MDS 05-6632A01, Rev. F MDS Orbit MCR/ECR Technical Manual 215
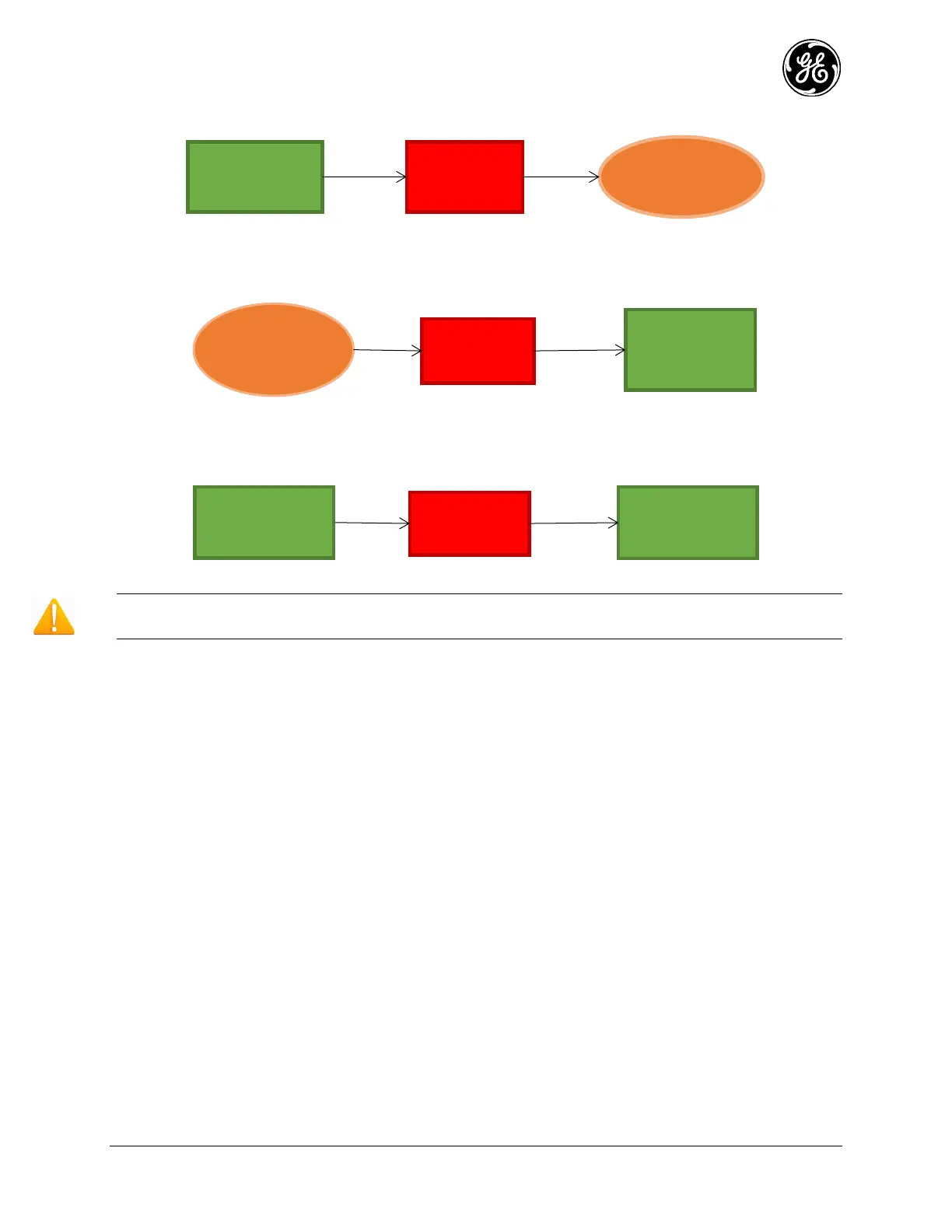
Figure 3-120. Packets Terminated at the Unit
Figure 3-121 shows flow of packets originating from the unit, such as DNS queries and/or VPN
connection setup traffic originating from local VPN service within the unit.
Figure 3-121. Packets Originating from the Unit
Figure 3-122 shows the flow of packets being forwarded (routed) through the unit, such as IP packets
arriving inside IPsec VPN tunnel, being routed from cellular WAN to the local Ethernet interface.
Figure 3-122. Packets Being Forwarded Through the Unit
NOTE If the firewall service is enabled and no filter is applied to an interface, then both incoming and
outgoing traffic is dropped on that interface.
Configuring
Packet filter configuration on the unit involves following these high level steps:
Create a filter and choose its default policy. For example, there are usually two ways to organize a 1.
filter:
Create a "restrictive" filter. The first rules are added to permit the desired types of traffic, and
a final rule, or default policy, is created that denies all other traffic. The example filter rules
below permit SSH traffic on TCP port 22, and ICMP messages such as pings and routing error
notifications. All other traffic is denied.
- Rule 1 = permit protocol=tcp, dst port=22
- Rule 2 = permit protocol=icmp
- Rule 3 = deny everything
Or create a "permissive" filter. The first rules are added to deny the undesired types of traffic,
and a final rule, or default policy, is created that permits all other traffic. The example filter
rules below deny HTTP traffic on TCP port 80, and ICMP message such as pings and routing
error notifications. All other traffic is permitted.
- Rule 1 = deny protocol=tcp, dst port=80
- Rule 2 = deny protocol=icmp
- Rule 3 = permit everything
Apply the filter to input or output direction of the interface. This selection depends on whether the 2.
rules should apply to traffic that ingresses or egresses the device.
Interface

 Loading...
Loading...