9. Navigation and guidance system
MiR600 User Guide (en) 08/2021 - v.1.0 ©Copyright 2021: Mobile Industrial Robots A/S. 94
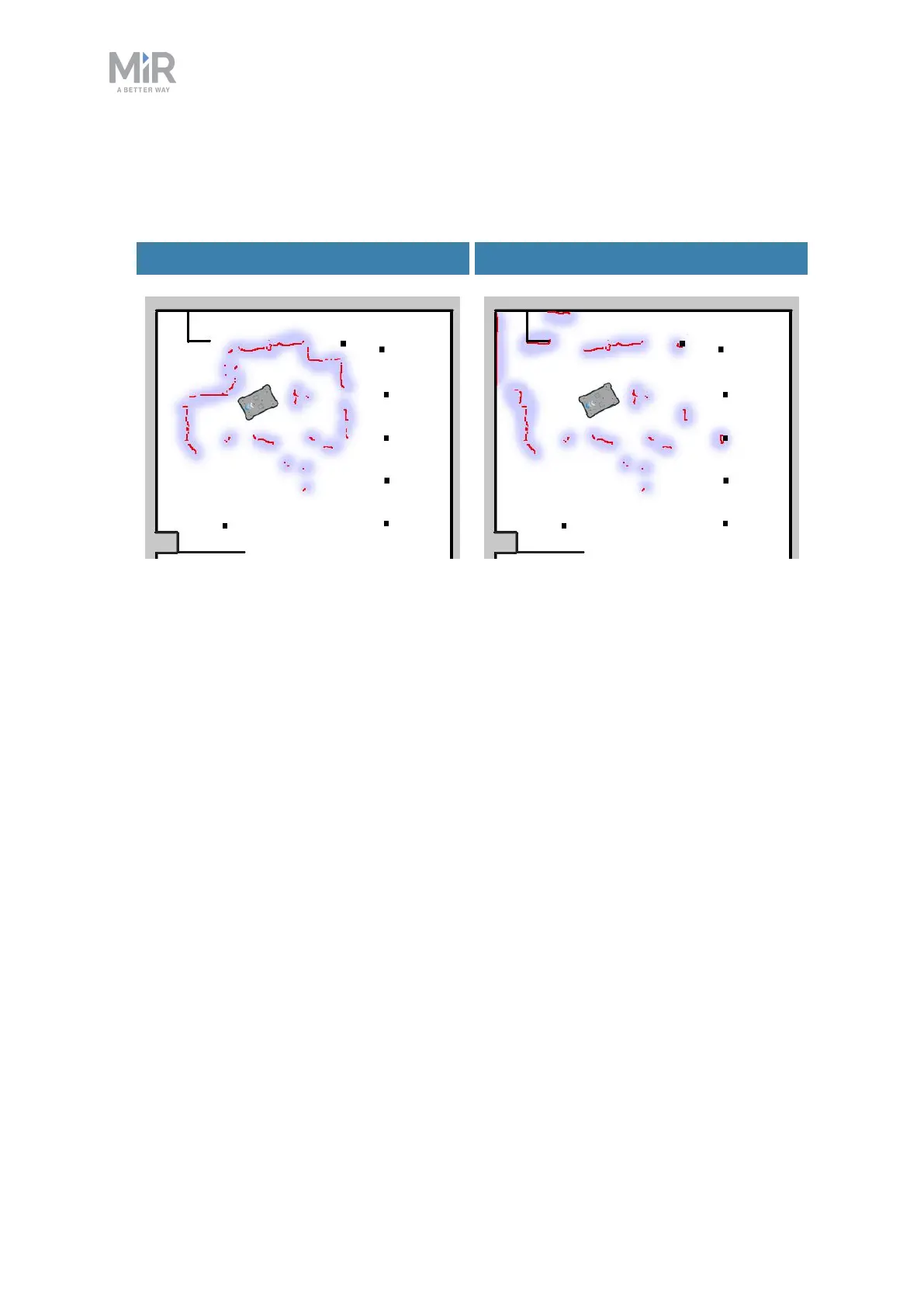
• The robot must be able to detect the static landmarks that are marked on the map to be
able to approximate its current position. Make sure there are not too many dynamic
obstacles around the robot so that it cannot detect any static landmarks.
Cannot detect any static landmarks Can detect enough static landmarks
• The robot does not compare the laser scanner data with the entire map, but only around
the area that it expects to be close to based on the IMU and encoder data and its initial
position. This is why it is important that the initial position you place the robot at on the
map is accurate.
• The robot can drive for a short distance without being correctly localized. As it drives, the
estimated positions should converge to a small area, indicating the robot has determined
an accurate estimate. If this does not occur within a set time limit, the robot reports a
localization error.
9.7 Motor controller and motors
The robot keeps adjusting how much power is sent to each motor based on sensory
input.This means that the robot can correct its speed when going up slopes or when carrying
a heavier payload, and it can change its driving direction to avoid moving obstacles.
9.8 Brakes
Once the approximated position of the robot determined from localization is the same as the
goal position calculated by the global planner, the robot stops by using regenerative braking
in the motors.
 Loading...
Loading...