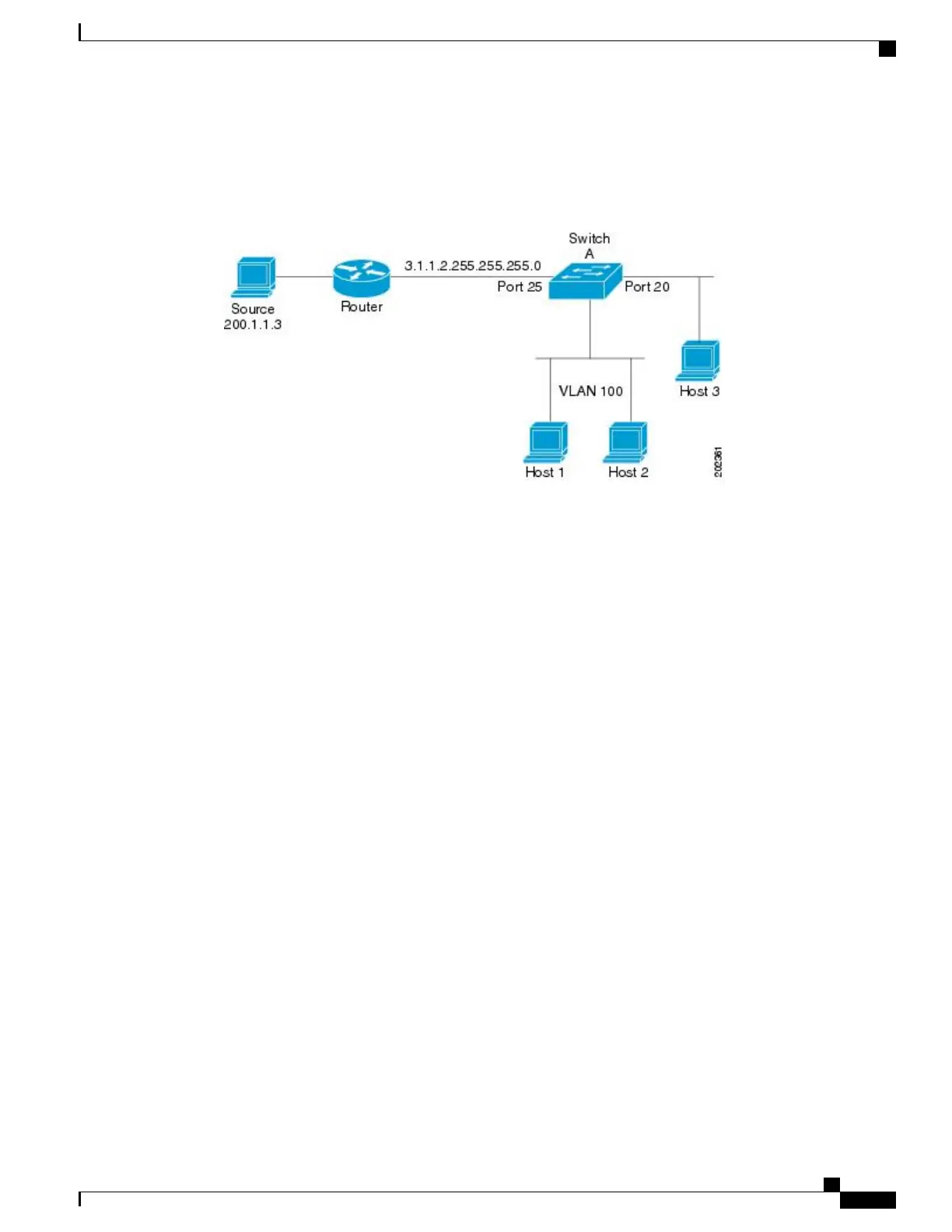
In the following figure, the Device A routed uplink port 25 is connected to the router and PIM stub routing
is enabled on the VLAN 100 interfaces and on Host 3. This configuration allows the directly connected hosts
to receive traffic from multicast source 200.1.1.3.
Figure 5: PIM Stub Router Configuration
Related Topics
Enabling PIM Stub Routing (CLI), on page 141
Example: Enabling PIM Stub Routing, on page 181
Example: Verifying PIM Stub Routing, on page 182
Restrictions for Configuring PIM Stub Routing, on page 123
IGMP Helper
PIM stub routing moves routed traffic closer to the end user and reduces network traffic. You can also reduce
traffic by configuring a stub router (switch) with the IGMP helper feature.
You can configure a stub router (switch) with the ip igmp helper-address ip-address interface configuration
command to enable the switch to send reports to the next-hop interface. Hosts that are not directly connected
to a downstream router can then join a multicast group sourced from an upstream network. The IGMP packets
from a host wanting to join a multicast stream are forwarded upstream to the next-hop device when this feature
is configured. When the upstream central router receives the helper IGMP reports or leaves, it adds or removes
the interfaces from its outgoing interface list for that group.
Rendezvous Points
A rendezvous point (RP) is a role that a device performs when operating in Protocol Independent Multicast
(PIM) Sparse Mode (SM). An RP is required only in networks running PIM SM. In the PIM-SM model, only
network segments with active receivers that have explicitly requested multicast data will be forwarded the
traffic. This method of delivering multicast data is in contrast to PIM Dense Mode (PIM DM). In PIM DM,
multicast traffic is initially flooded to all segments of the network. Routers that have no downstream neighbors
or directly connected receivers prune back the unwanted traffic.
An RP acts as the meeting place for sources and receivers of multicast data. In a PIM-SM network, sources
must send their traffic to the RP. This traffic is then forwarded to receivers down a shared distribution tree.
IP Multicast Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
OL-32598-01 129
Configuring PIM
IGMP Helper

 Loading...
Loading...











