculated by multiplying the absorption cross section by the so-called mass path
where is the volume mixing ratio of the gas, is the total pressure,
is Boltzmann’s constant, and is the
temperature.
The OSA software takes into account the total pressure, the partial pressure of the gas of interest, and the
temperature in order to calculate the absorption cross section and resulting spectrum. By clicking the “Calculate
Spectrum” button, the following dialog box will appear, which displays all the needed input parameters. Please
note that the usable x-axis data range will be limited by the data range from the HITRAN line-by-line reference.

 Loading...
Loading...