448
If a self-test fails, contact Hewlett Packard Enterprise Support.
Power-up self-tests
The power-up self-test examines the availability of FIPS-allowed cryptographic algorithms.
The device supports the following types of power-up self-tests:
• Known-answer test (KAT)
A cryptographic algorithm is run on data for which the correct output is already known. The
calculated output is compared with the known answer. If they are not identical, the KAT test
fails.
• Pairwise conditional test (PWCT)
Signature and authentication test—The test is run when a DSA, RSA, or ECDSA
asymmetrical key pair is generated. It uses the private key to sign the specific data, and
then uses the public key to authenticate the signed data. If the authentication is successful,
the test succeeds.
Encryption and decryption test—The test is run when an RSA asymmetrical key pair is
generated. It uses the public key to encrypt a plain text string, and then uses the private key
to decrypt the encrypted text. If the decryption result is the same as the original plain text
string, the test succeeds.
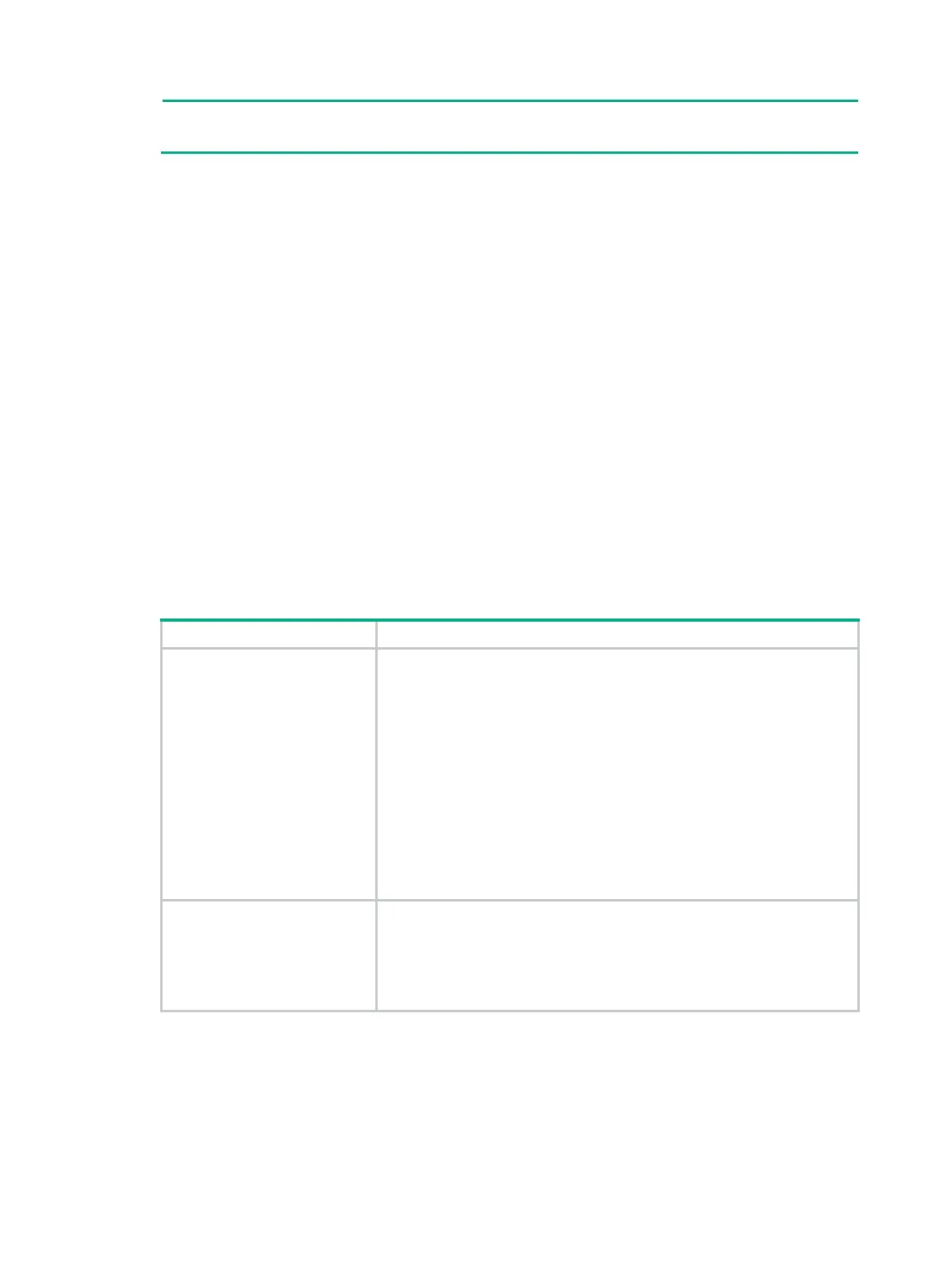
The power-up self-test examines the cryptographic algorithms listed in Table 21.
Table 21 Power-up self-test list
KAT
Tests the following algorithms:
• 3DES.
• SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, and SHA512.
• HMAC-SHA1, HMAC-SHA224, HMAC-SHA256, HMAC-SHA384,
and HMAC-SHA512.
• AES.
• RSA.
• ECDH.
• RNG.
• DRBG.
• GCM.
• GMAC.
PWCT
Tests the following algorithms:
• RSA (signature and authentication).
• RSA (encryption and decryption).
• DSA (signature and authentication).
• ECDSA (signature and authentication).
Conditional self-tests
A conditional self-test runs when an asymmetrical cryptographic module or a random number
generator module is invoked. Conditional self-tests include the following types:

 Loading...
Loading...



















