© Copyright IBM Corp. 2011 Chapter 21. Border Gateway Protocol 251
Aggregating Routes
Aggregation is the process of combining several different routes in such a way that
a single route can be advertised, which minimizes the size of the routing table. You
can configure aggregate routes in BGP either by redistributing an aggregate route
into BGP or by creating an aggregate entry in the BGP routing table.
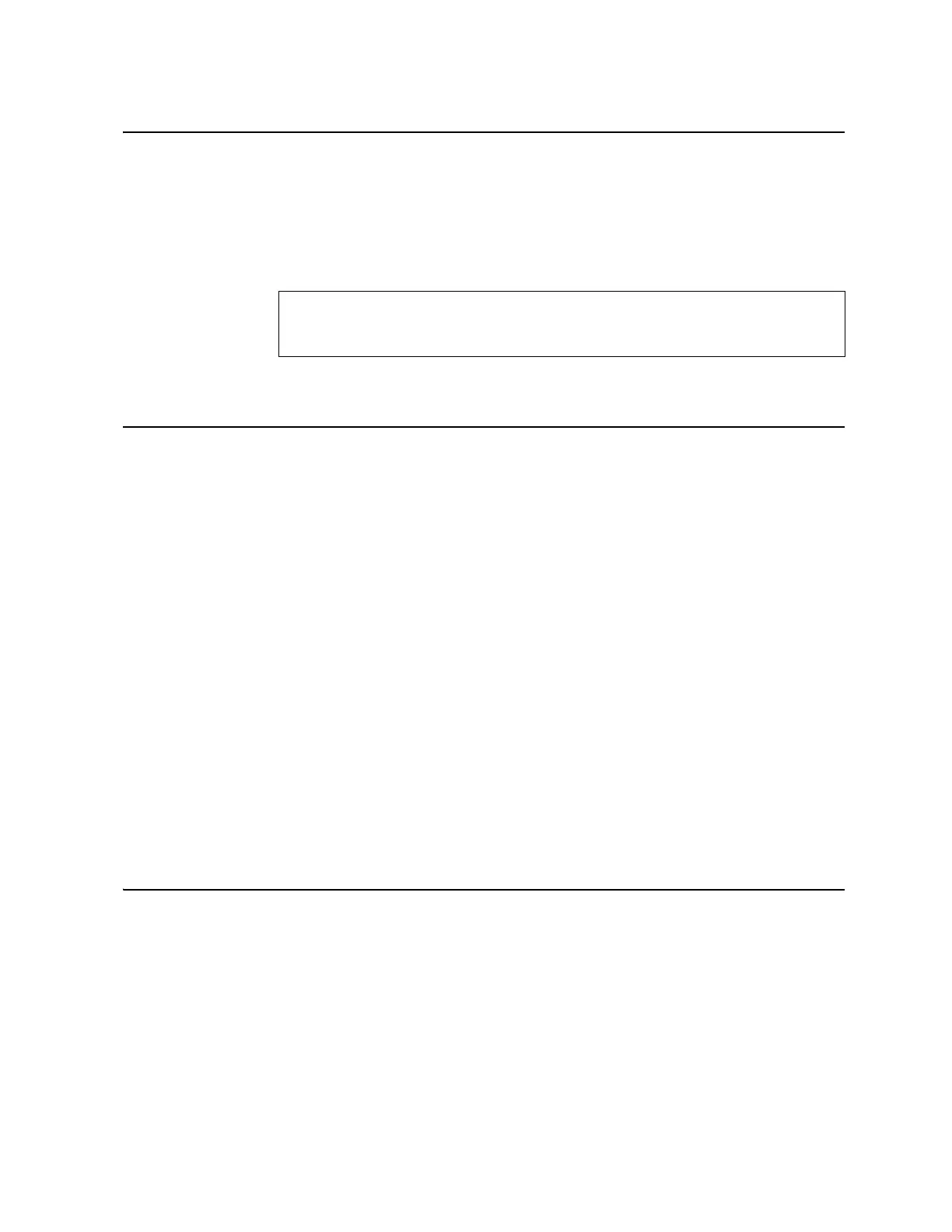
To define an aggregate route in the BGP routing table, use the following commands:
An example of creating a BGP aggregate route is shown in “Default Redistribution
and Route Aggregation Example” on page 254.
Redistributing Routes
In addition to running multiple routing protocols simultaneously, N/OS software can
redistribute information from one routing protocol to another. For example, you can
instruct the switch to use BGP to re-advertise static routes. This applies to all of the
IP-based routing protocols.
You can also conditionally control the redistribution of routes between routing
domains by defining a method known as route maps between the two domains. For
more information on route maps, see “What is a Route Map?” on page 247.
Redistributing routes is another way of providing policy control over whether to
export OSPF routes, fixed routes, and static routes. For an example configuration,
see “Default Redistribution and Route Aggregation Example” on page 254.
Default routes can be configured using the following methods:
• Import
• Originate—The router sends a default route to peers if it does not have any
default routes in its routing table.
• Redistribute—Default routes are either configured through the default gateway
or learned via other protocols and redistributed to peer routers. If the default
routes are from the default gateway, enable the static routes because default
routes from the default gateway are static routes. Similarly, if the routes are
learned from another routing protocol, make sure you enable that protocol for
redistribution.
•None
BGP Attributes
The following two BGP attributes are discussed in this section: Local preference and
metric (Multi-Exit Discriminator).
Local Preference Attribute
When there are multiple paths to the same destination, the local preference attribute
indicates the preferred path. The path with the higher preference is preferred (the
default value of the local preference attribute is 100). Unlike the weight attribute,
which is only relevant to the local router, the local preference attribute is part of the
routing update and is exchanged among routers in the same AS.
>> # router bgp
>> (config-router-bgp)#
aggregate-address <1-16> <IPv4 address> <mask>
>> (config-router-bgp)#
aggregate-address <1-16> enable

 Loading...
Loading...