Page 7-7
μ@@@EQ1@@ μ @@@EQ2@@. The equations are listed in the stack as follows (small
font option selected):
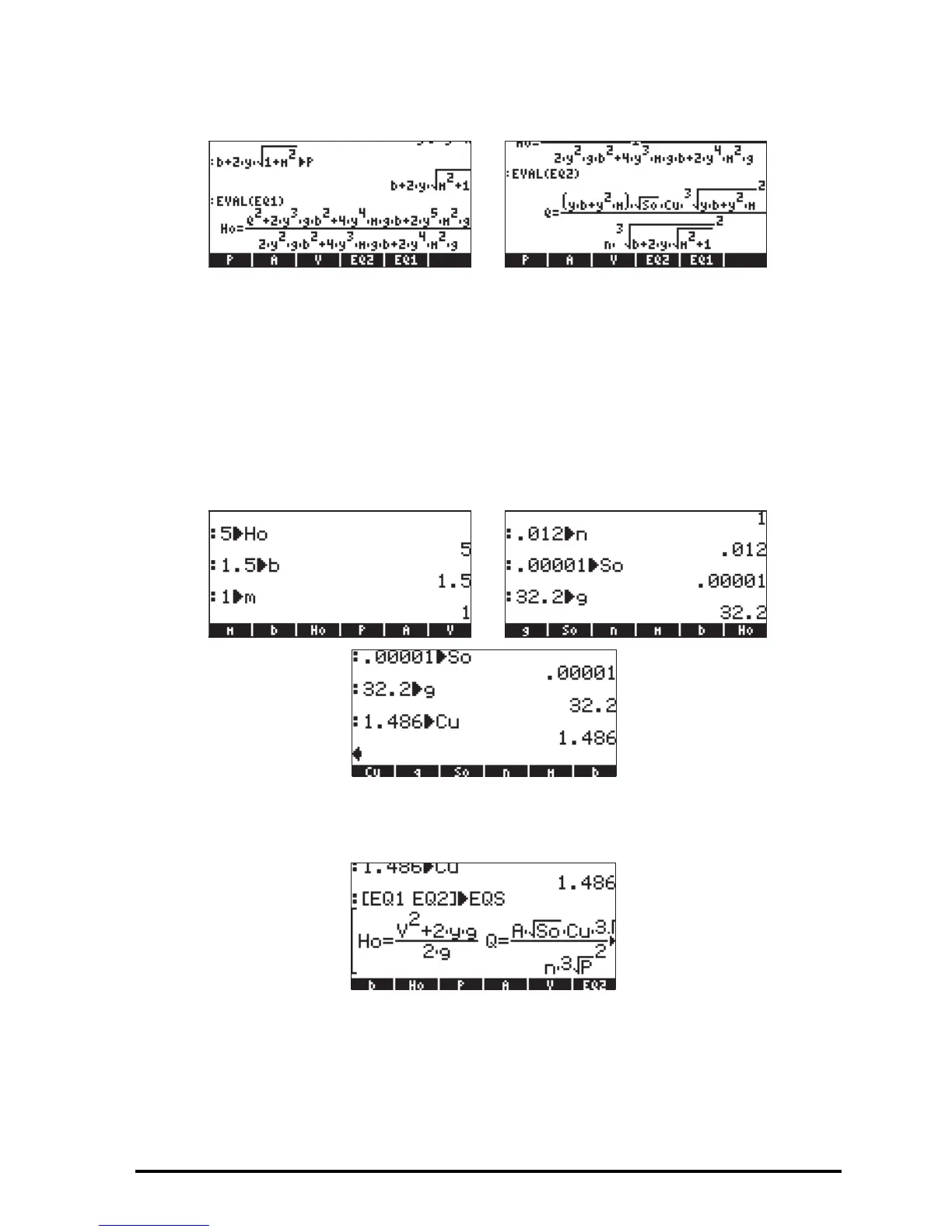
We can see that these equations are indeed given in terms of the primitive
variables b, m, y, g, S
o
, n, Cu, Q, and H
o
.
In order to solve for y and Q we need to give values to the other variables.
Suppose we use H
0
= 5 ft, b = 1.5 ft, m = 1, n = 0.012, S
0
= 0.00001, g =
32.2, and Cu = 1.486. Before being able to use MSLV for the solution, we
need to enter these values into the corresponding variable names. This can be
accomplished as follows:
Now, we are ready to solve the equation. First, we need to put the two
equations together into a vector. We can do this by actually storing the vector
into a variable that we will call EQS (EQuationS):
As initial values for the variables y and Q we will use y = 5 (equal to the value
of H
o
, which is the maximum value that y can take) and Q = 10 (this is a
guess). To obtain the solution we select function MSLV from the NUM.SLV
menu, e.g., ‚Ï6@@@OK@@@, to place the command in the screen:

 Loading...
Loading...




