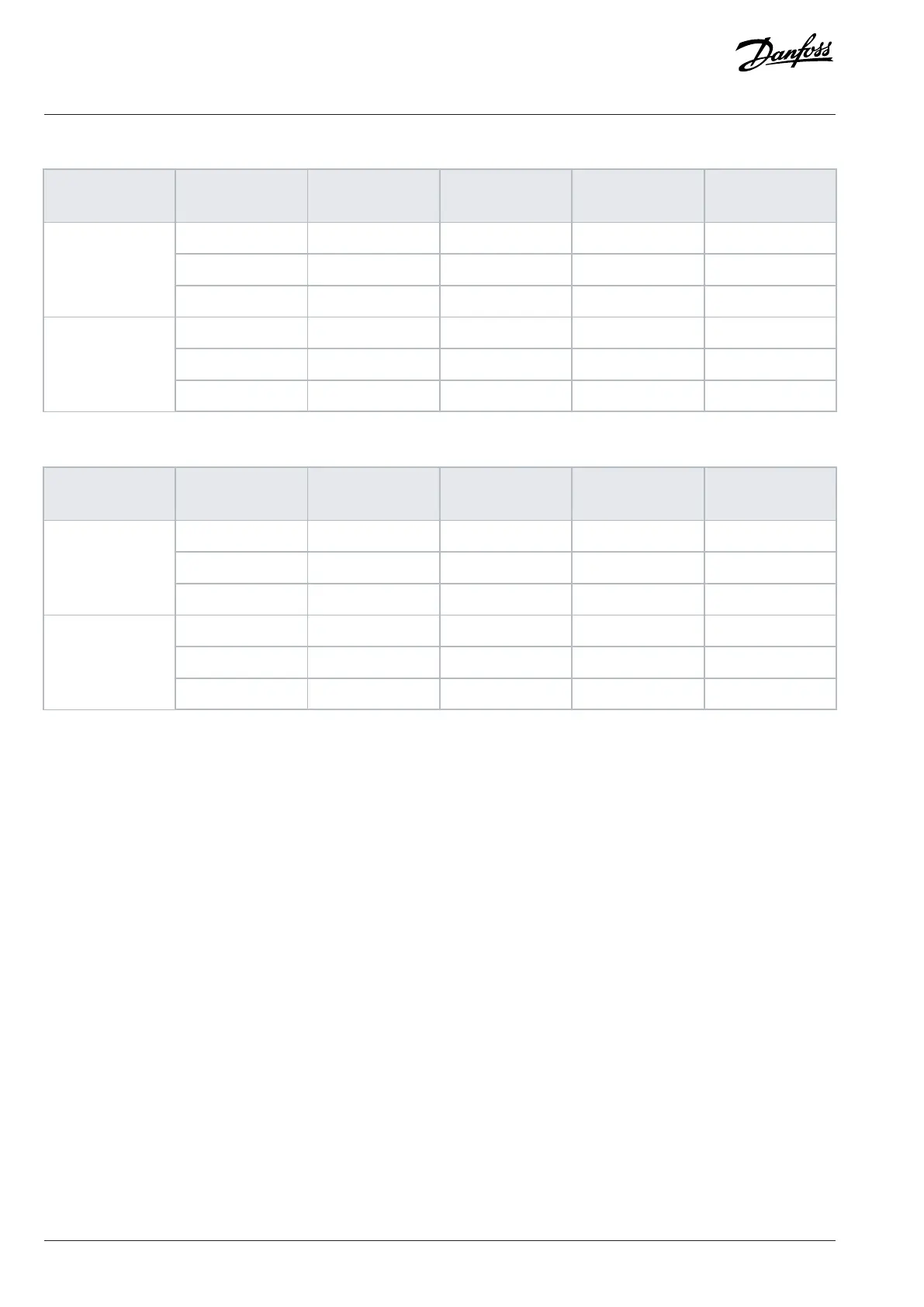
Table 16: IEC dU/dt Test Results for J8–J9 with Unshielded Cables and No Output Filter, 380–480 V
Power size [kW
(hp)]
Cable [m (ft)] Mains voltage [V] Rise time [μs] Peak voltage [V] dU/dt [V/μs]
30 (98) 500 0.71 1180 1339
150 (492) 500 0.76 1423 1497
90–160 (125–250)
300 (984) 500 0.91 1557 1370
30 (98) 500 1.10 1116 815
150 (492) 500 2.53 1028 321
200–315 (300–450)
300 (984) 500 1.29 835 517
Table 17: IEC dU/dt Test Results for J8–J9 with Shielded Cables and No Output Filter, 380–480 V
Power size [kW
(hp)]
Cable [m (ft)] Mains voltage [V] Rise time [μs] Peak voltage [V] dU/dt [V/μs]
30 (98) 500 – – –
150 (492) 500 0.66 1418 1725
90–160 (125–250)
300 (984) 500 0.96 1530 1277
30 (98) 500 – – –
150 (492) 500 0.56 1261 1820
200–315 (300–450)
300 (984) 500 0.78 1278 1295
7.13 Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
7.13.1 Overview
Electrical devices both generate interference and are affected by interference from other generated sources. The electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) of these effects depends on the power and the harmonic characteristics of the devices.
Uncontrolled interaction between electrical devices in a system can degrade compatibility and impair reliable operation. Interference
takes the form of the following:
l Electrostatic discharges.
l Rapid voltage fluctuations.
l High-frequency interference.
Electrical interference is most commonly found at frequencies in the range 150 kHz to 30 MHz. Airborne interference from the drive
system in the range 30 MHz to 1 GHz is generated from the inverter, motor cable, and the motor.
Capacitive currents in the motor cable, coupled with a high dU/dt from the motor voltage, generate leakage currents. See the following
illustration. Shielded motor cables have higher capacitance between the phase wires and the shield, and again between the shield
and ground. This added cable capacitance, along with other parasitic capacitance and motor inductance, changes the electromagnetic
emission signature produced by the unit. The change in electromagnetic emission signature occurs mainly in emissions less than 5 MHz.
Most of the leakage current (I1) is carried back to the unit through the PE (I3), leaving only a small electromagnetic field (I4) from the
shielded motor cable. The shield reduces the radiated interference but increases the low-frequency interference on the mains.
66 | Danfoss A/S © 2024.01 AJ435824192086en-000101 / 130R1295
Design Guide | VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360

 Loading...
Loading...
















