HEXRCHardware Manual Installation and Configuration
2.4.3. Opto-Isolated Outputs
The digital outputs are driven by optically-isolated solid state relays and may be connected in sourcing or
sinking configurations. The digital outputs are designed to connect to other ground referenced circuits and
are not intended to provide high-voltage isolation.
The outputs are software-configurable and must be connected in either all sinking or all sourcing mode.
Figure 2-23 and Figure 2-24 illustrate how to connect to an output in current sourcing and current sinking
modes, respectively.
The opto-isolator's common connections can be directly connected to the drive's power supply; however,
doing so will effectively defeat the isolation and will reduce noise immunity.
N O T E : Power supply connections must always be made to both the Output Common Plus (OP) and
OutputCommon Minus (OM) pins as shown in Figure 2-23 and Figure 2-24.
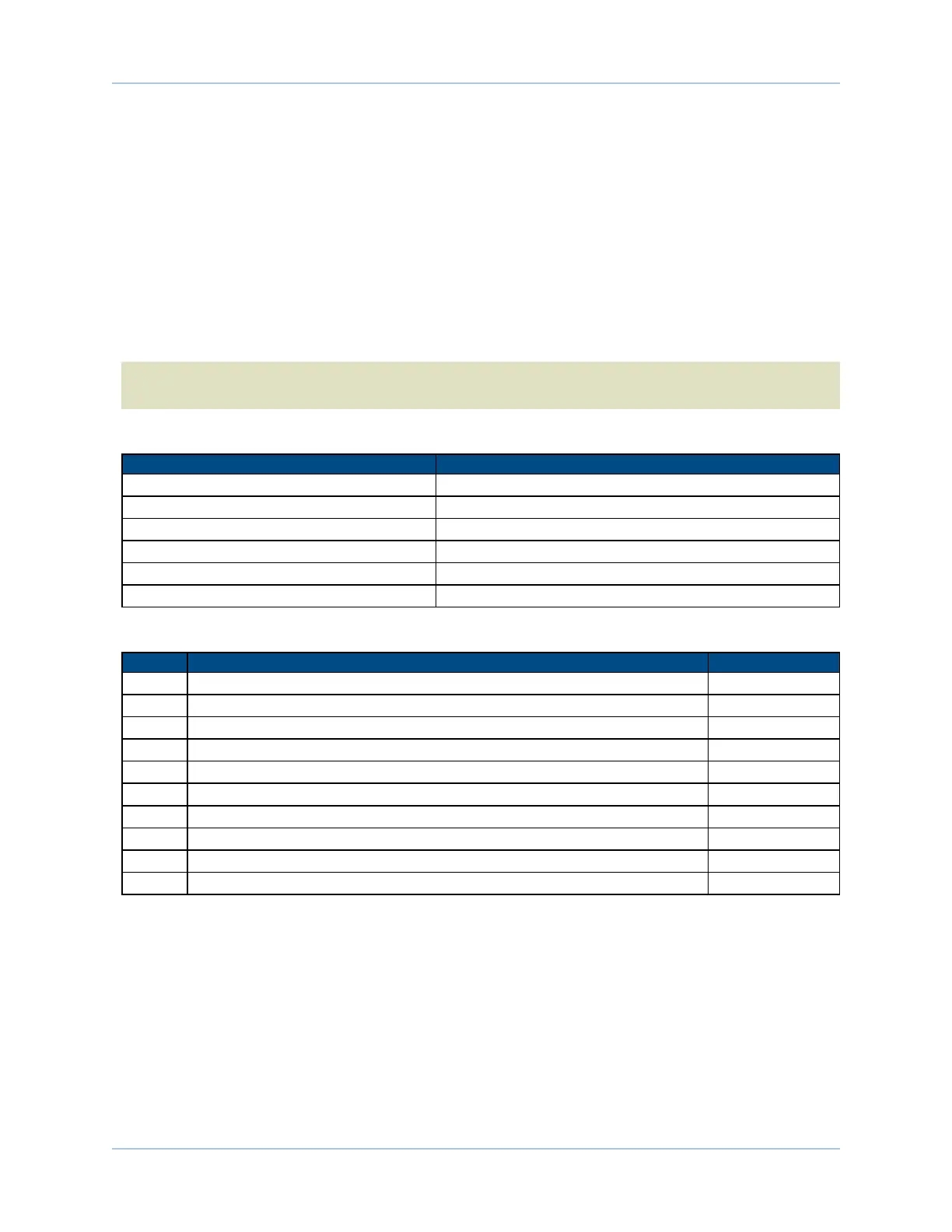
Table 2-18: Opto-Isolated Output Specifications
Opto Device Specifications Value
Maximum Voltage 24 V maximum
Maximum Sink/Source Current 80 mA/channel @ 20°C; 60 mA/channel @ 50°C
Output Saturation Voltage 2.75 V at maximum current
Output Resistance 33 Ω
Rise / Fall Time 250 usec (typical)
Maximum Output Frequency 1 kHz
Table 2-19: Opto-Isolated Output Connector Pin Assignment
Pin# Description In/Out/Bi
9 Output Common + Input
10 Optically-Isolated Output 0 Output
11 Optically-Isolated Output 1 Output
12 Optically-Isolated Output 2 Output
13 Optically-Isolated Output 3 Output
21 Output Common - Input
22 Optically-Isolated Output 4 Output
23 Optically-Isolated Output 5 Output
24 Optically-Isolated Output 6 Output
25 Optically-Isolated Output 7 Output
Suppression diodes must be installed on outputs driving relays or other inductive devices. This protects the
outputs from damage caused by inductive spikes. Suppressor diodes, such as the 1N914, can be installed
on all outputs to provide protection. It is important that the diode be installed correctly (normally reversed
biased). Refer to Figure 2-24 for an example of a current sinking output with diode suppression and Figure 2-
23 for an example of a current sourcing output with diode suppression.
34 Chapter 2 www.aerotech.com

 Loading...
Loading...