© Copyright IBM Corp. 2011 Chapter 6. 802.1X Port-Based Network Access Control 73
EAPoL Authentication Process
The clients and authenticators communicate using Extensible Authentication
Protocol (EAP), which was originally designed to run over PPP, and for which the
IEEE 802.1X Standard has defined an encapsulation method over Ethernet frames,
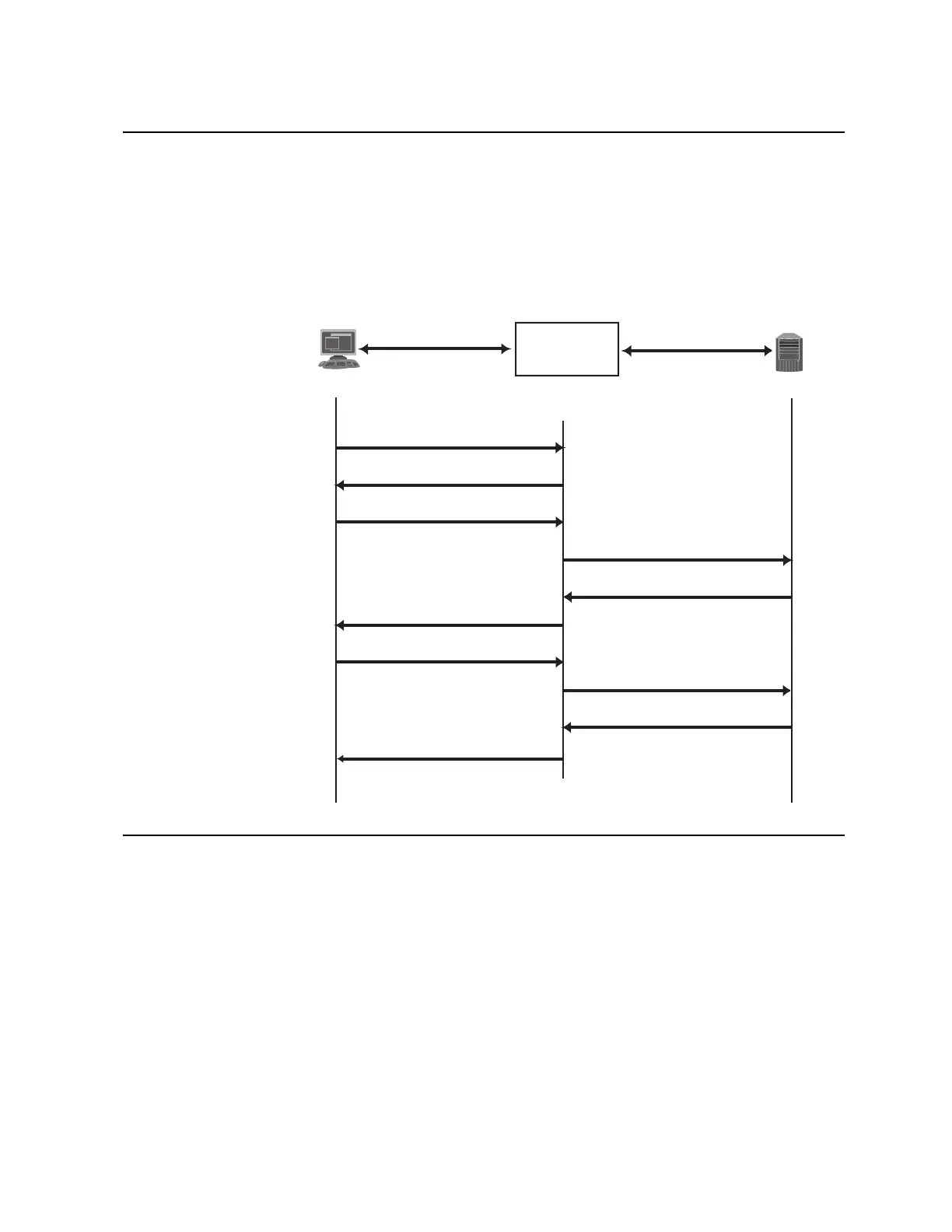
called EAP over LAN (EAPOL). Figure 1 shows a typical message exchange
initiated by the client.
Figure 1. Authenticating a Port Using EAPoL
EAPoL Message Exchange
During authentication, EAPOL messages are exchanged between the client and the
G8000 authenticator, while RADIUS-EAP messages are exchanged between the
G8000 authenticator and the RADIUS server.
Authentication is initiated by one of the following methods:
•
The G8000 authenticator sends an EAP-Request/Identity packet to the client
•
The client sends an EAPOL-Start frame to the G8000 authenticator, which
responds with an EAP-Request/Identity frame.
The client confirms its identity by sending an EAP-Response/Identity frame to the
G8000 authenticator, which forwards the frame encapsulated in a RADIUS packet to
the server.
802.1x Client
RADIUS
Server
Radius-Access-Request
Radius-Access-Challenge
Radius-Access-Request
Radius-Access-Accept
EAP-Request (Credentials)
EAP-Response (Credentials)
EAP-Success
EAP-Request (Credentials)
EAP-Response (Credentials)
EAPOL-Start
Port Authorized
Port Unauthorized
IBM Switch
Authenticator
(RADIUS Client)
EAPOL
Ethernet
RADIUS-EAP
UDP/IP

 Loading...
Loading...