83
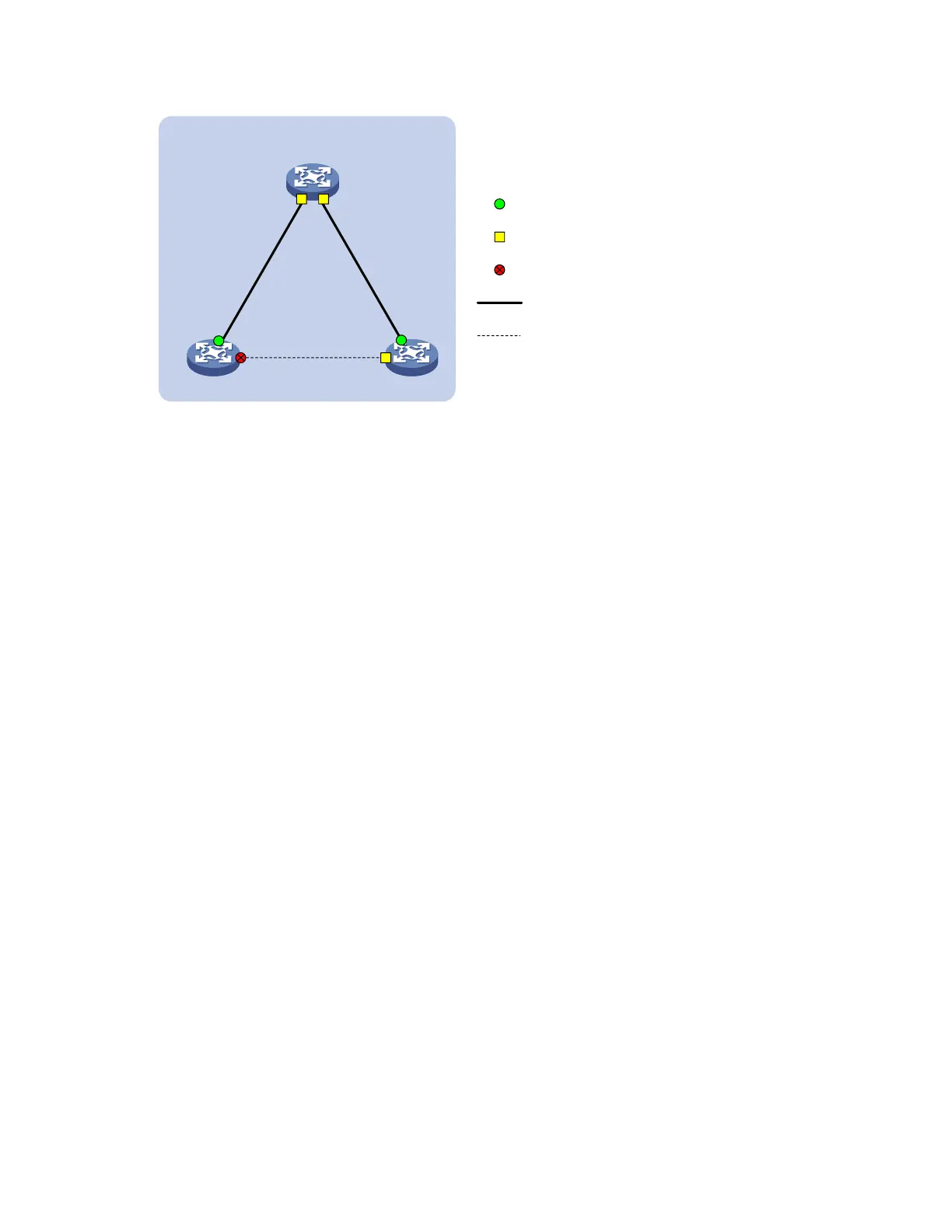
Figure 21 Digest Snooping configuration
Device C
(Root bridge)
GE1/0/1 GE1/0/2
GE1/0/1
GE1/0/2
GE1/0/1
GE1/0/2
Root port
Designated port
Normal link
Blocked link
Blocked port
Device A Device B
MST region
2. Configuration procedure
# Enable Digest Snooping on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device A and enable global Digest Snooping on
Device A.
<DeviceA> system-view
[DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] stp config-digest-snooping
[DeviceA-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceA] stp config-digest-snooping
# Enable Digest Snooping on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 of Device B and enable global Digest Snooping on
Device B.
<DeviceB> system-view
[DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] stp config-digest-snooping
[DeviceB-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
[DeviceB] stp config-digest-snooping
Configuring No Agreement Check
In RSTP and MSTP, the following types of messages are used for rapid state transition on designated
ports:
Proposal—Sent by designated ports to request rapid transition
Agreement—Used to acknowledge rapid transition requests
Both RSTP and MSTP devices can perform rapid transition on a designated port only when the port
receives an agreement packet from the downstream device. RSTP and MSTP devices have the following
differences:
For MSTP, the root port of the downstream device sends an agreement packet only after it receives
an agreement packet from the upstream device.
For RSTP, the downstream device sends an agreement packet regardless of whether an agreement
packet from the upstream device is received.
Figure 22 shows the rapid state transition mechanism on MSTP designated ports.

 Loading...
Loading...











