Chapter 12 Quality of Service (QoS)
VMG/EMG/AM/DM/GM Series User’s Guide
296
Token Bucket
The token bucket algorithm uses tokens in a bucket to control when traffic can be transmitted. The
bucket stores tokens, each of which represents one byte. The algorithm allows bursts of up to b bytes
which is also the bucket size, so the bucket can hold up to b tokens. Tokens are generated and added
into the bucket at a constant rate. The following shows how tokens work with packets:
• A packet can be transmitted if the number of tokens in the bucket is equal to or greater than the size
of the packet (in bytes).
• After a packet is transmitted, a number of tokens corresponding to the packet size is removed from
the bucket.
• If there are no tokens in the bucket, the Zyxel Device stops transmitting until enough tokens are
generated.
• If not enough tokens are available, the Zyxel Device treats the packet in either one of the following
ways:
In traffic shaping:
• Holds it in the queue until enough tokens are available in the bucket.
In traffic policing:
•Drops it.
• Transmits it but adds a DSCP mark. The Zyxel Device may drop these marked packets if the network
is overloaded.
4 4 2 010110
010100
010010
010000
5 5 3 011110
011100
011010
011000
<250
6 6 4 100110
100100
100010
100000
5 101110
101000
7 7 6 110000
111000
7
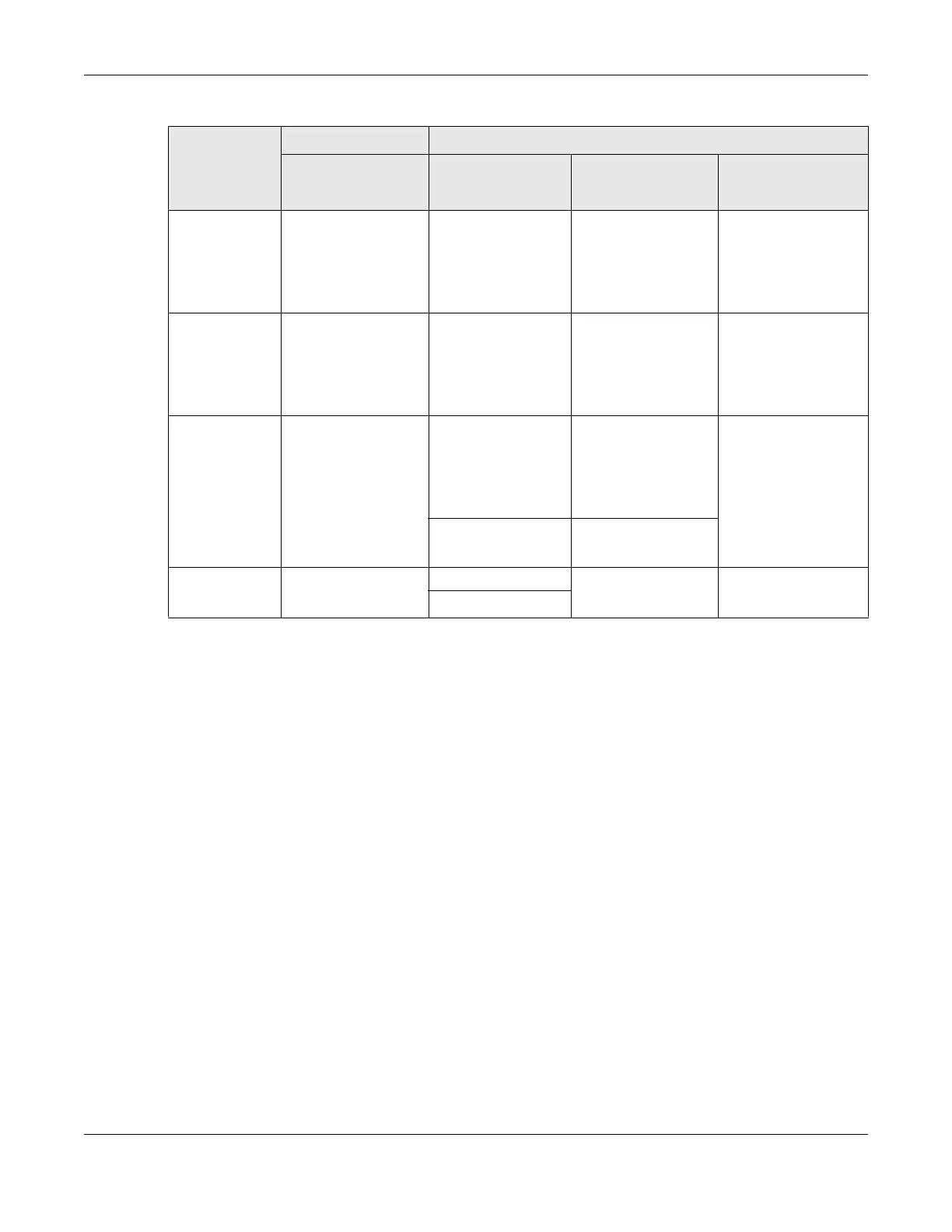
Table 85 Internal Layer2 and Layer3 QoS Mapping (continued)
PRIORITY
QUEUE
LAYER 2 LAYER 3
IEEE 802.1P USER
PRIORITY (ETHERNET
PRIORITY)
TOS (IP
PRECEDENCE)
DSCP
IP PACKET LENGTH
(BYTE)

 Loading...
Loading...











