Although the following illustration and example uses routers in the configuration, any device (router or
switch) can be used.
Note
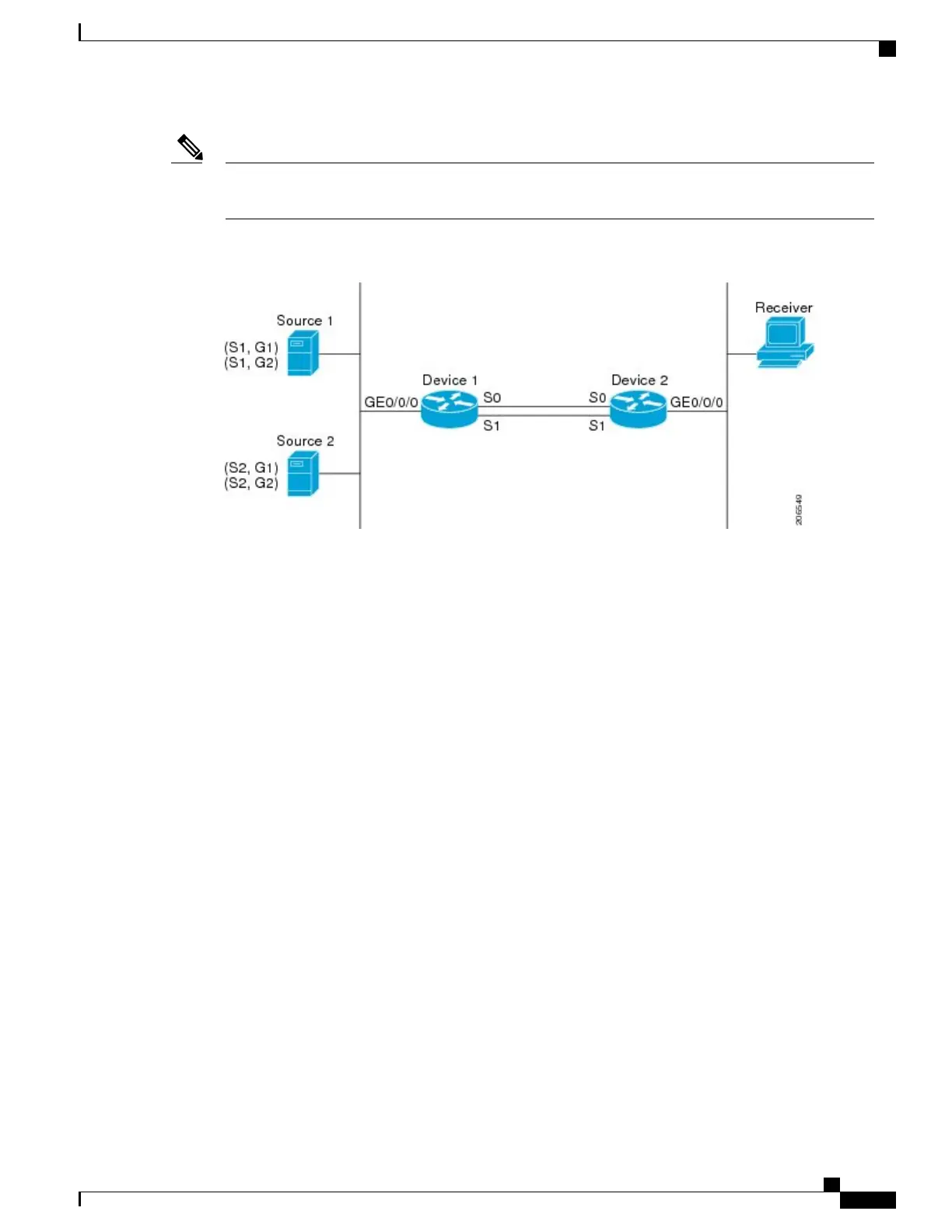
Figure 17: Default Behavior for IP Multicast When Multiple Equal-Cost Paths Exist
In the figure, two sources, S1 and S2, are sending traffic to IPv4 multicast groups, G1 and G2. Either PIM-SM,
PIM-SSM, or PIM-DM can be used in this topology. If PIM-SM is used, assume that the default of 0 for the
ip pim spt-threshold command is being used on Device 2, that an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) is being
run, and that the output of the show ip route command for S1 and for S2 (when entered on Device 2) displays
serial interface 0 and serial interface 1 on Device 1 as equal-cost next-hop PIM neighbors of Device 2.
Without further configuration, IPv4 multicast traffic in the topology illustrated in the figure would always
flow across one serial interface (either serial interface 0 or serial interface 1), depending on which interface
has the higher IP address. For example, suppose that the IP addresses configured on serial interface 0 and
serial interface 1 on Device 1 are 10.1.1.1 and 10.1.2.1, respectively. Given that scenario, in the case of
PIM-SM and PIM-SSM, Device 2 would always send PIM join messages towards 10.1.2.1 and would always
receive IPv4 multicast traffic on serial interface 1 for all sources and groups shown in the figure. In the case
of PIM-DM, Device 2 would always receive IP multicast traffic on serial Interface 1, only that in this case,
PIM join messages are not used in PIM-DM; instead Device 2 would prune the IP multicast traffic across
serial interface 0 and would receive it through serial interface 1 because that interface has the higher IP address
on Device 1.
IPv4 RPF lookups are performed by intermediate multicast device to determine the RPF interface and RPF
neighbor for IPv4 (*,G) and (S, G) multicast routes (trees). An RPF lookup consists of RPF route-selection
and route-path-selection. RPF route-selection operates solely on the IP unicast address to identify the root of
the multicast tree. For (*, G) routes (PIM-SM and Bidir-PIM), the root of the multicast tree is the RP address
for the group G; for (S, G) trees (PIM-SM, PIM-SSM and PIM-DM), the root of the multicast tree is the source
S. RPF route-selection finds the best route towards the RP or source in the routing information base (RIB),
and, if configured (or available), the Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) routing table,
the Multiprotocol Border Gateway Protocol (MBGP) routing table or configured static mroutes. If the resulting
route has only one available path, then the RPF lookup is complete, and the next-hop device and interface of
the route become the RPF neighbor and RPF interface of this multicast tree. If the route has more than one
path available, then route-path-selection is used to determine which path to choose.
For IP multicast, the following route-path-selection methods are available:
IP Multicast Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3.6E (Catalyst 3850 Switches)
OL-32598-01 351
IP Multicast Optimization: IP Multicast Load Splitting across Equal-Cost Paths
Default Behavior for IP Multicast When Multiple Equal-Cost Paths Exist

 Loading...
Loading...











