© Copyright IBM Corp. 2011 Chapter 22. OSPF 265
Default Routes
When an OSPF routing device encounters traffic for a destination address it does
not recognize, it forwards that traffic along the default route. Typically, the default
route leads upstream toward the backbone until it reaches the intended area or an
external router.
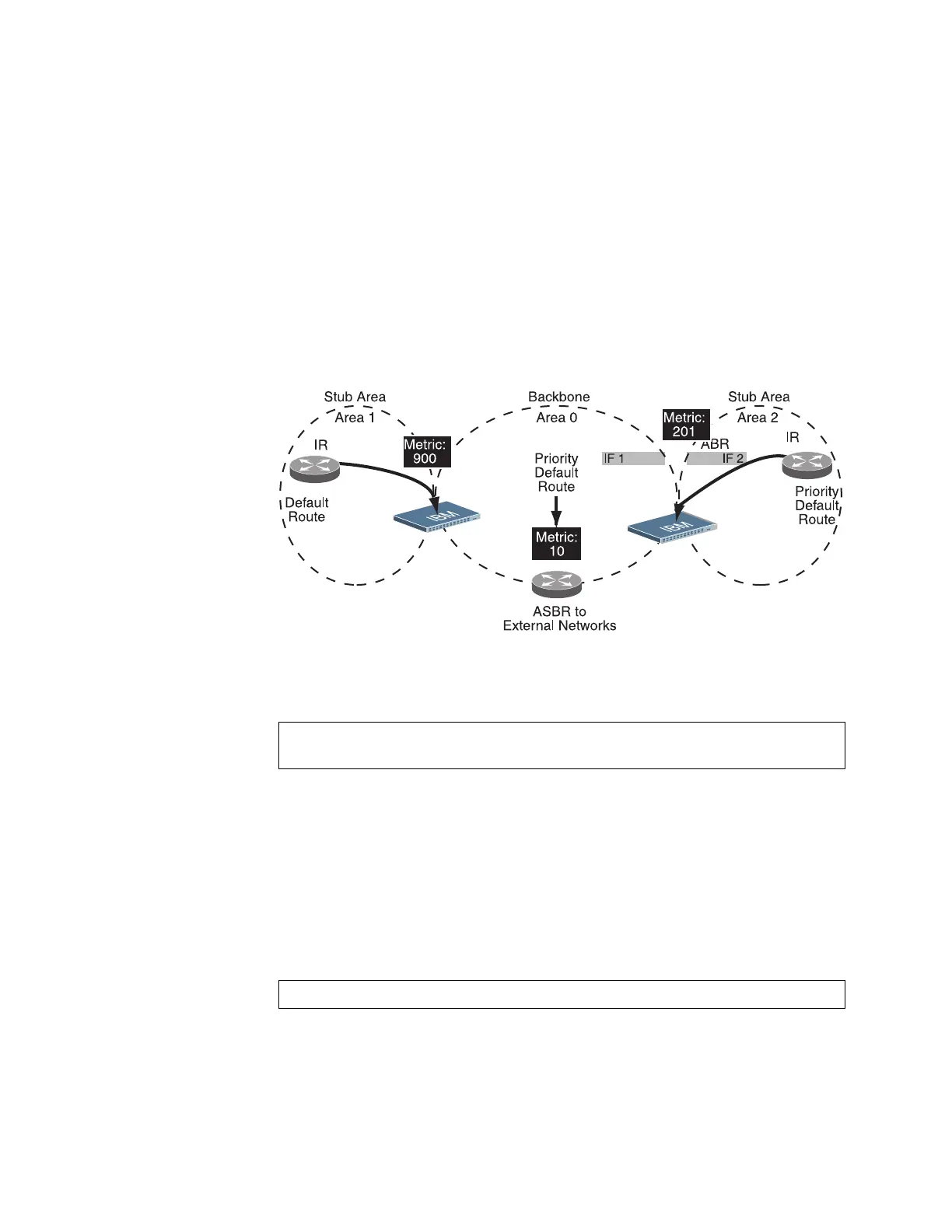
Each G8000 acting as an ABR automatically inserts a default route into each
attached area. In simple OSPF stub areas or NSSAs with only one ABR leading
upstream (see Area 1 in Figure 28), any traffic for IP address destinations outside
the area is forwarded to the switch’s IP interface, and then into the connected transit
area (usually the backbone). Since this is automatic, no further configuration is
required for such areas.
Figure 28. Injecting Default Routes
If the switch is in a transit area and has a configured default gateway, it can inject a
default route into rest of the OSPF domain. Use the following command to configure
the switch to inject OSPF default routes (Router OSPF mode):
In this command,
<metric value>
sets the priority for choosing this switch for default
route. The value
none
sets no default and 1 sets the highest priority for default
route. Metric type determines the method for influencing routing decisions for
external routes.
When the switch is configured to inject a default route, an AS-external LSA with link
state ID 0.0.0.0 is propagated throughout the OSPF routing domain. This LSA is
sent with the configured metric value and metric type.
The OSPF default route configuration can be removed with the command:
RS G8000(config-router-ospf)# default-information <metric value>
<metric type (1 or 2)>
RS G8000(config-router-ospf)# no default-information
 Loading...
Loading...