SECTION 2 – DESIGN
Page 8 of 39 Fike Clean Agent System w/ FM-200™ UL / ULC Ex4623
Revision Date: January, 2010 Manual P/N: 06-215 (Rev G) FM 3010715
2.4.3.2 ALTITUDE CORRECTION FACTORS
The design quantity of HFC-227ea shall be adjusted to compensate for ambient pressures that vary more than
eleven percent [equivalent to approximately 3000 ft. (915 m) of elevation change] from standard sea level
pressures [29.92 in. Hg at 70
o
F]. (Reference: NPFA 2001, Section 3-5.3.3, 2000 edition)
The amount of agent required must be adjusted using the correction factors shown below to compensate for
these effects. (Reference: NFPA 2001, Table 3-5.3.3)
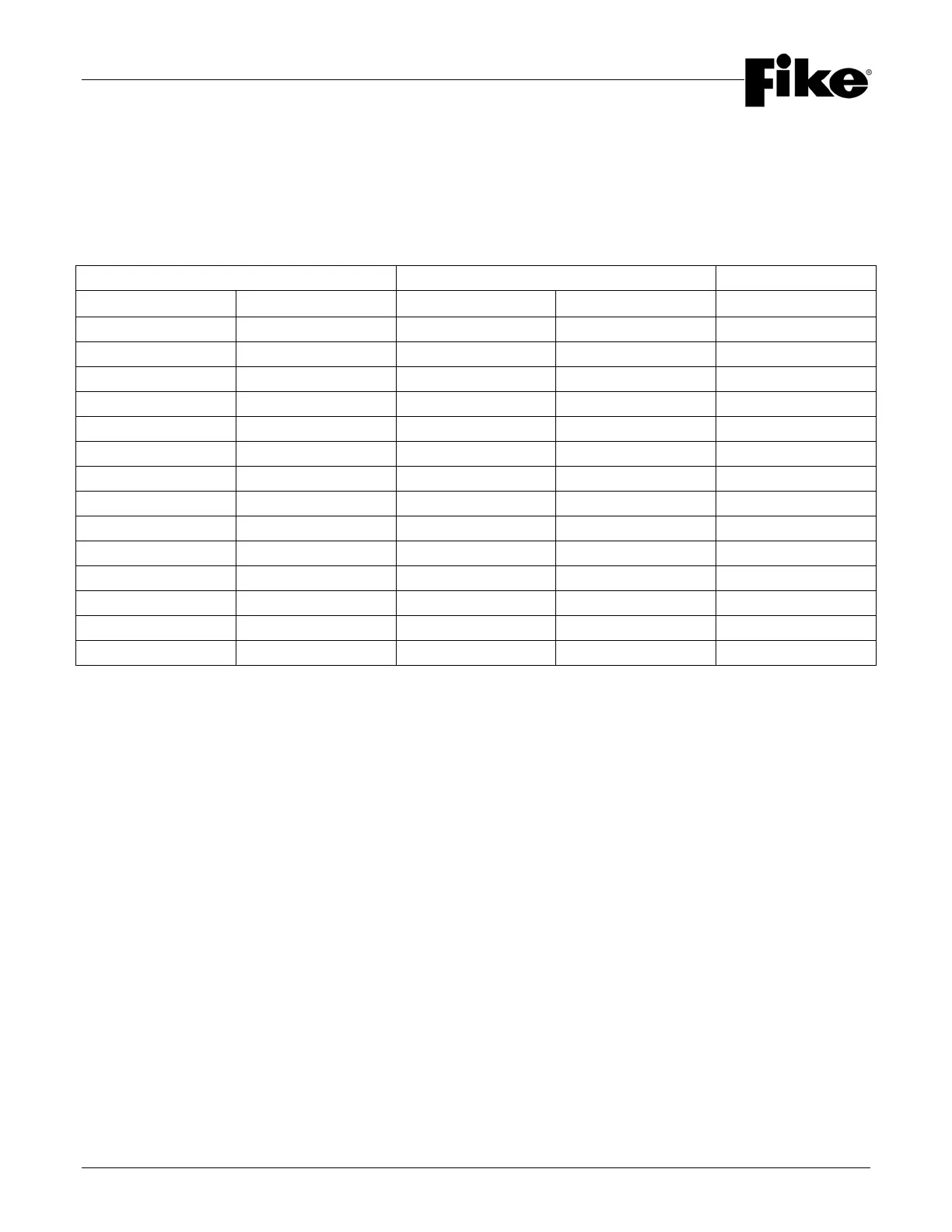
Altitude Enclosure Pressure
Correction
Feet Kilometers psia mm Hg
Factor
-3,000 -0.92 16.25 840 1.11
-2,000 -0.61 15.71 812 1.07
-1,000 -0.30 15.23 787 1.04
0 0.00 14.71 760 1.00
1,000 0.30 14.18 733 0.96
2,000 0.61 13.64 705 0.93
3,000 0.91 13.12 679 0.89
4,000 1.22 12.58 650 0.86
5,000 1.52 12.04 622 0.82
6,000 1.83 11.53 596 0.78
7,000 2.13 11.03 570 0.75
8,000 2.45 10.64 550 0.72
9,000 2.74 10.22 528 0.69
10,000 3.05 9.77 505 0.66
2.4.3.3 DETERMINE ACTUAL CONCENTRATION AT MAXIMUM TEMPERATURE
The next step is to determine the expected concentration level at the maximum temperature for the hazard(s).
This is a necessary step when designing systems for occupied spaces in order to properly evaluate the exposure
and egress time limitations discussed in Section 2.3.
The expected concentration can be determined by applying the following formula.
100WS
C = ----------
V + WS
Where: W = Agent Weight in lbs. (kg)
V = Hazard Volume / ft
3
(m
3
)
C = Design Concentration, % by volume
S = Specific Vapor in ft
3
/lb (m
3
/kg)
Refer to Section 2.4.2 of this Manual for determining the S value.

 Loading...
Loading...