MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide 106
UG984 (v2018.2) June 21, 2018 www.xilinx.com
Chapter 2: MicroBlaze Architecture
• Event trace: Stores event trace information including cycle count events. Events include
all program exceptions, interrupts, and breaks, as well as all cross-trigger events
defined in Table 2-62. Each event is optionally preceded by a stored program counter.
The program counter can also optionally be stored for call instructions to trace function
calls in the program, and for return instructions to trace function call returns.
Software can inject an event by using an “xori r0, rA, IMM” instruction. Typically this is
used to trace operating system events like context switches and system calls, but it can
be used by any program to trace significant events.
Tracing can be started using the Trace Command Register, by hitting a program breakpoint
or watchpoint configured as a tracepoint in the Trace Control Register, or by a cross trigger
event (see
Table 2-62).
Tracing is automatically stopped when the trace buffer becomes full, and can be stopped
using the Trace Command Register or by a cross trigger event (see
Table 2-62).
The cycle count can measure up to 32768 clock cycles when using complete trace, and up
to 8192 cycles between instructions when using program flow and cycle count. If the cycle
count exceeds this value, the Trace Status Register overflow bit is set to one.
It is possible to configure trace to halt the processor when the trace buffer becomes full or
when the cycle count overflows. This allows continuous trace of the entire program flow,
albeit not in real time due to the time required to read the trace buffer.
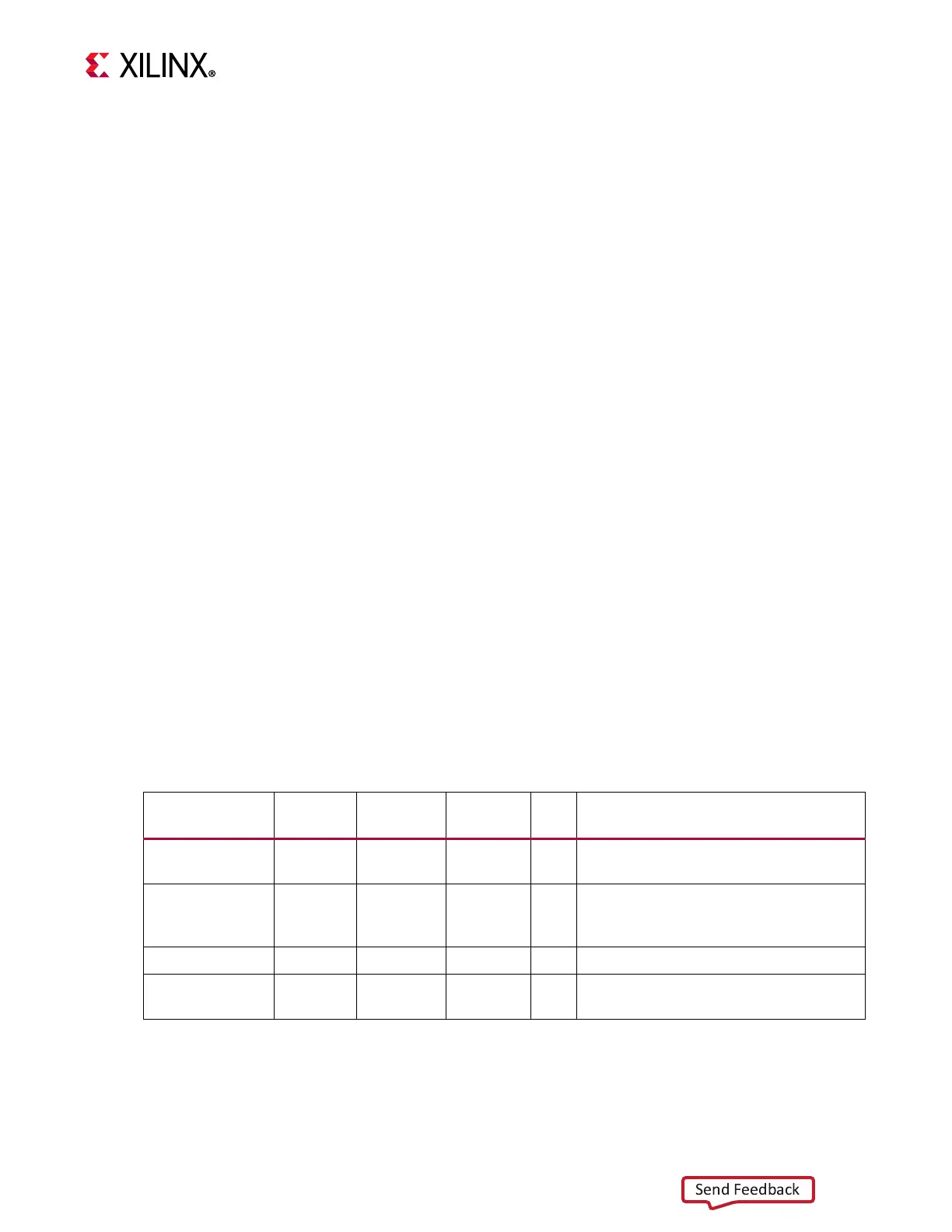
The debug registers used to configure and control tracing, and to read the Embedded Trace
Buffer, are listed in the following table.
The DBG_CTRL value indicates the value to use in the MDM Debug Register Access Control
Register to access the register, used with MDM software access to debug registers.
Table 2-49: MicroBlaze Program Trace Debug Registers
Register Name Size (bits)
MDM
Command
DBG_CTRL
Value
R/W Description
Trace Control 22 0110 0001 4C215 W
Set tracepoints, trace compression level
and optionally stored trace information
Trace Command 4 0110 0010 4C403 W
Command to clear trace buffer, start or
stop trace, and sample number of
current buffer items
Trace Status 18 0110 0011 4C611 R Read the sampled trace buffer status
Trace Data Read
1
1. This register is not available when C_DEBUG_EXTERNAL_TRACE is set
18 0110 0110 4CC11 R
Read the oldest item from the
Embedded Trace Buffer
 Loading...
Loading...









