Description
3.4 Theory of Operation
FUE1010 IP65 NEMA 4X
Operating Instructions, 12/2014, A5E03086491-AC
27
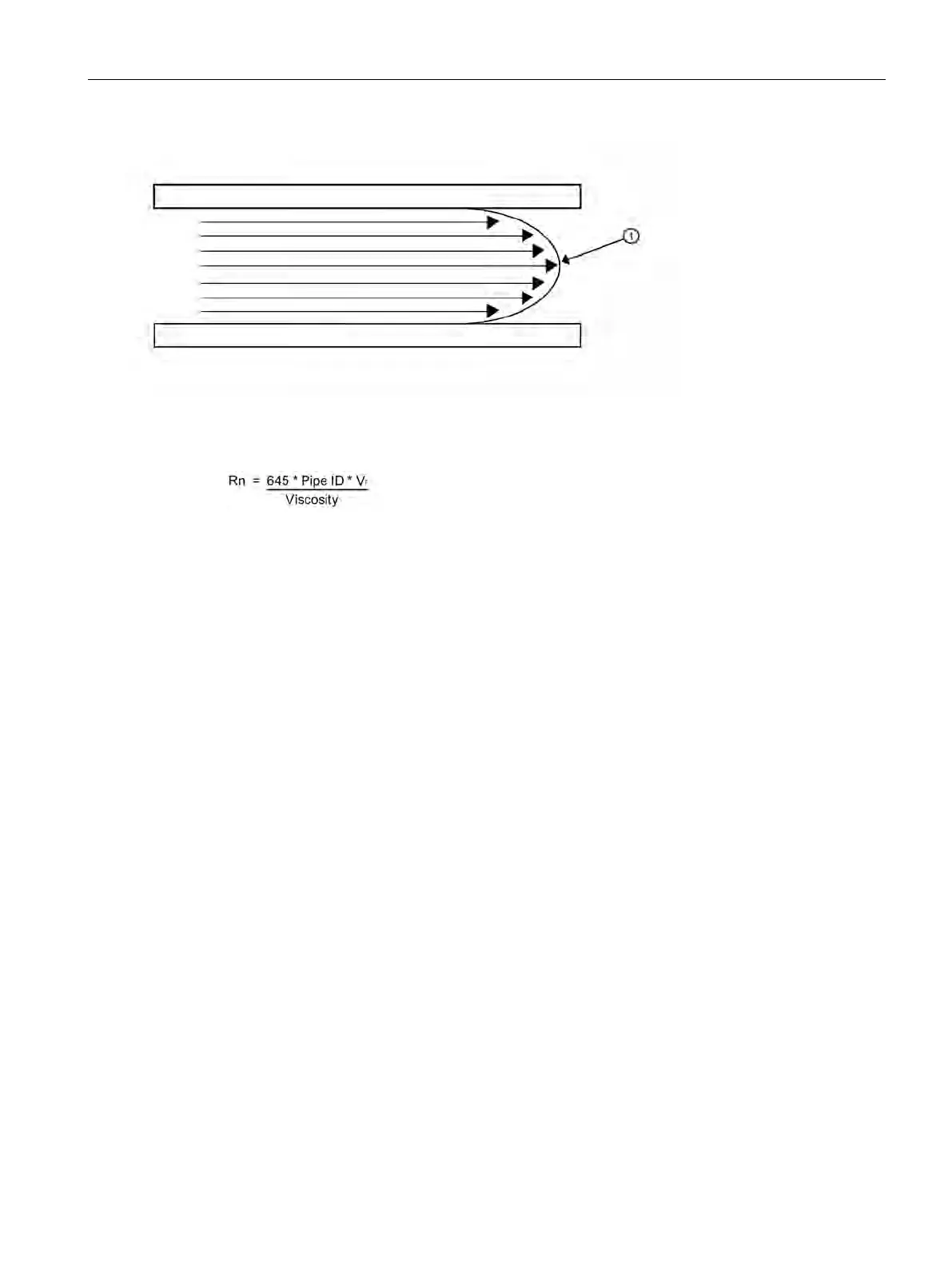
Fluid velocity near the axis of the flow stream tends to be greater.
The Reynolds number is then computed as follows:
where:
viscosity = cS = cP/density
Pipe ID = inches
The flow meter then uses this computation of Reynolds number to compensate the raw flow
velocity for conditions of laminar or turbulent flow profile as defined by an internal Reynolds
compensation table. The flow meter then converts the compensated flow velocity to
volumetric flow rate.
Rate = V
F
* Comp(Rn) * Pipe area
The meter automatically conditions Installation Menu choices to suit the selected meter type.
The following paragraphs introduce the available flow meter types that include:
● 2-Channel
● 2-Path
● Channel 1+2
● Channel 1-2
● Reflexor

 Loading...
Loading...











