xviii
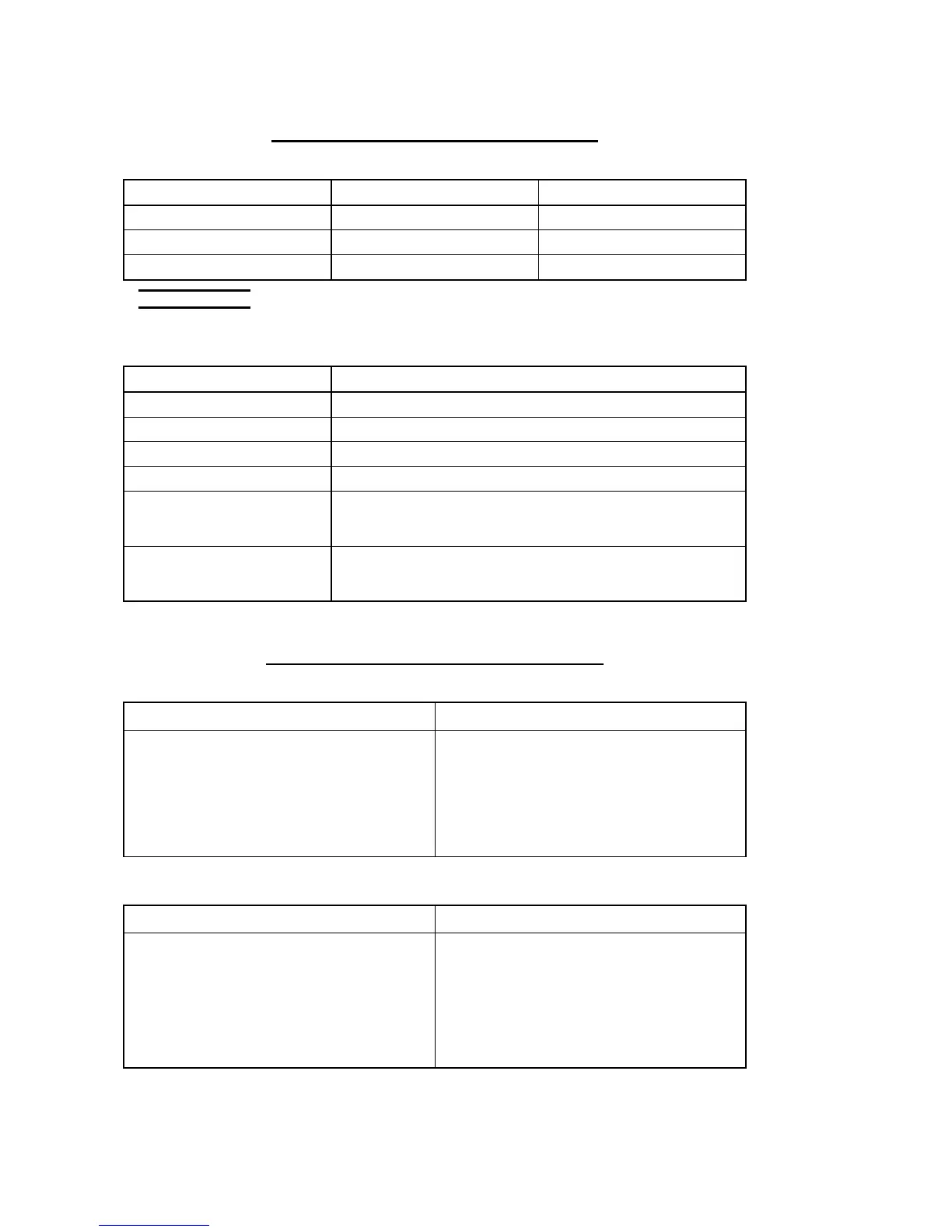
Appendix 1: Classification of cutting fluids
Water-soluble cutting fluids
Color when diluted Main composition
Soluble Milky white or clear Mineral oil
Semi-synthetic Clear Mineral oil
Synthetic Clear Polymer
NOTE
O Dilute each product to the specified ratio.
Oil-based cutting fluids
Main composition
Straight mineral oil Mineral oil
Fatty oil Animal or vegetable oil
Mixed oil Mixture of straight mineral oil and fatty oil
Chlorinated oil Straight mineral oil or mixed oil with addition of chlorine compound
Sulfurized oil
Active: Heavy cutting
Inert: Light cutting
Straight mineral oil or mixed oil with addition of sulfur compound
Sulfochlorinated oil
Active: Heavy cutting
Inert: Light cutting
Straight mineral oil or mixed oil with addition of chlorine and sulfur
compounds
Appendix 2: Characteristics of cutting fluids
Water-soluble cutting fluids
Advantage Disadvantage
• Have high cooling effect
• Not flammable
• Economical
• Do not require cleaning of cut products
(especially when soluble)
• Remove paint
• Lose rust protection effect when deteriorated
• Foam
• Putrefy
• Decline in performance, depending on quality of
water used for dilution
Oil-based cutting fluids
Advantage Disadvantage
• Have high lubricating effect (suited for heavy
cutting)
• Have high cooling effect at elevated
temperatures
• Prevent chip weldment (suited for heavy cutting)
• Provide high corrosion protection for nonferrous
materials (inert type)
• Smoke
• Flammable
• Corrosive to nonferrous materials (active type)
 Loading...
Loading...