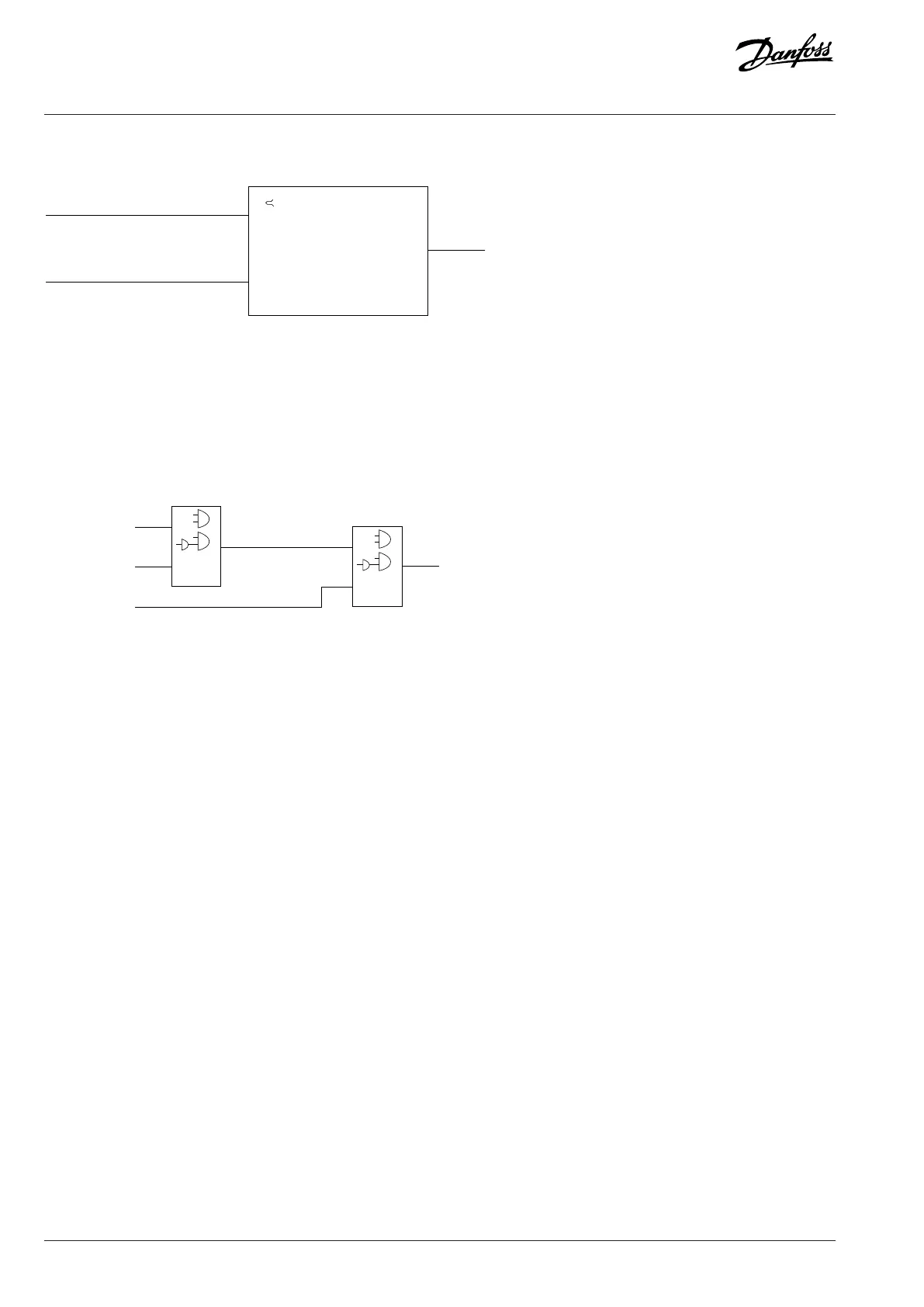
Comparator Operator
=
TRUE longer than.
. . .
. . .
Par. 13-10
Comparator Operand
Par. 13-12
Comparator Value
e30bb672.10
Figure 4: Comparators
Logic rules
Combine up to 3 boolean inputs (TRUE/FALSE inputs) from timers, comparators, digital inputs, status bits, and events using the logical
operators AND, OR, and NOT.
Par. 13-43
Logic Rule Operator 2
Par. 13-41
Logic Rule Operator 1
Par. 13-40
Logic Rule Boolean 1
Par. 13-42
Logic Rule Boolean 2
Par. 13-44
Logic Rule Boolean 3
e30bb673.10
Figure 5: Logic Rules
3.4 Dynamic Braking
Dynamic braking slows the motor using 1 of the following methods:
l AC brake
The brake energy is distributed in the motor by changing the loss conditions in the motor (parameter 2-10 Brake Function = [2]). The
AC brake function cannot be used in applications with high cycling frequency since this situation overheats the motor.
l DC brake
An over-modulated DC current added to the AC current works as an eddy current brake (parameter 2-02 DC Braking Time ≠ 0 s).
3.5 Back-channel Cooling
3.5.1 Overview
A unique back channel duct passes cooling air over the heat sinks with minimal air passing through the electronics area. There is an IP54/
Type 12 seal between the back-channel cooling duct and the electronics area of the drive. This back-channel cooling allows 90% of the
heat losses to be exhausted directly outside the enclosure. This design improves reliability and prolongs component life by dramatically
reducing interior temperatures and contamination of the electronic components. Different back-channel cooling kits are available to
redirect the airflow based on individual needs.
22 | Danfoss A/S © 2024.01 AJ435824192086en-000101 / 130R1295
Design Guide | VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360

 Loading...
Loading...
















