Wrist Camera Instruction Manual
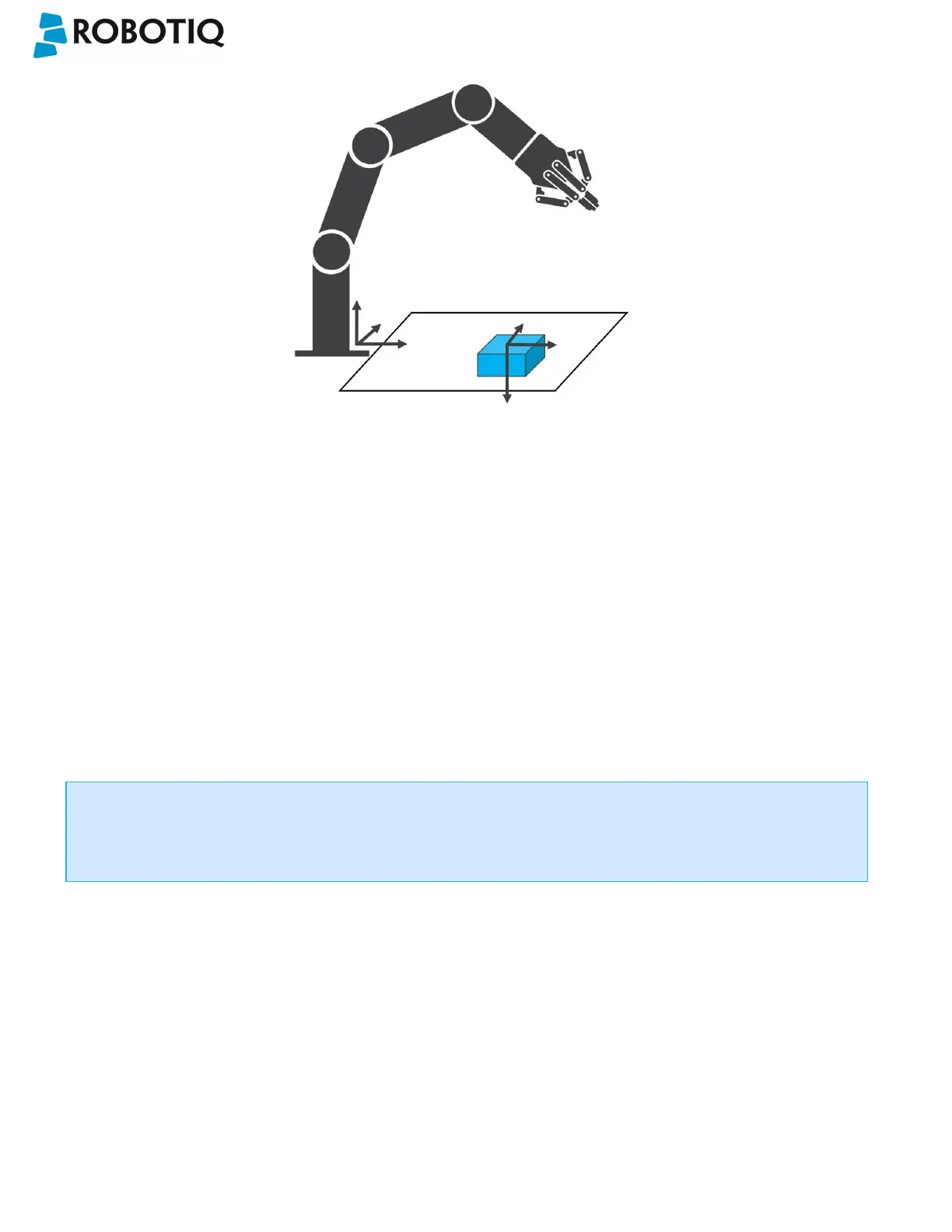
Fig. 6-5: object_location pose on the workplane used for the calibration.
object_location is a variable with the pose structure (x, y, z, x rotation, y rotation, z rotation):
x: x position of the object detected, relative to the robot's base reference frame.
y: y position of the object detected, relative to the robot's base reference frame.
z: z position of the object detected, relative to the robot's base reference frame.
x rotation: x rotation from the robot's base frame to the detected object feature reference frame. The object's X axis is
parallel to the workplane on which the calibration has been performed.
y rotation: y rotation from the robot's base frame to the detected object feature reference frame. The object's Y axis is
parallel to the workplane on which the calibration has been performed.
z rotation: z rotation from the robot's base frame to the detected object feature reference frame. The object's Z axis is
normal to the workplane on which the calibration has been performed, points downwards from it, into the workplane.
If you move the robot's TCP to the object_location pose, the TCP will go and point the object on the workplane.
The height value of the object on the workplane should not be taken into account - the TCP might be directly on
the object when moving it to the object_location pose.
©Robotiq inc. 2016-2018
87
 Loading...
Loading...