IP Multicast Routing Protocols
The software supports the following protocols to implement IP multicast routing:
•
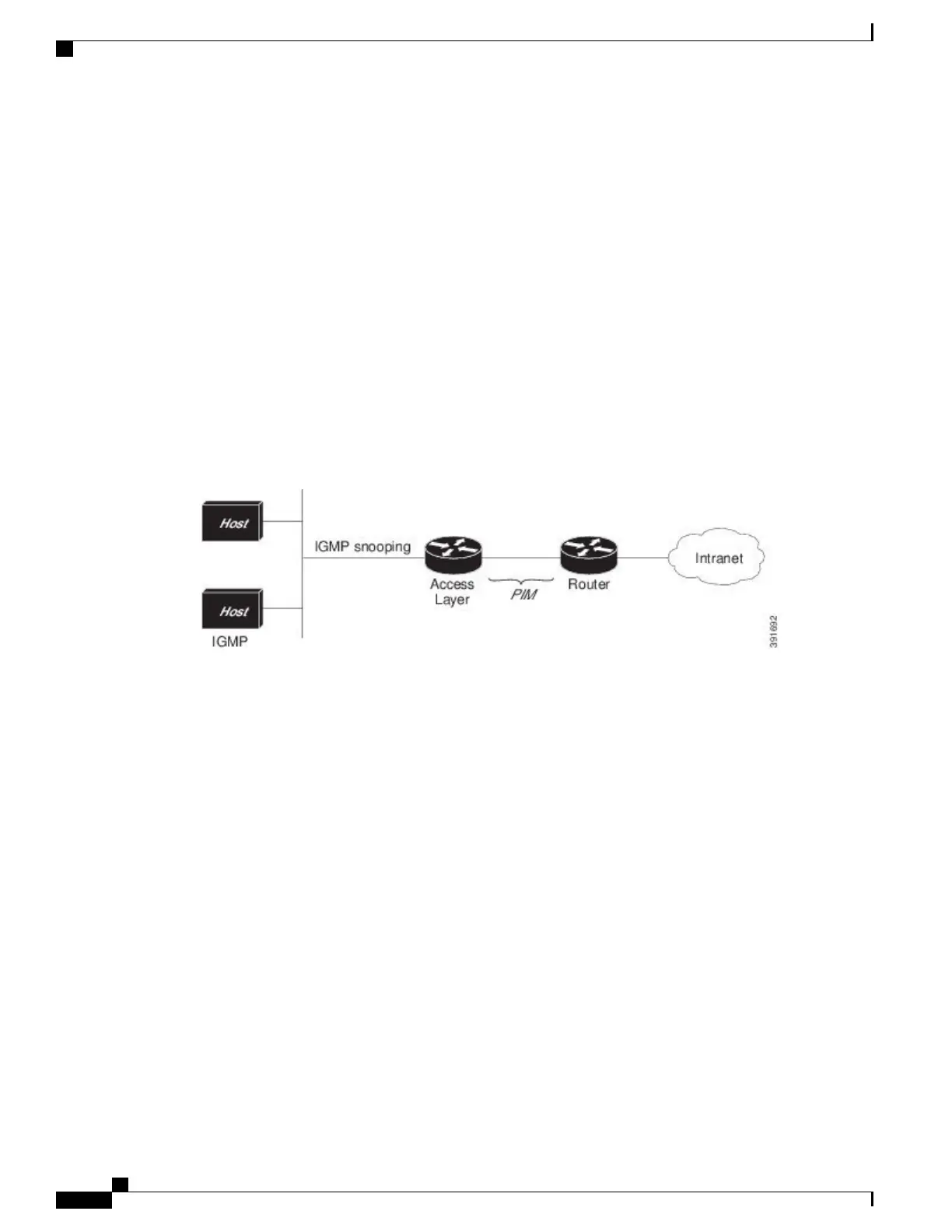
IGMP is used between hosts on a LAN and the routers (and multilayer devices) on that LAN to track
the multicast groups of which hosts are members. To participate in IP multicasting, multicast hosts,
routers, and multilayer devices must have the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) operating.
•
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) is used between routers so that they can track which multicast
packets to forward to each other and to their directly connected LANs.
•
IGMP Snooping is used for multicasting in a Layer 2 switching environment. It helps reduce the flooding
of multicast traffic by dynamically configuring Layer 2 interfaces so that multicast traffic is forwarded
to only those interfaces associated with IP multicast devices.
This figure shows where these protocols operate within the IP multicast environment.
Figure 1: IP Multicast Routing Protocols
According to IPv4 multicast standards, the MAC destination multicast address begins with 0100:5e and is
appended by the last 23 bits of the IP address. For example, if the IP destination address is 239.1.1.39, the
MAC destination address is 0100:5e01:0127.
A multicast packet is unmatched when the destination IPv4 address does not match the destination MAC
address. The device forwards the unmatched packet in hardware based upon the MAC address table. If the
destination MAC address is not in the MAC address table, the device floods the packet to the all port in the
same VLAN as the receiving port.
Related Topics
Configuring Basic IP Multicast Routing, on page 290
Prerequisites for Basic IP Multicast Routing, on page 287
Multicast Group Transmission Scheme
IP communication consists of hosts that act as senders and receivers of traffic as shown in the first figure.
Senders are called sources. Traditional IP communication is accomplished by a single host source sending
packets to another single host (unicast transmission) or to all hosts (broadcast transmission). IP multicast
provides a third scheme, allowing a host to send packets to a subset of all hosts (multicast transmission). This
subset of receiving hosts is called a multicast group. The hosts that belong to a multicast group are called
group members.
IP Multicast Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
22 OL-32598-01
IP Multicast Routing Technology Overview
IP Multicast Routing Protocols

 Loading...
Loading...











