Redundancy
HMG-838PT & HMG-838EPT Web Configuration 7-8
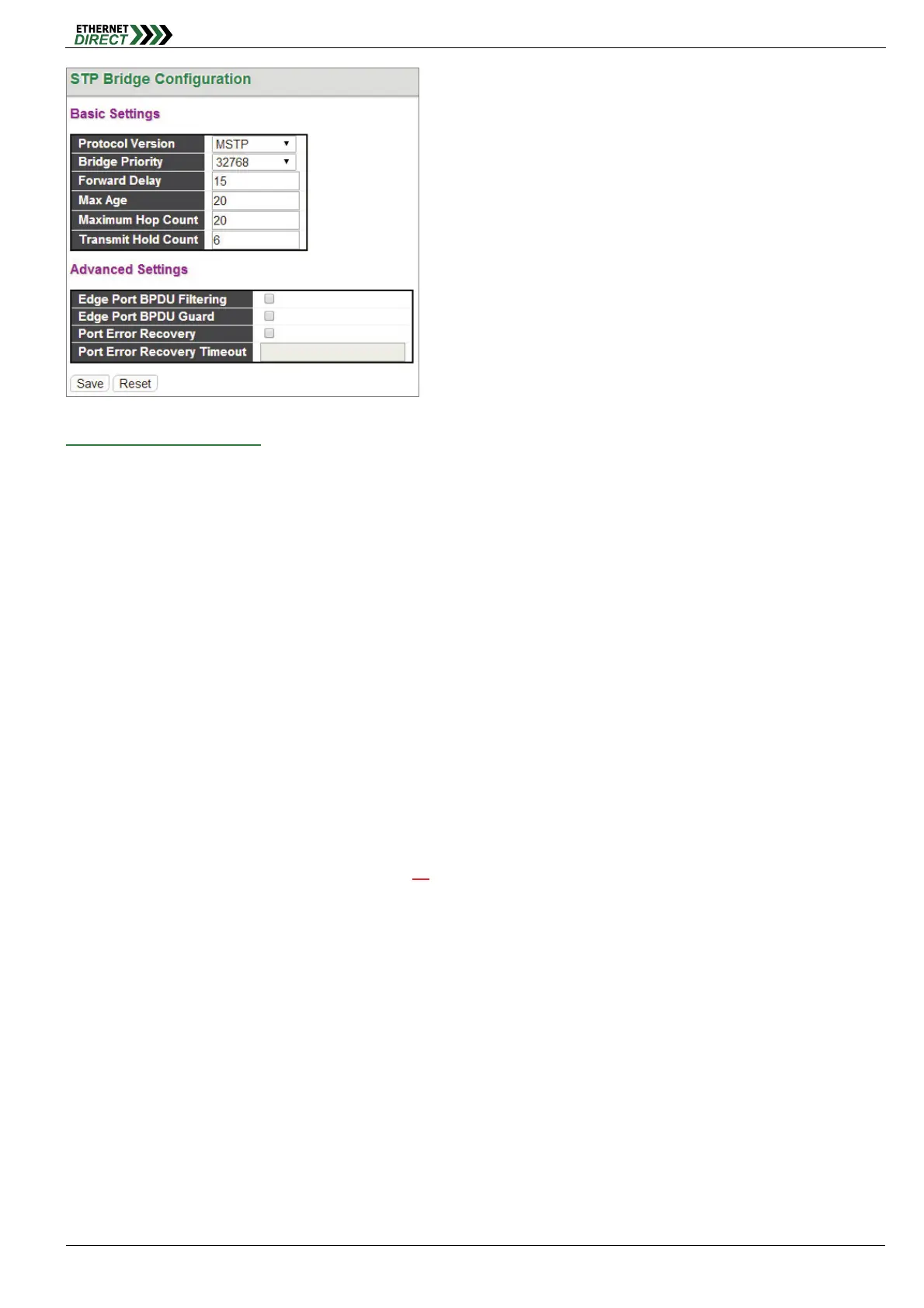
STP Bridge Configuration:
Basic Settings
Protocol Version: Select the appropriate spanning tree protocol. Protocol versions provided include “STP”,
“RSTP” and “MSTP”.
Bridge Priority: Each switch has a relative priority and cost that is used to decide what the shortest path is to
forward a packet. The lowest cost path (lowest numeric value) has a higher priority and is always used unless it is
down. If you have multiple bridges and interfaces then you need to adjust the priorities to achieve optimized
performance. For MSTP operation, this is the priority of the CIST. Otherwise, this is the priority of the STP/RSTP
bridge.
Forward Delay: Fort STP bridges, the Forward Delay is the time spent in each Listening and Learning state
before the Forwarding state is entered. This delay occurs when a new bridge comes onto a network. Valid values
are 4-30 seconds.
Max Age: If another switch in the spanning tree does not send out a hello packet for a period of time, it is
considered to be disconnected. Valid values are 6 to 40 seconds, and Max Age values must be smaller than or
equal to (Forward Delay-1)*2.
Maximum Hop Count: The maximum number of hops allowed for MST region before a BPDU is discarded. Each
bridge decrements the hop counts by one before passing on the BPDU. When the hop count reaches zero, the
BPDU is discarded. The default hop count is 20
.
Transmit Hold Count: The number of BPDU sent by a bridge port per second. When exceeded, transmission of
the next BPDU will be delayed. By default, it is set to 6. The allowed transmit hold count is 1 to 10. Please note
that increasing this value might have a significant impact on CPU utilization and decreasing this value might slow
down convergence. It is recommended to remain Transmit Hold Count to the default setting.
Advanced Settings
Edge Port BPDU Filtering: The purpose of Port BPDU Filtering is to prevent the switch from sending BPDU
frames on ports that are connected to end devices.
Edge Port BPDU Guard: Edge ports generally connect directly to PC, file servers or printers. Therefore, edge
ports are configured to allow rapid transition. Under normal situations, edge ports should not receive configuration
BPDUs. However, if they do, this probably is due to malicious attacks or mis-settings. When edge ports receive
configuration BPDUs, they will be automatically set to non-edge ports and start a new spanning tree calculation
process.
 Loading...
Loading...