5
Motor or Generator Differential Protection (87M/G)
7UT51 v3
74 PRIM-2330C
5.5 Through
-
Fault Restraint
CT saturation caused by a high-current internal fault
(or by long system time constants) affects the
differential current,
I
diff
, and the restraining current,
I
rest
, about equally; therefore, the trip characteristic
(see Section 5.4 on page 71) can handle this situation.
However, a high-current through-fault can cause
considerable differential current due to unequal CT
saturation at the different CT measuring locations. To
restrain tripping in this situation, the differential
protection function has a special feature.
High-current external fault is characterized by an initial
rise in the restraining current that is much more rapid
than the initial rise in the differential current. If the
operating point moves quickly (within 0.5 cycle) into
the through-fault-detection area shown in Figure 5.3,
the 87M/G function will restrained for a configurable
duration. The restraint will be released if for two
complete cycles the ratio of the differential current to
the restraining current is less than 0.9 (that is, the
operating point moves up to within 90% of the
I
diff
=I
rest
line on Figure 5.3), which would indicate an
internal fault is evolving during the external fault.
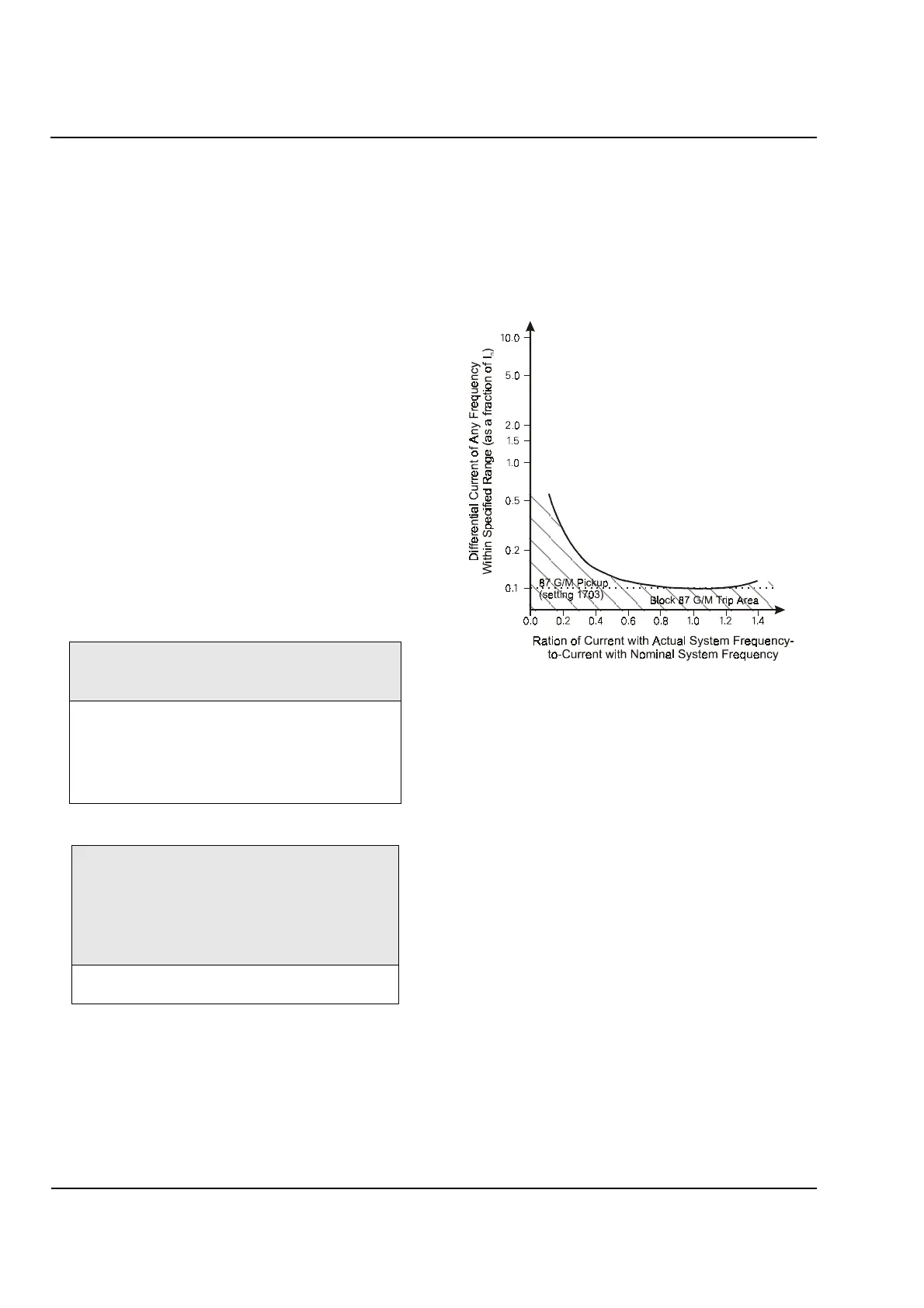
5.6 Blocking by Frequency
Variance
If the system frequency varies too far from the rated
nominal frequency, the motor/generator differential
protection will be blocked, as illustrated in Figure 5.4.
Figure 5.4
Blocking of Motor/Generator Differential
Protection (87M/G) by Variance from Nominal
System Frequency.
1717 T
-
SAT
-
BLK
Maximum duration of through
-
fault CT
-
saturation
restraint of the 87M/G function.
Range: 2
–
250 cycles, or ∞ (until drop
-
off of pickup)
Default: 8 cycles
The timer starts when the operating point enters the
through
-
fault restraint area (see Figure 5.3). Enter ∞
for the restraint to continue until dropout of the
differential protection pickup.
1718 SAT
-
RESTR.
Minimum restraint current required to activate
through
-
fault CT
-
saturation restraint. This value sets
the left edge of the through
-
fault restraint area
shown in Figure 5.3. The top of the area is a line
passing through the origin whose slope is one
-
half
the slope of Slope 1 (Address 1706).
Range: 5.00
–
15.00
I
n
Default: 7.00
I
n

 Loading...
Loading...










