Sun Microelectronics
131
7. UltraSPARC External Interfaces
7.16 Transaction Sequences
This section describes the basic coherent transaction sequences, illustrating the
sequence of events that transpire as a function of cache states and transaction
type.
The transaction sequences are described in separate tables for each interesting
combination of transaction and initial state. Time moves downwards through the
table; events specified in the same row occur at the same time. The cache state of
the requested block in a processor is denoted by the Etag entry. If a processor
does not have the missed block, the block state for the datum is denoted by
Etag{I}.
Note: These tables do not necessarily indicate what happens in each clock cycle;
instead, they show the transfer of control between the processors and the SC.
Thus, each table row may represent zero or more clock ticks.
7.16.1 ReadToShare Block
Condition: Load miss on Processor 1; no other processor has the data.
7.16.2 ReadToShareAlways Block
Condition: I-Cache miss on Processor 1; no other processor has the data.
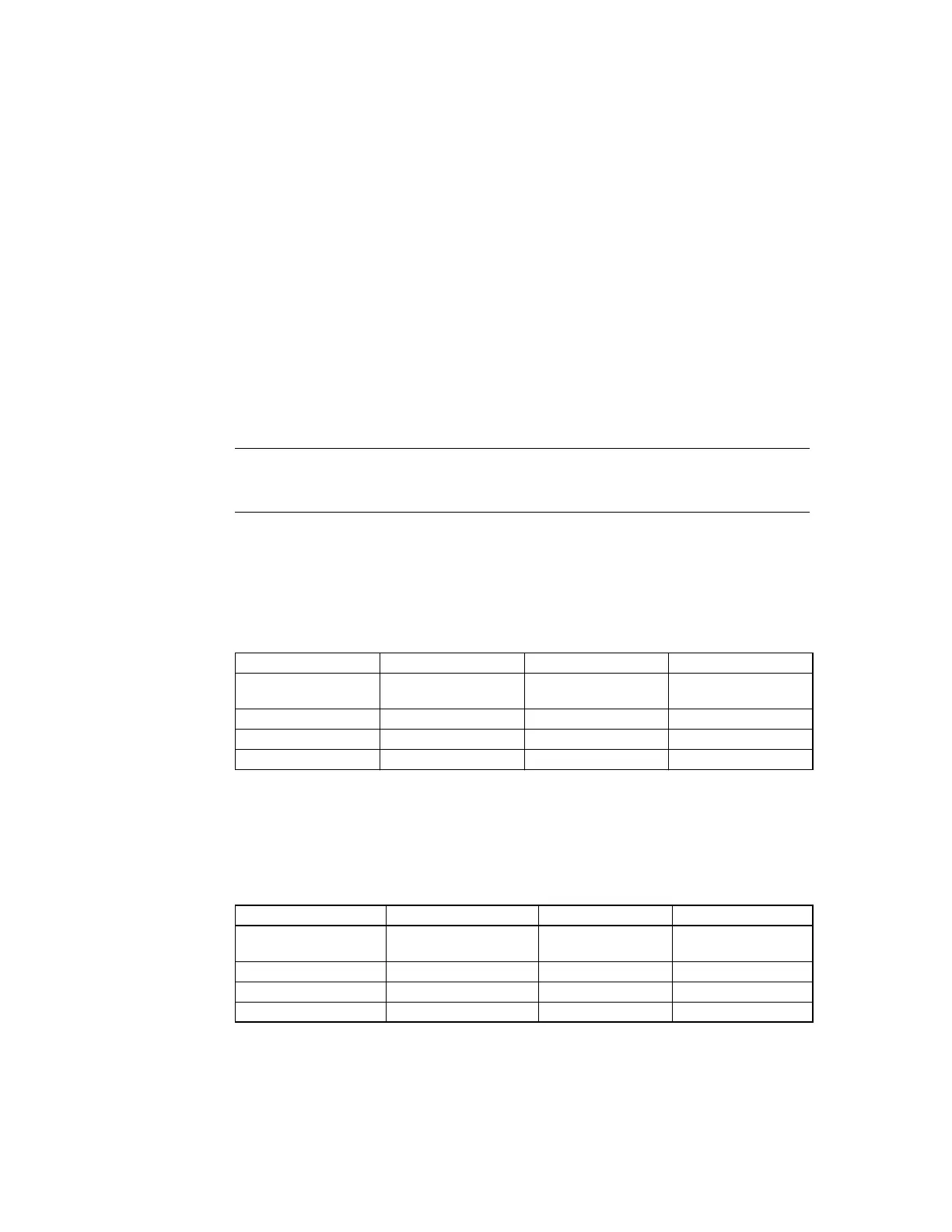
Table 7-25 ReadToShare First Read
Processor 1 SC Processor 2 Processor 3
Initial state: Etag{I}
P_RDS_REQ to System
Initial state: Etag{I} Initial state: Etag{I}
Start read from memory
S_RBU reply to P1
P1 updates Etag{I → E} Final state: No change Final state: No change
Table 7-26 ReadToShareAlways Instruction Miss
Processor 1 System Processor 2 Processor 3
Initial state: Etag{I}
P_RDSA_REQ to System
Initial state: Etag{I} Initial state: Etag{I}
Start read from memory
S_RBS reply to P1
P1 updates Etag{I → S} Final state: No change Final state: No change
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com

 Loading...
Loading...