261
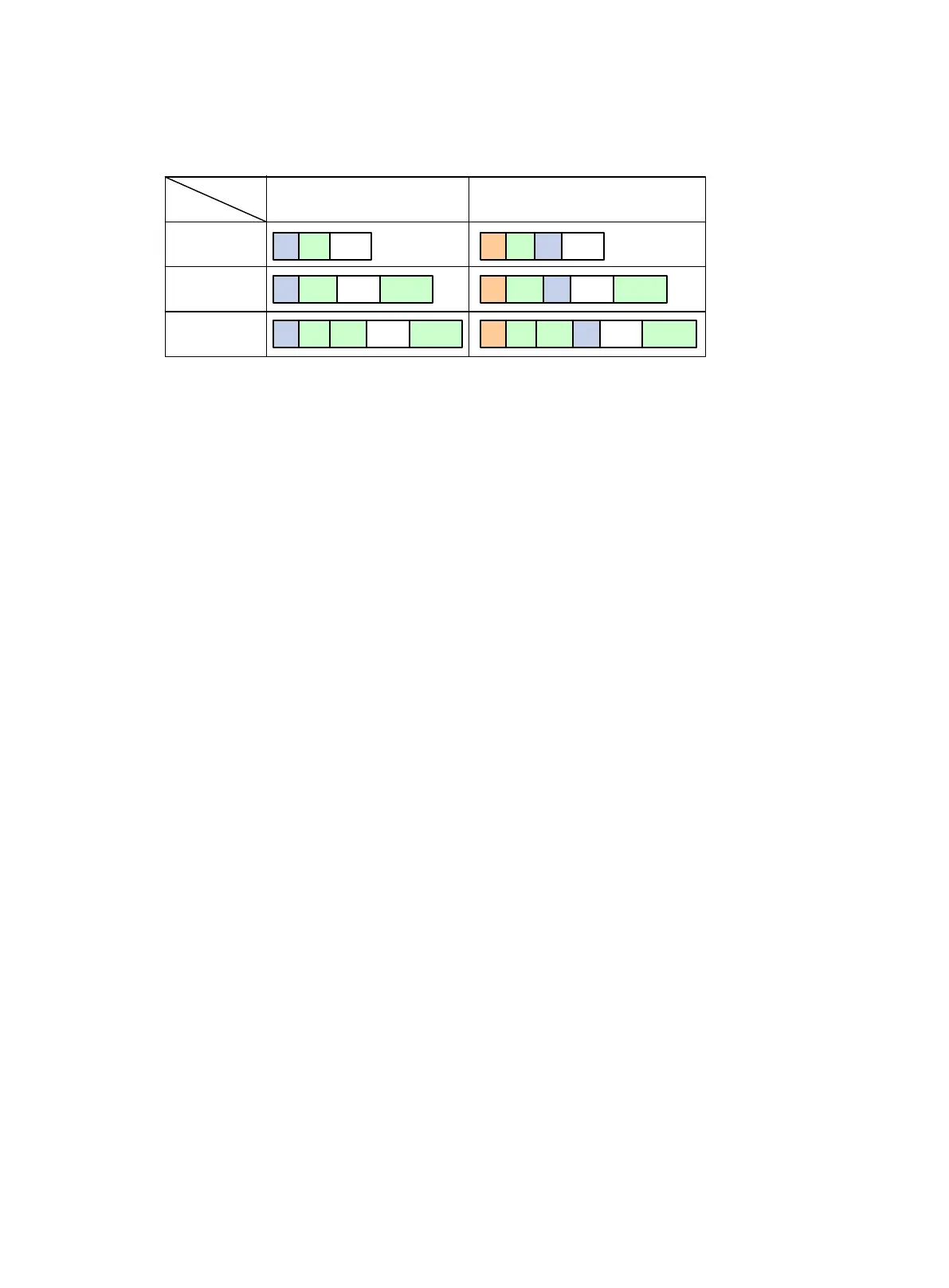
Figure 85 shows how the security protocols encapsulate an IP packet in different encapsulation
modes.
Figure 85 Security protocol encapsulations in different modes
Security association
A security association (SA) is an agreement negotiated between two communicating parties called
IPsec peers. An SA comprises the following parameters for data protection:
• Security protocols (AH, ESP, or both).
• Encapsulation mode (transport mode or tunnel mode).
• Authentication algorithm (HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA1).
• Encryption algorithm (DES, 3DES, or AES).
• Shared keys and their lifetimes.
An SA is unidirectional. At least two SAs are needed to protect data flows in a bidirectional
communication. If two peers want to use both AH and ESP to protect data flows between them, they
construct an independent SA for each protocol in each direction.
An SA is uniquely identified by a triplet, which consists of the security parameter index (SPI),
destination IP address, and security protocol identifier. An SPI is a 32-bit number that identifies an
SA. It is transmitted in the AH/ESP header.
An SA can be set up manually or through IKE.
• Manual mode—Configure all parameters for the SA through commands. This configuration
mode is complex and does not support some advanced features (such as periodic key update),
but it can implement IPsec without IKE. This mode is mainly used in small and static networks
or when the number of IPsec peers in the network is small.
• IKE negotiation mode—The peers negotiate and maintain the SA through IKE. This
configuration mode is simple and has good expansibility. As a best practice, set up SAs through
IKE negotiations in medium- and large-scale dynamic networks.
A manually configured SA never ages out. An IKE-created SA has a lifetime, which comes in two
types:
• Time-based lifetime—Defines how long the SA can be valid after it is created.
• Traffic-based lifetime—Defines the maximum traffic that the SA can process.
If both lifetime timers are configured for an SA, the SA becomes invalid when either of the lifetime
timers expires. Before the SA expires, IKE negotiates a new SA, which takes over immediately after
its creation.
Mode
Protocol
Transport
Tunnel
AH
ESP
AH
-ESP
ESP-
T
IP
Data
ESP
AH
IP
ESP
-T
IP Data
ESP
IP
IP
Data
AH
IPIP
DataAH
ESP
-T
IP
Data
ESP
ESP
-T
IP
DataESP
AH

 Loading...
Loading...



















