CHAPTER 7 - PROGRAMMING INFORMATION AND SUGGESTIONS
153
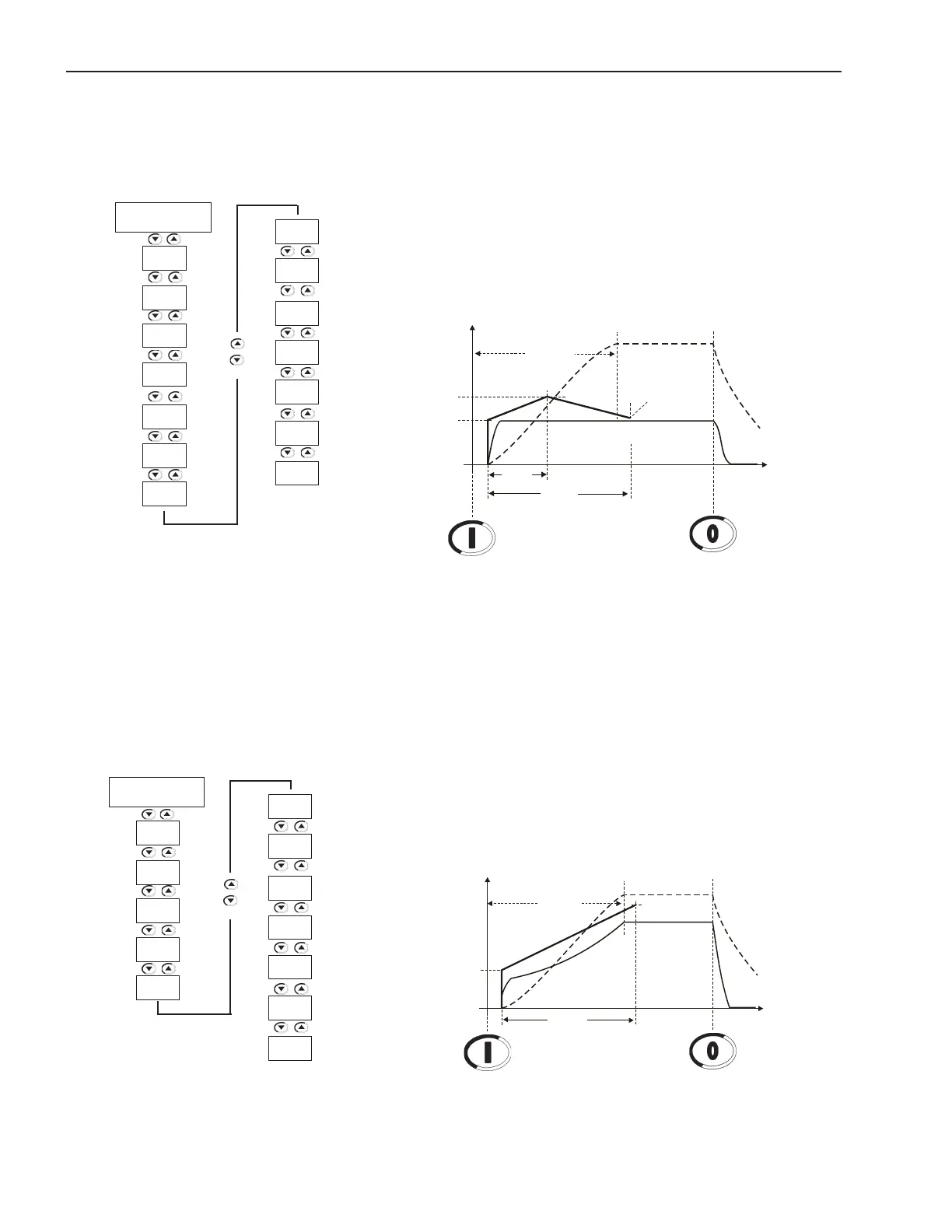
7.1.6.3LoadswithConstant
Torque and S Speed
Curve (P202=3 and 120=3
points)
1) Through the load curve you can set the torque 10% to 20% higher
than the load torque for the initial and the end points, P121 and
P122, and 30% to 40% higher than load torque for the middle
point P123;
2) Maintain P124 between 45% to 55% and set P102 according to
the starting time;
3) Fortherststartyoucanuseaspeedmeasuringinstrument,thus
ensuring the desired acceleration or the desired speed curve;
4) If no load curve is available, but you are sure that the torque is
constant, you can use the torque limit, P120=1 for executing the
rststartsandchangingtothisfunctionafterwards.
Figure 7.13 - Starting with quadratic torque control, 3 points, with constant load
7.1.6.4 LoadswithQuadratic
Torque and S Speed
Curve
(P202=3 and P120=2
points)
1) Through the linear torque ramp you can obtain a speed curve
very similar to a S-curve with quadratic load, but not very steep;
2) Through the load curve you can set the torque 10% to 20%
higher than the load torque for the initial point P121, and 20%
to 30% higher than the load torque for the end point, P122;
3) If no load curves are available, proceed as follows:
3.1) Set P121 to the required torque to start rotating the motor +
load;
3.2) Set P122 to 110% to 130% of the nominal motor torque;
3.3) AtrstsetP102tolowvalues,10sto15sandthenndthebest
value.
Figure 7.14 - Starting with linear torque control, 2 points, quadratic load
Tn(%)
Start
Speed
P124
0
Enable
Disable
t(s)
Maximum Time
P121
Tn Nominal
LoadTorque
Torque Control
P123
P102
P122
P120 =3
P102
Torque
Control
P401
P400
P122
P121
P640
P406
P404
P402
P405
P123
P124
P104 =0
Tn(%)
Start
Speed
0
Enable
Disable
t(s)
Maximum Time
P121
Tn Nominal
LoadTorque
Torque Control
P102
P122
P401
P400
P640
P406
P404
P402
P405
P120 =2
P102
Torque
Control
P122
P121
P104 =0

 Loading...
Loading...