49
CQM1 Interrupt Functions Section 1-5
The “Z” in “Z-phase” is an abbreviation for “Zero.” It is a signal that shows that
the encoder has completed one cycle.
High-speed Counter Interrupt Count
For high-speed counter 0 interrupts, a comparison table is used instead of a
“count up.” The count check can be carried out by either of the two methods
described below. In the comparison table, comparison conditions (for compar-
ing to the PV) and interrupt routine combinations are saved.
Target value: A maximum of 16 comparison conditions (target val-
ues and count directions) and interrupt routine com-
binations are saved in the comparison table. When
the counter PV and the count direction match the
comparison conditions, then the specified interrupt
routine is executed.
Range comparison: Eight comparison conditions (upper and lower limits)
and interrupt routine combinations are saved in the
comparison table. When the PV is greater than or
equal to the lower limit and less than or equal to the
upper limit, then the specified interrupt routine is exe-
cuted.
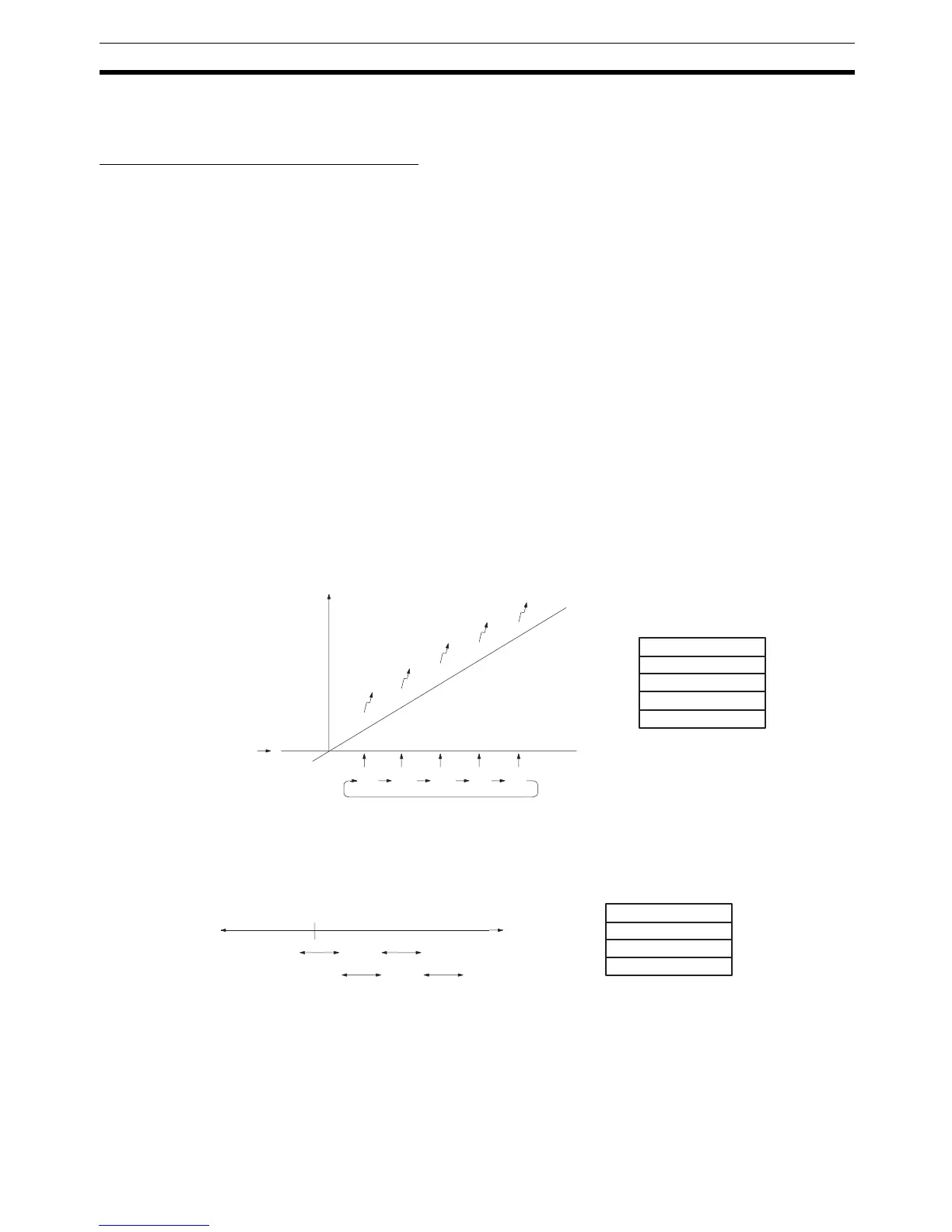
Target Value Comparisons The current count is compared to the target values in the order that target val-
ues are set in the comparison table and interrupts are generated as the count
equals each target value. Once the count has equaled all of the target values
in the table, the target value is set to the first target value in the table, which is
again compared to the current counted until the two values are equal.
Range Comparisons The current count is compared in cyclic fashion to all of the ranges at the
same time and interrupts are generated based on the results of the compari-
sons.
Note When performing target value comparisons, do not repeatedly use the INI
instruction to change the current value of the count and start the comparison
operation. The interrupt operation may not work correctly if the comparison
operation is started immediately after changing the current value from the pro-
gram. (The comparison operation will automatically return to the first target
value once an interrupt has been generated for the last target value. Repeti-
tious operation is thus possible merely by changing the current value.)
Target value 1
Target value 2
Target value 3
Target value 4
Target value 5
Comparison Table
Count
Initial value
Target value
Interrupts
12 3 4 5
Rage setting 1
Rage setting 2
Rage setting 3
Rage setting 4
Comparison Table
Count
13
0
24

 Loading...
Loading...