D-Link DWC-2000 User Manual 139
Section 5 - Advanced Network Conguration
Protocol Based VLANs
Path: Network > VLAN > Advanced VLAN > Protocol Based VLAN
In a protocol‐based VLAN, trac is bridged through specied ports based on the protocol associated with the
VLAN. User‐dened packet lters determine whether a particular packet belongs to a particular VLAN. Protocol‐
based VLANs are most often used in situations where network segments contain hosts running multiple protocols.
You can use a protocol‐based VLAN to dene ltering criteria for untagged packets. By default, if you do not
congure any port‐based (IEEE 802.1Q) or protocol‐based VLANs, untagged packets are assigned to VLAN 1. You
can override this behavior by dening either port‐based VLANs, protocol‐based VLANs, or both. Tagged packets
are always handled according to the IEEE 802.1Q standard and are not included in protocol‐based VLANs.
If you assign a port to a protocol‐based VLAN for a specic protocol, untagged frames received on that port for that
protocol will be assigned the protocol‐based VLAN ID. Untagged frames received on the port for other protocols
will be assigned the Port VLAN ID (PVID), which is either the default PVID (1) or a PVID you have specically
assigned to the port using the Port VLAN Conguration screen. Use the Protocol‐based VLAN Conguration
page to congure which protocols go to which VLANs, and then enable certain ports to use these settings.
You dene a protocol‐based VLAN by creating a group. Each group has a one‐to‐one relationship with a VLAN ID,
can include one or more protocol denitions, and can include multiple ports.
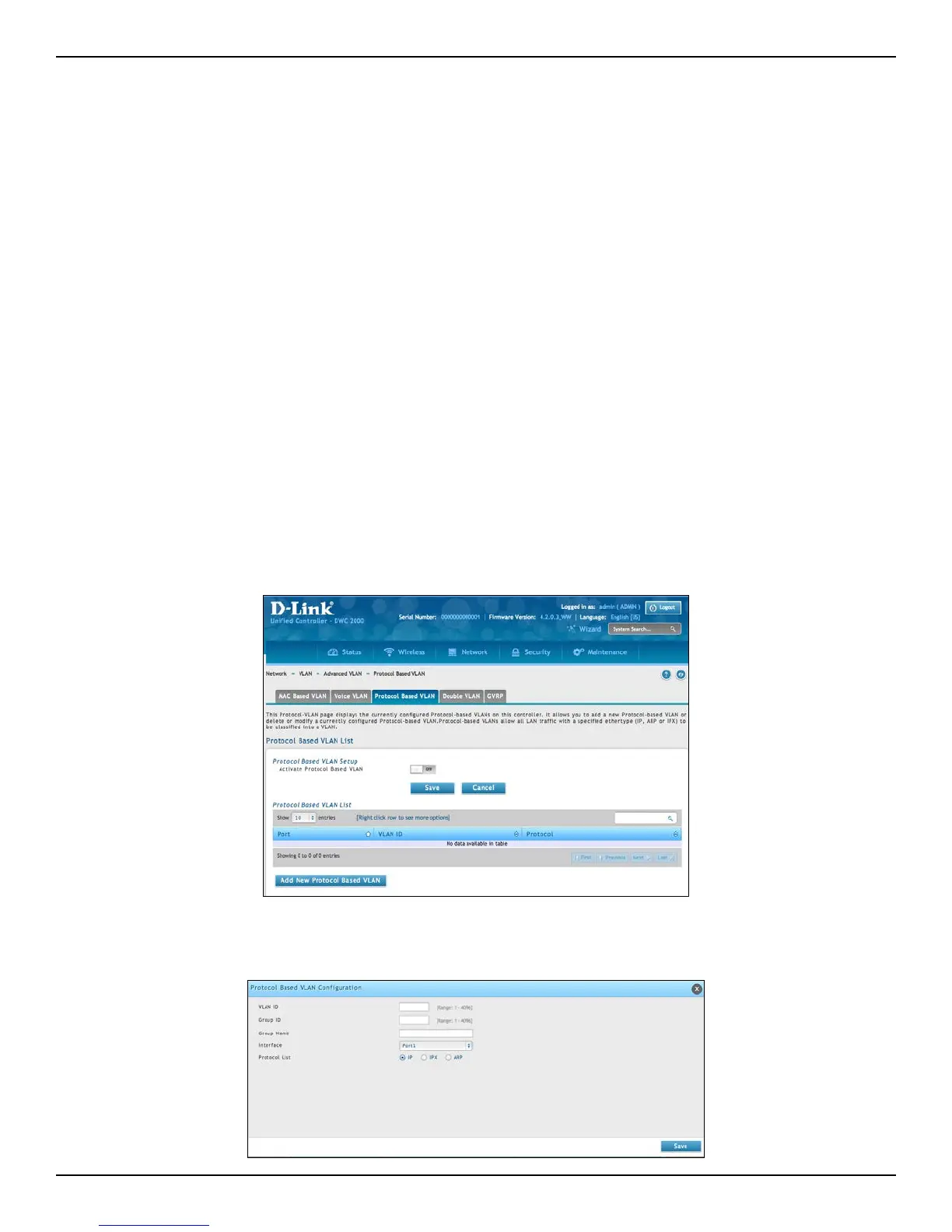
1. Go to Network > VLAN > Advanced VLAN > Protocol Based VLAN tab.
2. Toggle Activate Protocol Based VLAN to ON and click Save.
3. Click Add New Protocol Based VLAN.
 Loading...
Loading...