Security: 802.1X Authentication
Overview of 802.1X
Cisco Small Business 200 Series Smart Switch Administration Guide 268
20
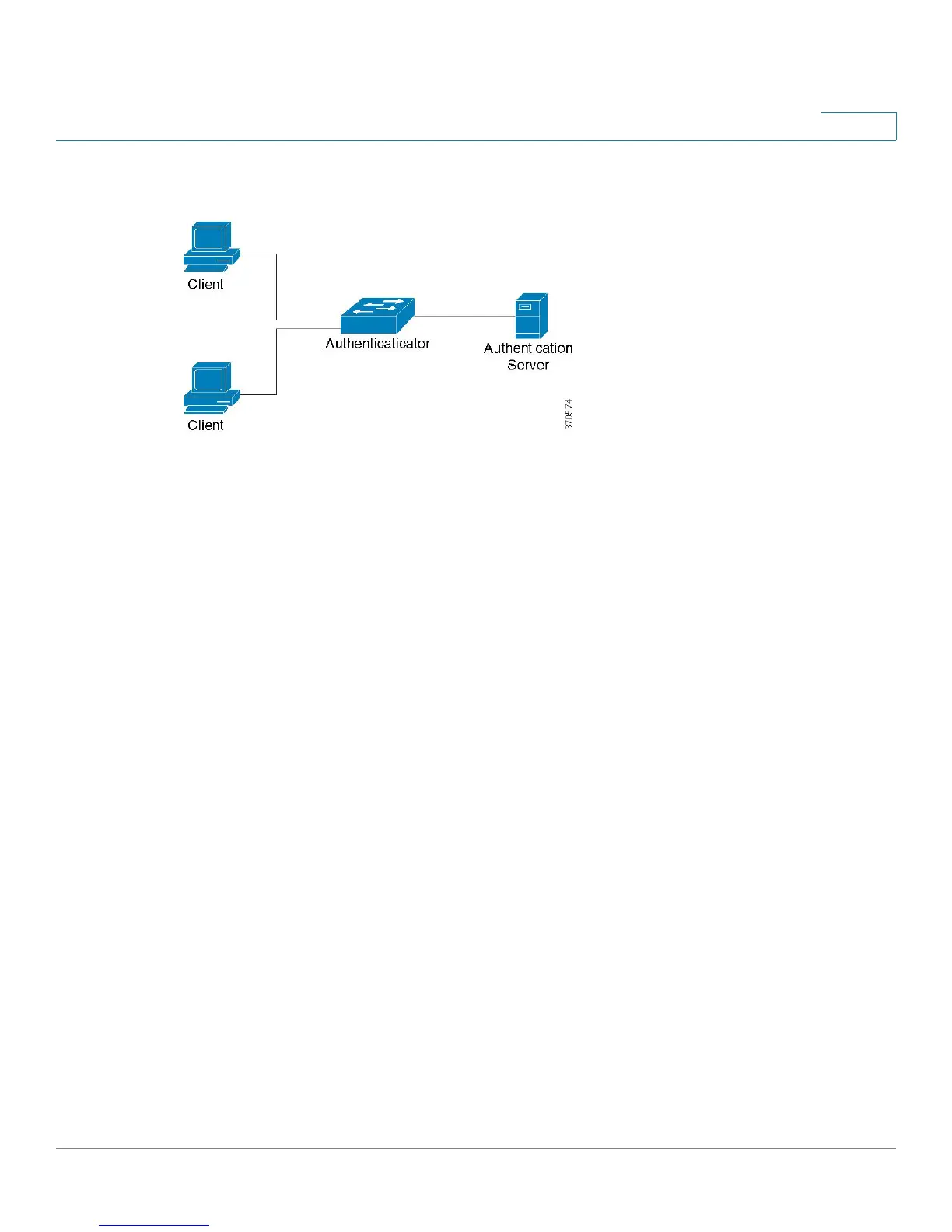
This is described in the figure below:
A network device can be either a client/supplicant, authenticator or both per port.
Client or Supplicant
A client or supplicant is a network device that requests access to the LAN. The client is connected to an
authenticator.
If the client uses the 802.1x protocol for authentication, it runs the supplicant part of the 802.1x protocol and
the client part of the EAP protocol.
Authenticator
An authenticator is a network device that provides network services and to which supplicant ports are
connected.
The following authentication modes on ports are supported (these modes are set in Security > 802.1X >
Host and Authentication):
• Single-host—Supports port-based authentication with a single client per port.
• Multi-host—Supports port-based authentication with a multiple clients per port.
• Multi-sessions—Supports client-based authentication with a multiple clients per port.
See Port Host Modes for more information.
In 802.1x-based authentication, the authenticator extracts the EAP messages from the 802.1x messages
(EAPOL frames) and passes them to the authentication server, using the RADIUS protocol.

 Loading...
Loading...











