TROUBLESHOOTING ST80/ST80L Flow Meter
80 Fluid Components International LLC
Verify Standard vs. Actual Process Conditions
The flow meter measures the mass flow rate. The mass flow rate is the mass of the gas flowing through a pipe per time. Other flow meters,
such as an orifice plate or a pitot tube, measure the volumetric flow rate. The volumetric flow rate is the volume of gas per time. If the
readings displayed do not agree with another instrument, some calculations may be necessary before comparing them. To calculate the
mass flow rate and the volumetric flow rate the pressure and temperature at the point of measurement must be known. Use the following
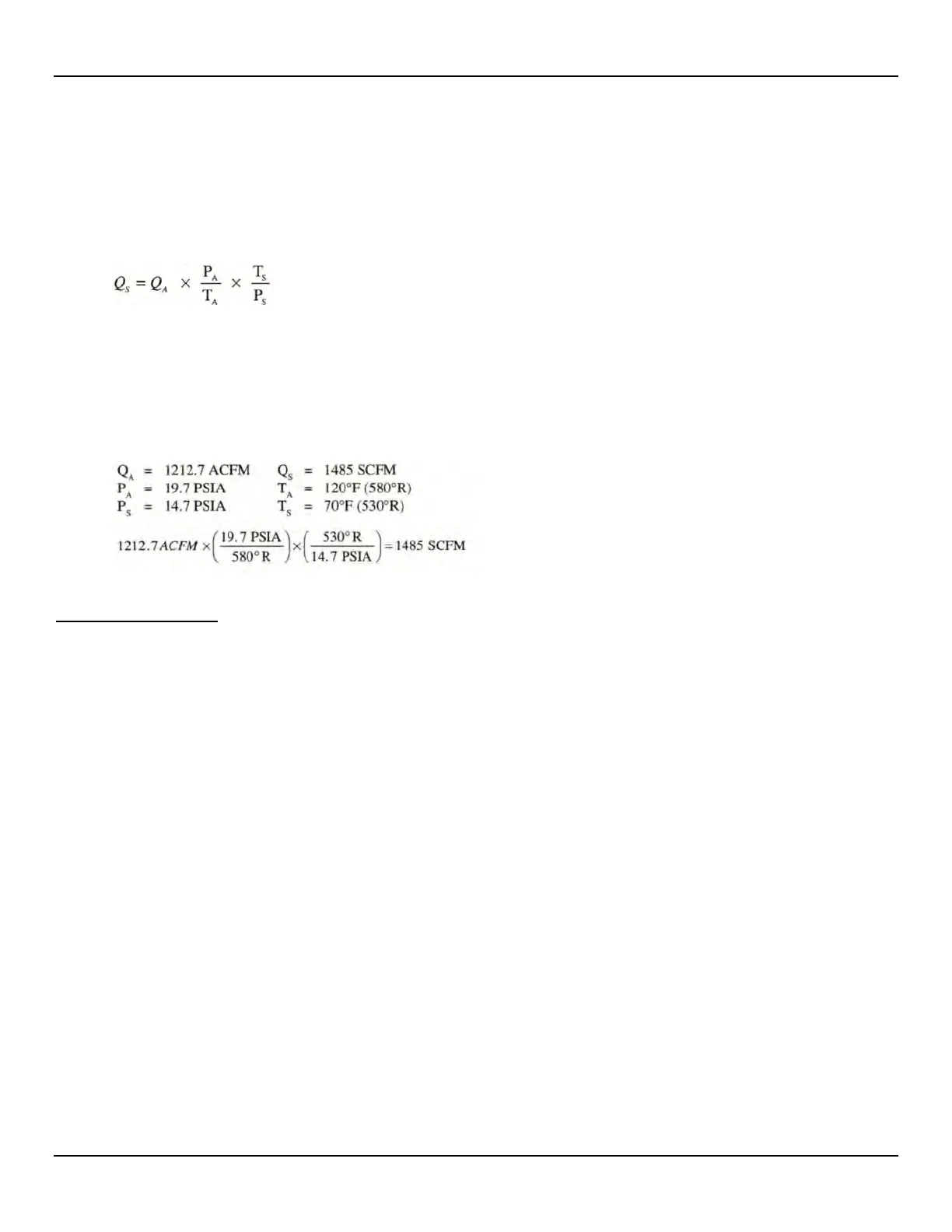
equation to calculate the mass flow rate (Standard Volumetric Flow rate) for the other instrument.
Equation:
Where:
Q
A
= Volumetric Flow Q
S
= Standard Volumetric Flow
P
A
= Actual Pressure T
A
= Actual Temperature
P
S
= Standard Pressure T
S
= Standard Temperature
Pressure in PSIA and Temperature is in degrees Rankine
Example:
General Function Check
Tools Needed
● Digital Multimeter (DMM)
● ST80/ST80L Configuration Software Application
● USB Cable Type B (male) to Type A (male); passive, straight-through type as supplied with instrument
● Small size flat blade screwdriver (for sensor wiring connection)
Verifying Setup
Connect the flow meter via USB to a computer or laptop running the ST80/ST80L configuration software supplied with the instrument.
Refer to the ST80/ST80L Configuration Software manual 06EN003491 for details.
Confirm the setup of the flow meter by reviewing the setup windows in the configurator. Contact your local representative or FCI for
instructions if a setup discrepancy exists.
Checking NAMUR Fault Indication
If the instrument’s flow output is set up for NAMUR, check the output to see if it is driven to a NAMUR level. Refer to NAMUR Setup, page
37 for NAMUR information. Refer to Table 8 on page 38 for the list of faults that trigger NAMUR.

 Loading...
Loading...