Core peripherals PM0214
248/262 PM0214 Rev 9
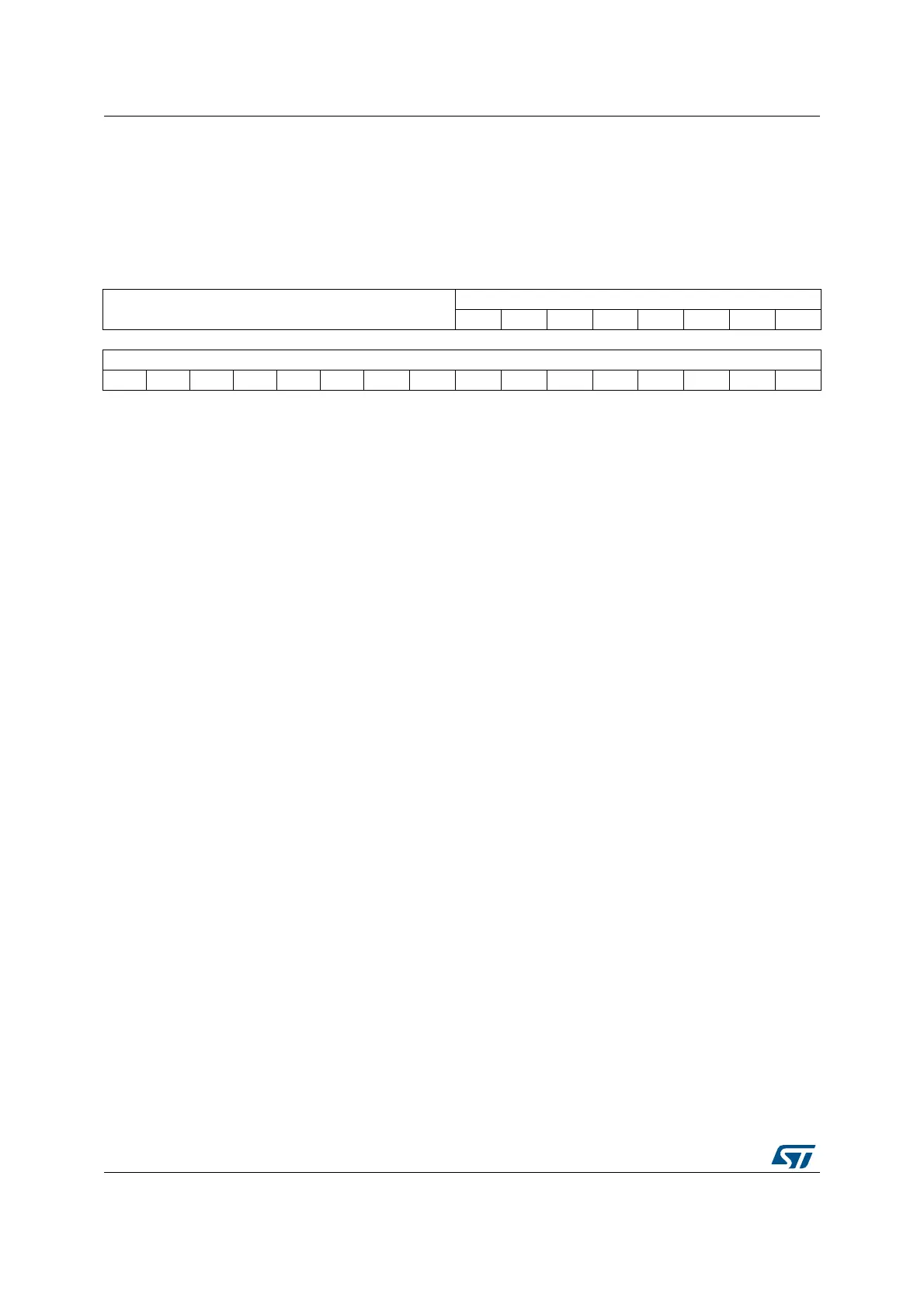
4.5.2 SysTick reload value register (STK_LOAD)
Address offset: 0x04
Reset value: 0x0000 0000
Required privilege: Privileged
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Reserved
RELOAD[23:16]
rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw
1514131211109876543210
RELOAD[15:0]
rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw rw
Bits 31:24 Reserved, must be kept cleared.
Bits 23:0 RELOAD: RELOAD value
The LOAD register specifies the start value to load into the STK_VAL register when the
counter is enabled and when it reaches 0.
Calculating the RELOAD value
The RELOAD value can be any value in the range 0x00000001-0x00FFFFFF. A start value of
0 is possible, but has no effect because the SysTick exception request and COUNTFLAG are
activated when counting from 1 to 0.
The RELOAD value is calculated according to its use:
l To generate a multi-shot timer with a period of N processor clock cycles, use a RELOAD
value of N-1. For example, if the SysTick interrupt is required every 100 clock pulses, set
RELOAD to 99.
l To deliver a single SysTick interrupt after a delay of N processor clock cycles, use a
RELOAD of value N. For example, if a SysTick interrupt is required after 100 clock
pulses, set RELOAD to 99.

 Loading...
Loading...