Introduction
OXY5500 Operator’s Manual 1
–7
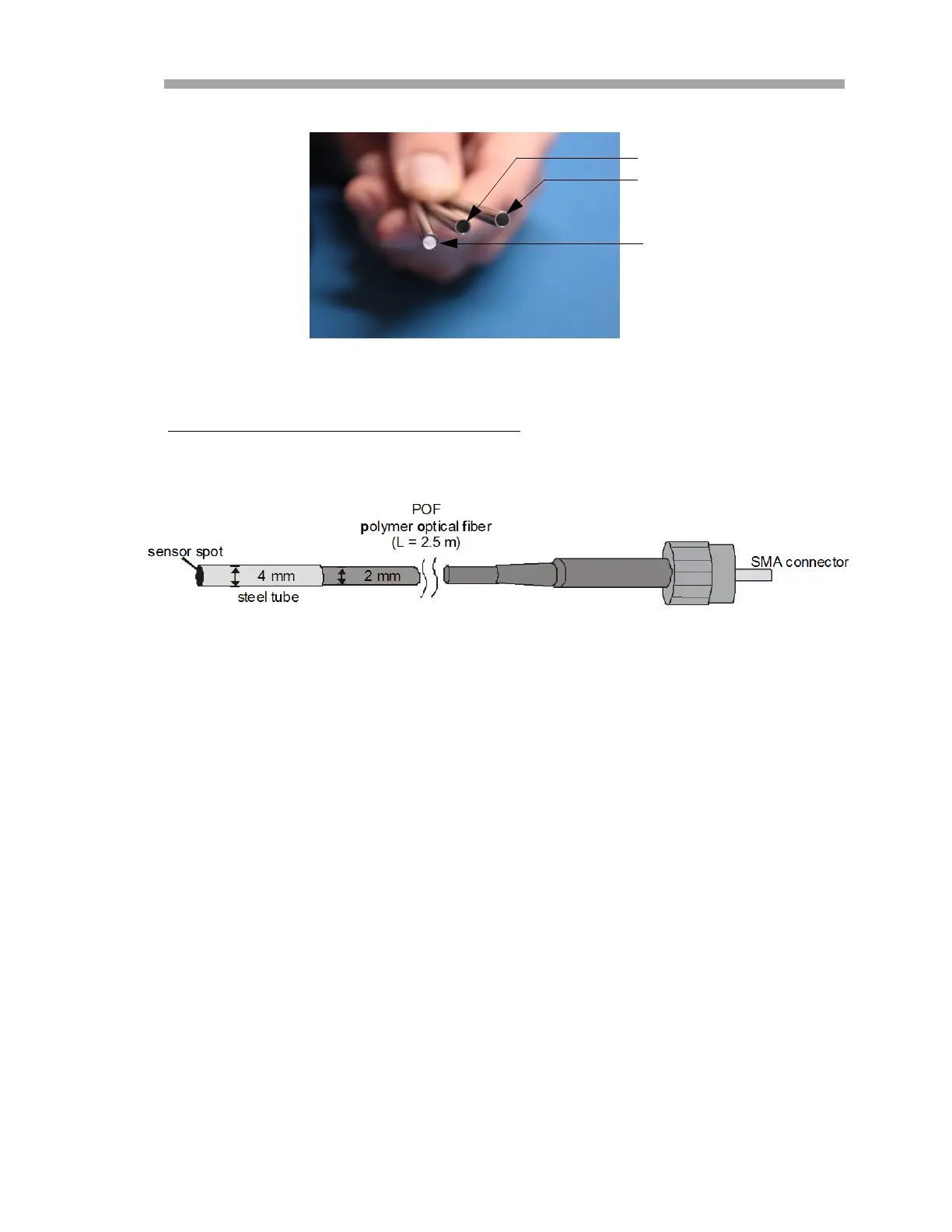
Schematic drawing for the Oxygen Probe
Refer to Figure 1–5 for a schematic of the trace oxygen probe.
This probe has a very rugged sensor with excellent long-term stability (more
than 100000 data points without drift) and is usable for process applications.
How does an oxygen sensor work?
The principle of measurement is based on the effect of dynamic luminescence
quenching by molecular oxygen. The following scheme explains the principle of
dynamic luminescence quenching by oxygen.
Principle of dynamic quenching of luminescence by molecular oxygen (refer to
Figure 1–6):
• Luminescence process in absence of oxygen (1)
• Deactivation of the luminescent indicator molecule by molecular
oxygen (2)
The collision between the oxygen-sensitive material in its excited state and the
quencher (oxygen) results in radiation-less deactivation and is called collisional
or dynamic quenching. After collision, energy transfer takes place from the
excited indicator molecule to oxygen which consequently is transferred from its
ground state (triplet state) to its excited singlet state. As a result, the indicator
molecule does not emit luminescence and the measurable luminescence signal
decreases.
Figure 1–4 OXY5500 probe tips
OP-3
OP-6
OP-9
Figure 1–5 Trace oxygen probe schematic

 Loading...
Loading...