SECTION 2 – DESIGN
Page 6 of 39 Fike Clean Agent System w/ FM-200™ UL / ULC Ex4623
Revision Date: January, 2010 Manual P/N: 06-215 (Rev G) FM 3010715
2.4.3 ADDITIONAL CONSIDERATIONS
Additional quantities of agent are required through the use of design factors to compensate for special conditions
that may affect the ability of the system to extinguish the fire. Therefore, additional agent may be necessary for
either of the following situations: NFPA 2001 Tee Design Factor or altitude adjustments. The system designer
MUST be aware of these criteria and make adjustments as necessary.
2.4.3.1 TEE DESIGN FACTOR
Where a single agent supply is used to protect multiple hazards, a design factor must be applied in accordance
with NFPA 2001, Section 3.
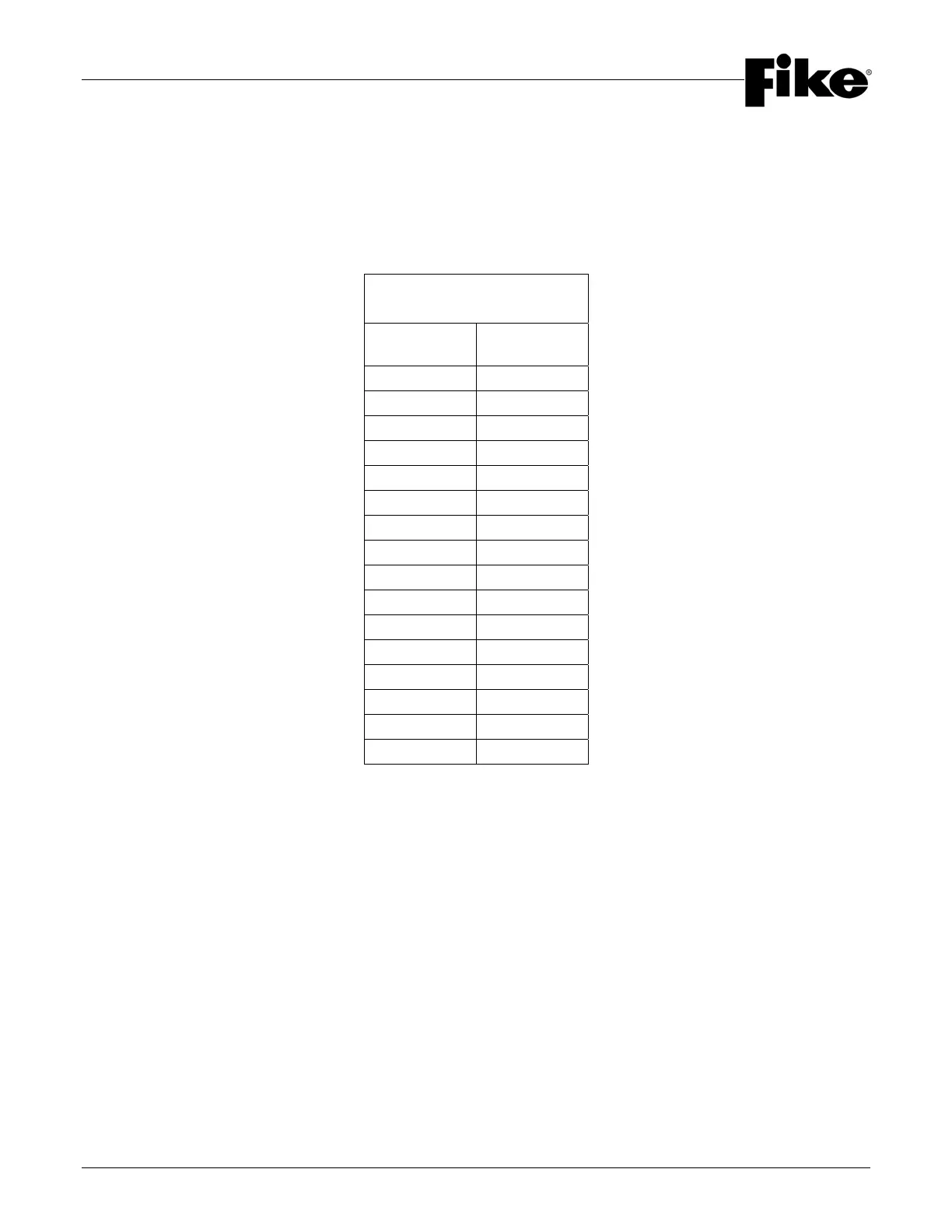
Tee Design Factors
(NFPA 2001, Table 3-5.3.1)
Tee
Count
Design
Factor
0 - 4 0.00
5 0.01
6 0.02
7 0.03
8 0.04
9 0.05
10 0.06
11 0.07
12 0.07
13 0.08
14 0.09
15 0.09
16 0.10
17 0.11
18 0.11
19 0.12
The Tee Design Factor is determined for each hazard protected in accordance with the following.
Starting from the point where the piping enters the hazard that is located farthest (hydraulically) from
the supply tank(s), count the number of tees in the direct flow path as it returns to the supply tank(s).
Do Not include the tees that are used in the manifold (if applicable).
Any tee within the hazard that supplies agent to another hazard shall be included in the tee count.
After counting the tees, compare that number to the chart above to determine the Tee Design Factor.
Apply the Tee Design Factor to the Agent Quantity calculations by multiplying the Tee Design Factor
by the amount of agent previously determined in the volumetric calculations.
NOTE: If you are not sure which hazard is farther away, count the tees in the flow path from each hazard and use
the highest number.
 Loading...
Loading...