-SCS Pulse Card (PGU and PMU) User's Manual Section 3:
Setting up PMUs and PGUs in Clarius
4200A-PMU-900-01 Rev. B March 2023 3-37
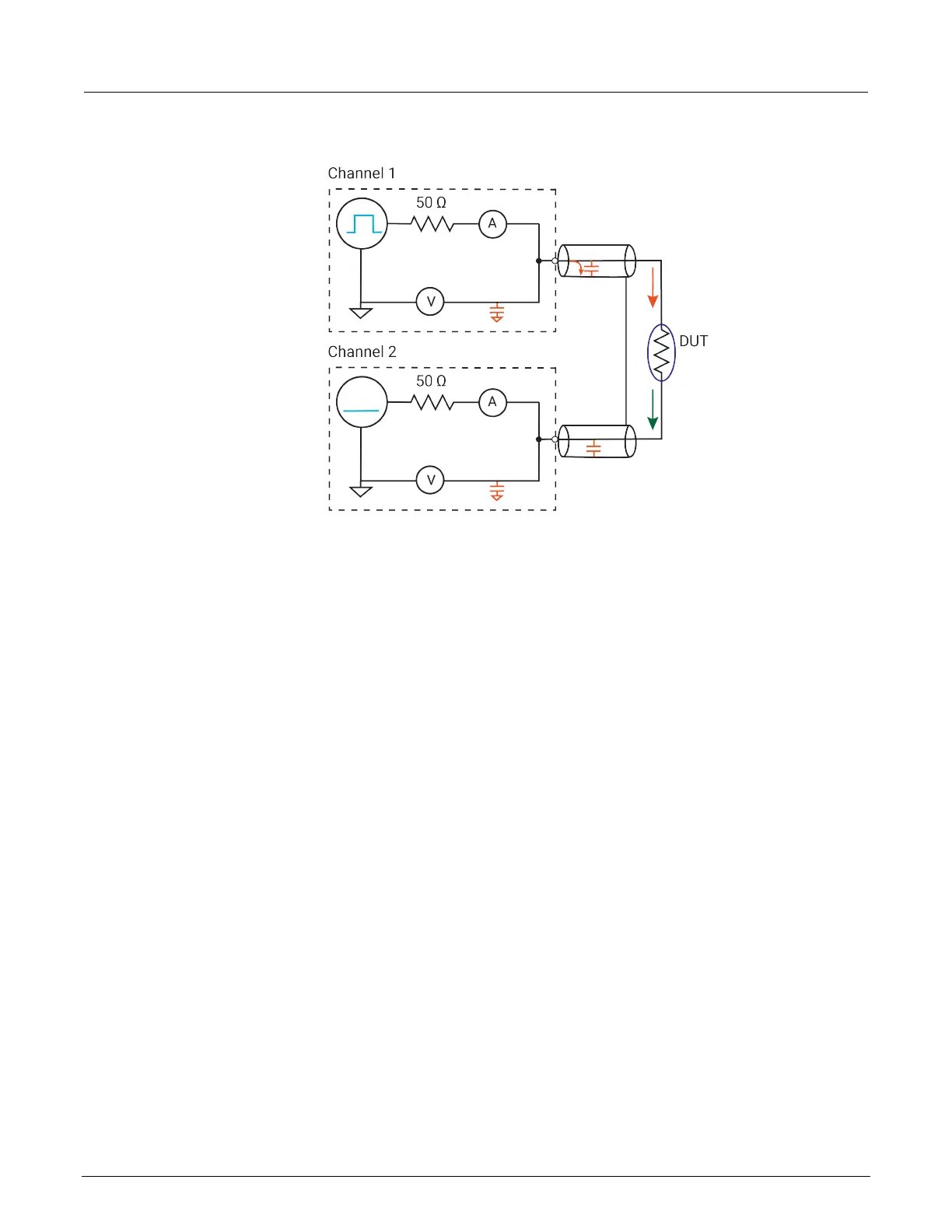
Figure 67: Setup for low-side measurement
In the previous figure, the voltage pulse is applied by channel 1; channel 2 does not pulse. Therefore,
there is no dV/dt, and therefore there are no charging or discharging currents during the pulse
transition. The red arrows show charging and DUT current for channel 1. The green arrow illustrates
the DUT current only for channel 2.
PMU and RPM measure ranges are not source ranges
Unlike a source-measure unit (SMU), the PMU and RPM current measure ranges are measure
ranges only, not source and measure ranges. For example, the SMU 10 mA measure range has a
maximum source and measure value of ±10.5 mA, including the five percent overrange. The 10 mA
measure range of the PMU 10 V range has a maximum measurement of about ±10 mA, but the full
source capability of the 10 V source, which is ±200 mA. An alternate way to present this difference is
that the SMU range has a source compliance equal to the measurement limit, but the PMU and RPM
ranges have a source compliance larger than the measure range. Note that for the maximum PMU
current measure ranges (200 mA for the 10 V range, 800 mA for the 40 V range), the source limit is
the same as the measure limit, so the 200 mA and 800 mA ranges act similar to the SMU
current range.
This measure-only limit is necessary for the best performance of the pulse when using the PMU alone
or with the RPM. Generally, the purpose of a pulse measurement is to minimize the time required to
make a measurement in order to minimize device self-heating or some other time-based
device behavior.
To minimize the measurement time, the signal at the device under test (DUT) must get to the
specified voltage level and settle as quickly as possible. A key aspect of this goal is handling the
capacitive charging effects during the pulse transitions.

 Loading...
Loading...