Reengineer cells for high traffic areas 91
The information in this table is used to determine the number of
cells that require reengineering.
--End--
Determining cell reengineering
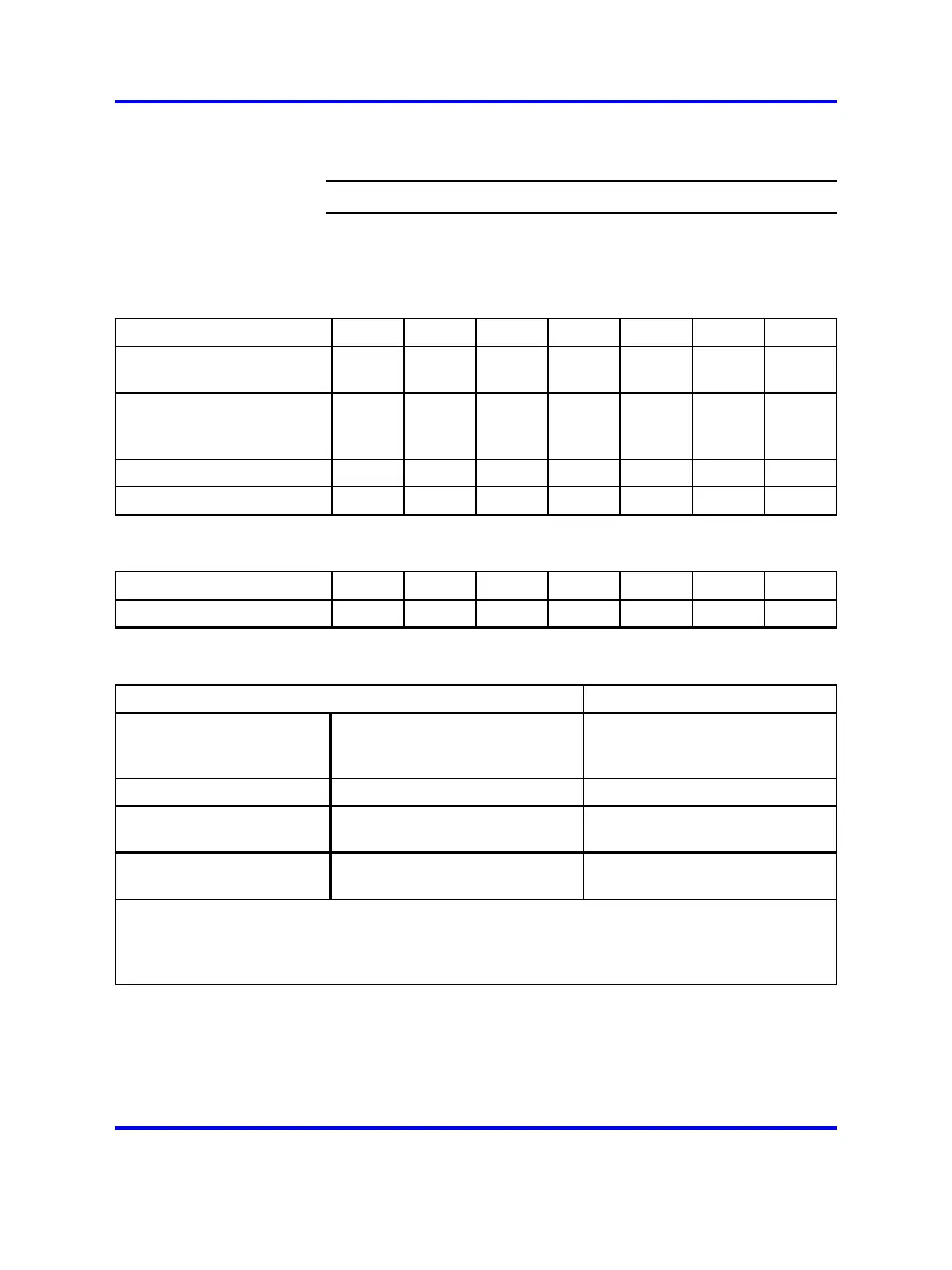
Table 16
Example of a completed estimate table
Estimate for:
1C1 1C2 1C3 1C4 1C5 1C6 1C7
Users inside the cell with an
office
8.4 0.7 21.0 14.7 0.7 4.9 2.1
Users with an office outside
of a cell who walk into the
cell
3.2 3.7 2.3 2.7 3.7 3.4 3.6
Users without an office
0000000
Users in a cell
11.6 4.4 23.3 17.7 4.4 8.3
5.7
Table 17
Example of a completed telephone types table
Telephone type
1C1 1C2 1C3 1C4 1C5 1C6 1C7
User telephone types H&W H&W M M H&W H&W H&W
Table 18
Cell reengineering
Estimate for:
Users with both a
handset and a wired
telephone
Users with only a handset Action
From 0 up to 20 From 0 up to 12 Keep cell size as deployed.
Greater than 20 but no
more than 80
Greater than 12, but no more
than 40
Install a 12-channel basestation
or subdivide the cell
a
.
Greater than 80 Greater than 40 Subdivide the cell
a
to meet the
preceding conditions.
a. For details about how to subdivide cells, see “High handset density deployment” (page 95). Use
a 12-channel basestation in areas of high traffic capacity. Cell subdivision is appropriate if it helps
to improve coverage where the loop resistance exceeds 100 ohms or if a Digital Mobility Controller
(DMC) cannot support more than two 12-channel units.
Note: Use Table 18 "Cell reengineering" (page 91) only for user types
H&W and H. For user type M see “A mix of users with and without wired
telephones in a cell” (page 93).
Nortel Communication Server 1000
SIP DECT Fundamentals
NN43120-123 01.07
6 January 2009
Copyright © 2008-2009 Nortel Networks
.

 Loading...
Loading...