10–4 Chapter 10: Interrupts
Interrupts for Root Ports
Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express November 2011 Altera Corporation
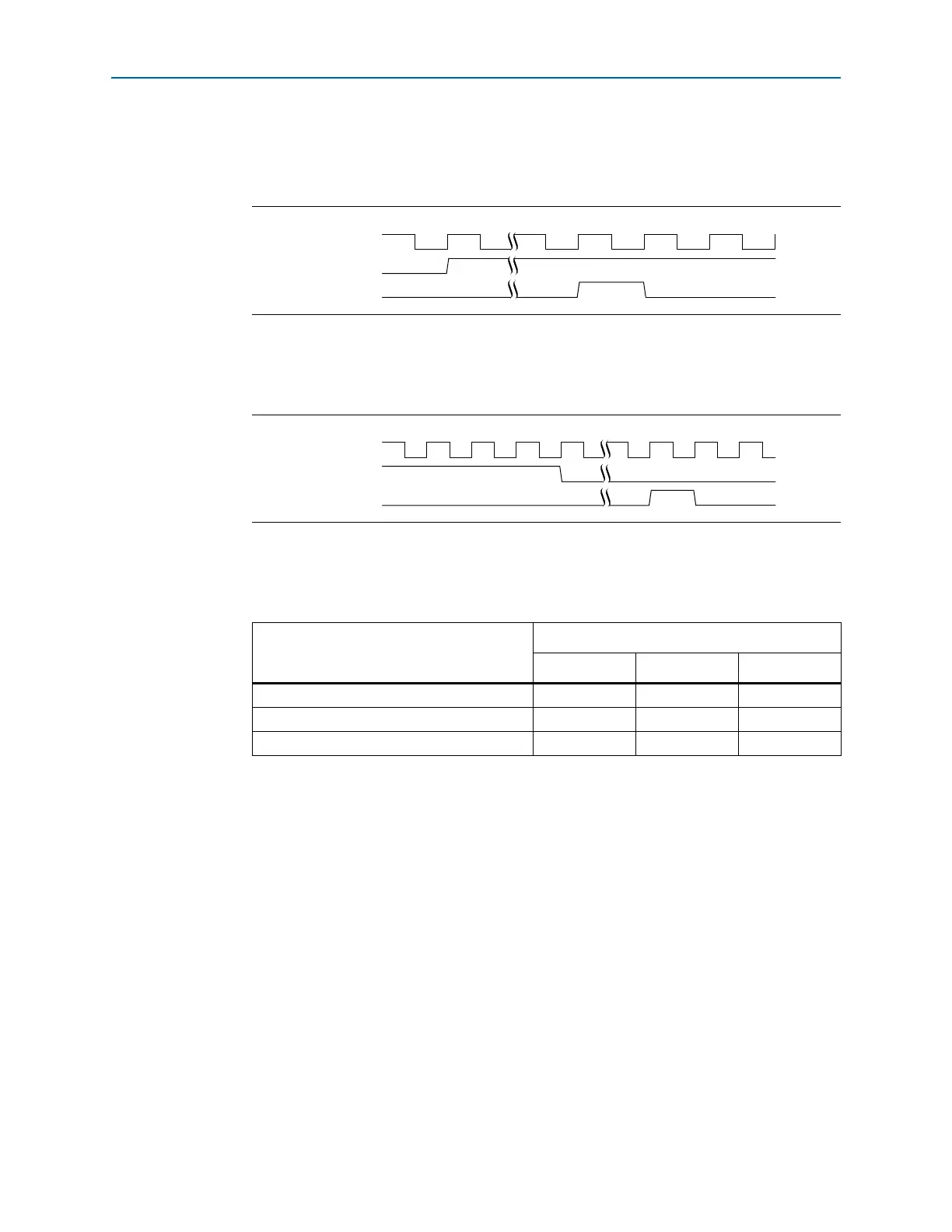
Figure 10–5 illustrates interrupt timing for the legacy interface. In this figure the
assertion of
app_int_ack
instructs the Hard IP for PCI Express to send a
Assert_INTA
message TLP.
Figure 10–6 illustrates the timing for deassertion of legacy interrupts. The assertion of
app_int_ack
instructs the Hard IP for PCI Express to send a
Deassert_INTA
message.
Table 10–1 describes 3 example implementations; 1 in which all 32 MSI messages are
allocated and 2 in which only 4 are allocated.
MSI interrupts generated for Hot Plug, Power Management Events, and System
Errors always use TC0. MSI interrupts generated by the Application Layer can use
any Traffic Class. For example, a DMA that generates an MSI at the end of a
transmission can use the same traffic control as was used to transfer data.
Interrupts for Root Ports
In Root Port mode, the Cyclone V Hard IP for PCI Express IP core receives interrupts
through two different mechanisms:
■ MSI—Root Ports receive MSI interrupts through the Avalon-ST RX TLP of type
MWr
. This is a memory mapped mechanism.
■ Legacy—Legacy interrupts are translated into TLPs of type
Message
Interrupt
which is sent to the Application Layer using the
int_status[3:0]
pins.
Figure 10–5. Legacy Interrupt Assertion
Figure 10–6. Legacy Interrupt Deassertion
Table 10–1. MSI Messages Requested, Allocated, and Mapped
MSI
Allocated
32 4 4
System error 31 3 3
Hot plug and power management event 30 2 3
Application Layer 29:0 1:0 2:0
coreclkout
app_int_sts
app_int_ack
coreclkout
app_int_sts
app_int_ack
 Loading...
Loading...