5.3 Description of Function Codes 5.3.1 F codes (Fundamental functions)
At the start of
acceleration
At the end of
acceleration
At the start of
deceleration
At the end of
deceleration
S-curve (arbitrary)
Setting range:
0 to 100%
H57
When accelerating
No. 1 S-curve
range
(when starting)
H58
When accelerating
No. 2 S-curve
range
(when finished)
H59
When decelerating
No. 1 S-curve
range
(when starting)
H60
When decelerating
No. 2 S-curve
range
(when finished)
Acceleration/deceleration time
<S-curve acceleration/deceleration (Weak): When frequency change is 10 % or higher than the maximum
frequency>
Acceleration or deceleration time (s) = (2 5/100 + 90/100+ 2 5/100) reference acceleration or
deceleration time
= 1.1 reference acceleration or deceleration time
<S-curve acceleration/deceleration (Arbitrary: When 10 % at the start, 20 % at the end): When frequency
change is 30 % or higher than the maximum frequency.>
Acceleration or deceleration time (s) = (2 10/100 + 70/100 + 2 20/100) (reference acceleration or
deceleration time)
= 1.3 (reference acceleration or deceleration time)
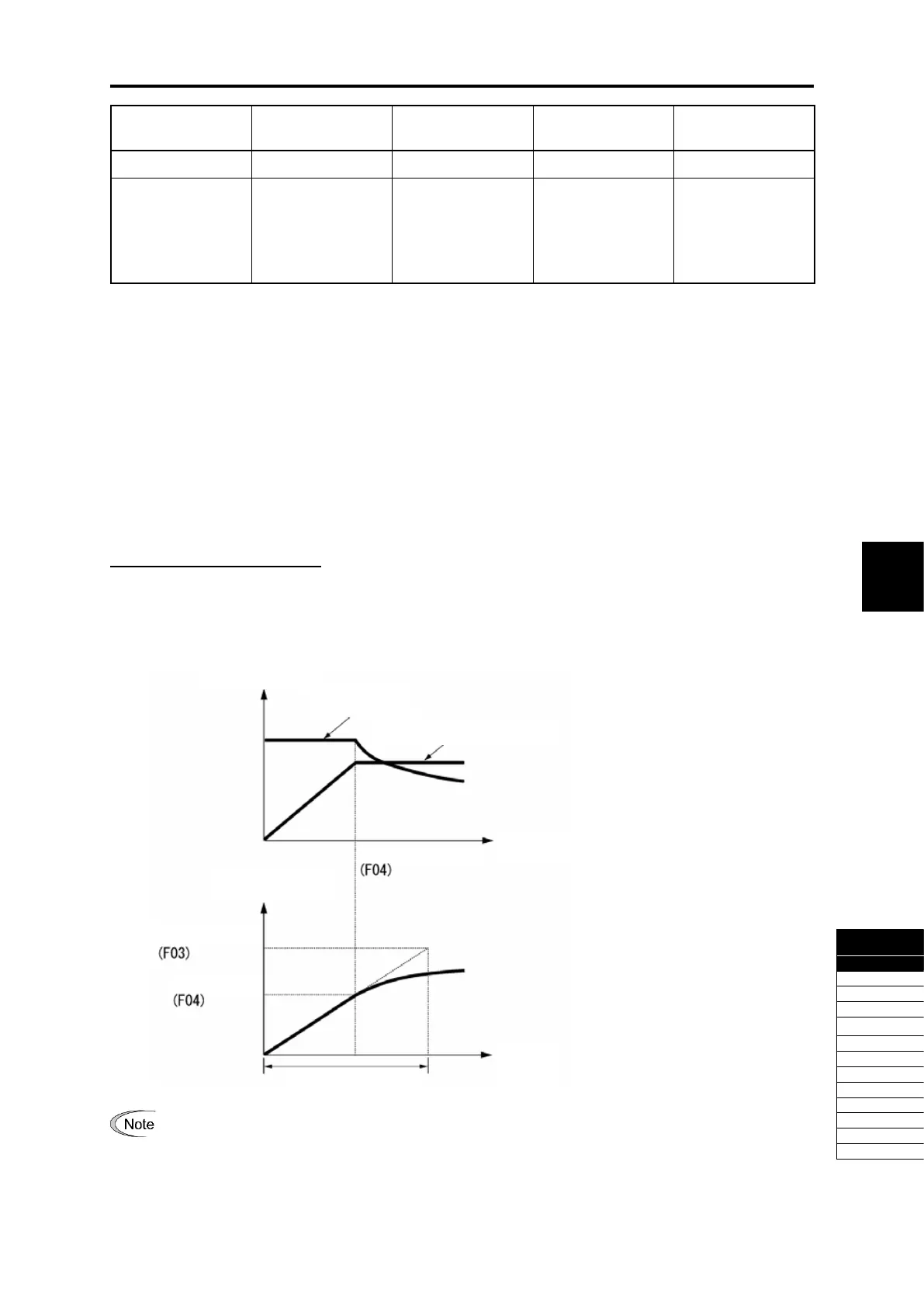
Curve acceleration/deceleration
This is a pattern to perform linear acceleration/deceleration (rated torque) at or below base frequency and
acceleration becomes gradually slower at or higher than the base frequency, and acceleration/deceleration with
constant load rate (rated output).
It is possible to accelerate/decelerate with the maximum capability of the motor to be driven by the inverter.
The diagram on the left
shows pattern at
acceleration.
This is the same as at
deceleration.
• When S-curve acceleration/deceleration and curve acceleration/deceleration is selected by curve
acceleration/deceleration H07, the actual acceleration/deceleration time becomes longer than the set
value.
• If acceleration/deceleration time is set shorter than necessary, current limiting function, torque limit or
anti-regenerative function may operate and acceleration/deceleration time may become longer than
the set value.
Specified acceleration time

 Loading...
Loading...











