MicroBlaze Processor Reference Guide 295
UG984 (v2018.2) June 21, 2018 www.xilinx.com
Chapter 5: MicroBlaze Instruction Set Architecture
swi
Store Word Immediate
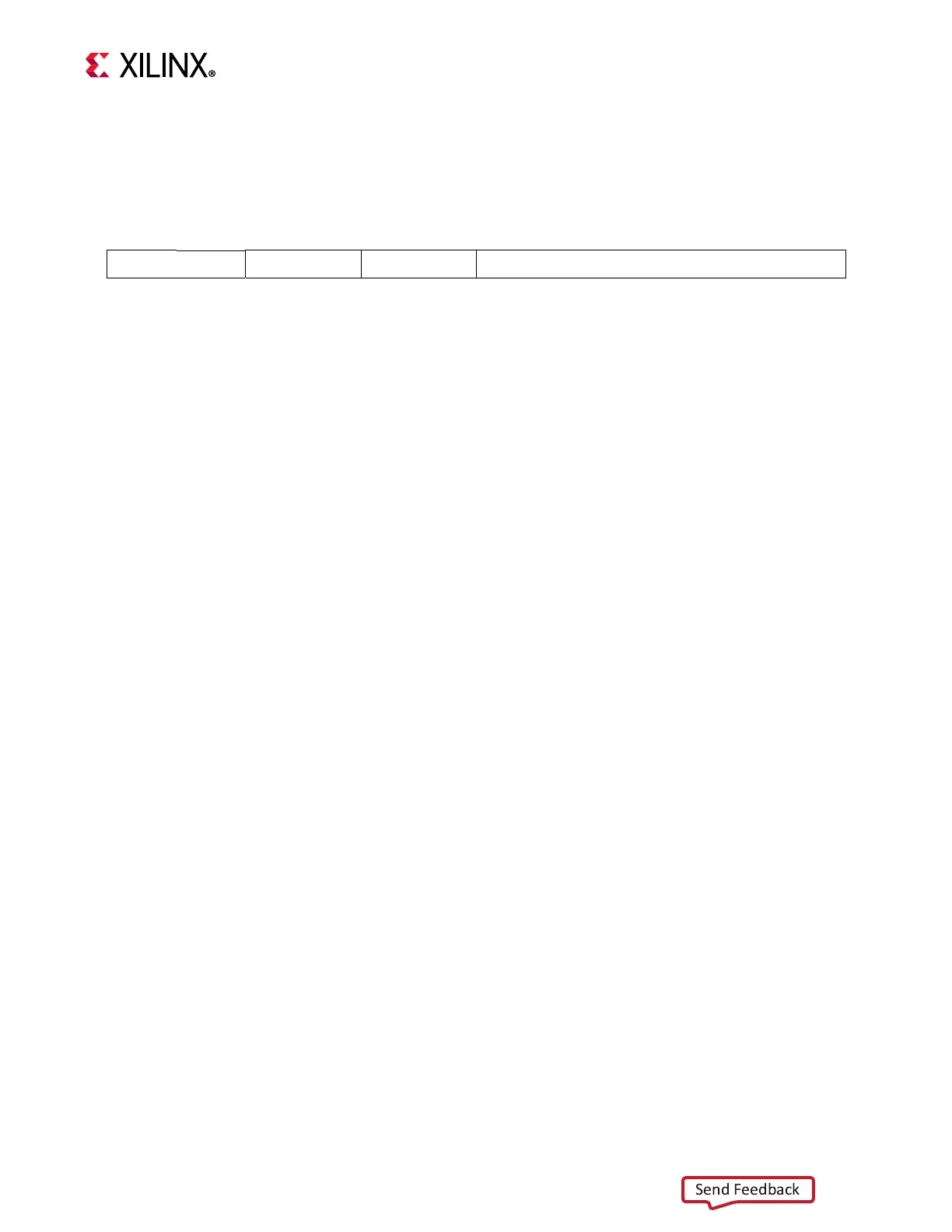
swi
rD, rA, IMM
1 1 1 1 1 0 rD rA IMM
0 6 11 16
31
Description
Stores the contents of register rD, into the word aligned memory location that results from adding the
contents of registers rA and the value IMM, sign-extended to 32 bits.
A data TLB miss exception occurs if virtual protected mode is enabled, and a valid translation entry
corresponding to the address is not found in the TLB.
A data storage exception occurs if virtual protected mode is enabled, and access is prevented by no-
access-allowed or read-only zone protection. No-access-allowed can only occur in user mode.
An unaligned data access exception occurs if the two least significant bits in the address are not zero.
Pseudocode
Addr ← (rA) + sext(IMM)
if TLB_Miss(Addr) and MSR[VM] = 1 then
ESR[EC]
← 10010;ESR[S]← 1
MSR[UMS] ← MSR[UM]; MSR[VMS] ← MSR[VM]; MSR[UM] ← 0; MSR[VM] ← 0
else if Access_Protected(Addr) and MSR[VM] = 1 then
ESR[EC]
← 10000;ESR[S]← 1; ESR[DIZ] ← No-access-allowed
MSR[UMS]← MSR[UM]; MSR[VMS] ← MSR[VM]; MSR[UM] ← 0; MSR[VM] ← 0
else if Addr[30:31] ≠ 0 then
ESR[EC]
← 00001; ESR[W] ← 1; ESR[S] ← 1; ESR[Rx] ← rD
else
Mem(Addr) ← (rD)[0:31]
Registers Altered
• MSR[UM], MSR[VM], MSR[UMS], MSR[VMS], if a TLB miss exception or a data storage
exception is generated
• ESR[EC], ESR[S], if an exception is generated
• ESR[DIZ], if a data storage exception is generated
• ESR[W], ESR[Rx], if an unaligned data access exception is generated
Latency
• 1 cycle with C_AREA_OPTIMIZED=0 or 2
• 2 cycles with
C_AREA_OPTIMIZED=1
Note
By default, Type B Instructions will take the 16-bit IMM field value and sign extend it to 32 bits to use
as the immediate operand. This behavior can be overridden by preceding the Type B instruction with
an imm instruction. See the instruction
“imm” for details on using 32-bit immediate values.
 Loading...
Loading...









