GENERAL TRANSMISSION
7C - 3
DESCRIPTION
The transmission is designed to provide high speed shifting by use of hydraulically actuated clutch packs. It has three
forward and three reverse speeds. Gears are mounted on four shafts; directional (input) shaft (12), range (output) shaft
(8), countershaft (17) and reverse idler shaft (18).
Directional (Input) Shaft
The directional (input) shaft (12) rotates on two tapered roller bearings. It consists of a forward drive gear (11), reverse
drive gear (10) and dual hydraulic clutch packs.
Reverse Idler Shaft
The reverse idler shaft (18) is bolted to the housing (1). It consists of a reverse idler gear (19) which rides on two
tapered roller bearings and is in constant mesh with reverse drive gear (10) and 2nd speed drive gear (15).
Countershaft
The countershaft (17) rotates on two tapered roller bearings. It consists of 3rd speed drive gear (16), 2nd speed drive
gear (15) and 1st speed drive gear (14).
Range (Output) Shaft
The range (output) shaft (8) rotates on two tapered roller bearings. It consists of the 3rd speed driven gear (7), the 2nd
speed driven gear (6) and the 1st speed driven gear (5). It also contains dual hydraulic clutch pack for 2nd and 3rd
speeds and a single clutch pack assembly for 1st speed.
OPERATION
Main pressure oil is detected from the range selector valve through passages
in the trans case to the manifolds and on through the shafts to engage the
desired clutch pack. Lubrication oil is always directed through passages to
lubricate the bearings, clutches and shafts.
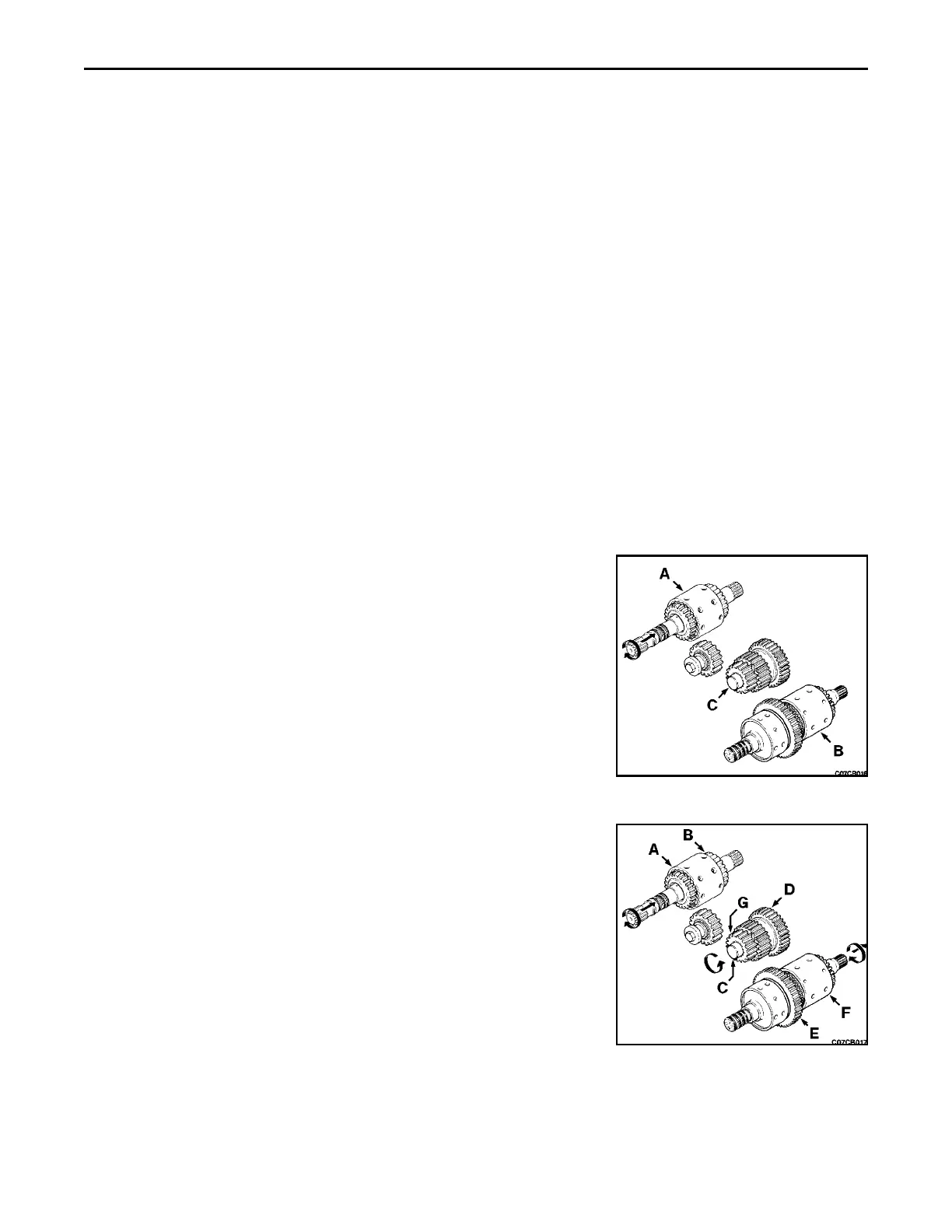
Neutral
Engine power and torque are delivered through the converter and drive shaft
to the transmission directional (input) shaft (A). As the forward and reverse
clutch packs are not engaged, the shaft turns freely inside the gears. No
power is transmitted to the countershaft (C) or to the range (output) shaft (B).
1st Speed Forward
Engine power and torque are delivered through the converter and drive shaft
to the directional (input) shaft (A). As the forward clutch pack is activated, it
engages the forward gear (B) and rotates it in the same direction as the shaft.
The countershaft (C), through the 3rd speed drive gear (D), is rotated in the
opposite direction. As the 1st speed clutch pack is activated, it engages the
1st speed driven gear (E) to the range (output) shaft (F). Power from the
countershaft is transferred, through the 1st speed drive gear (G), to the range
(output) shaft in the opposite direction of rotation. Power is delivered from the
range (output) shaft to the steering and sprocket drives and on to the tracks.

 Loading...
Loading...