Quad-SPI interface (QUADSPI) RM0440
586/2126 RM0440 Rev 4
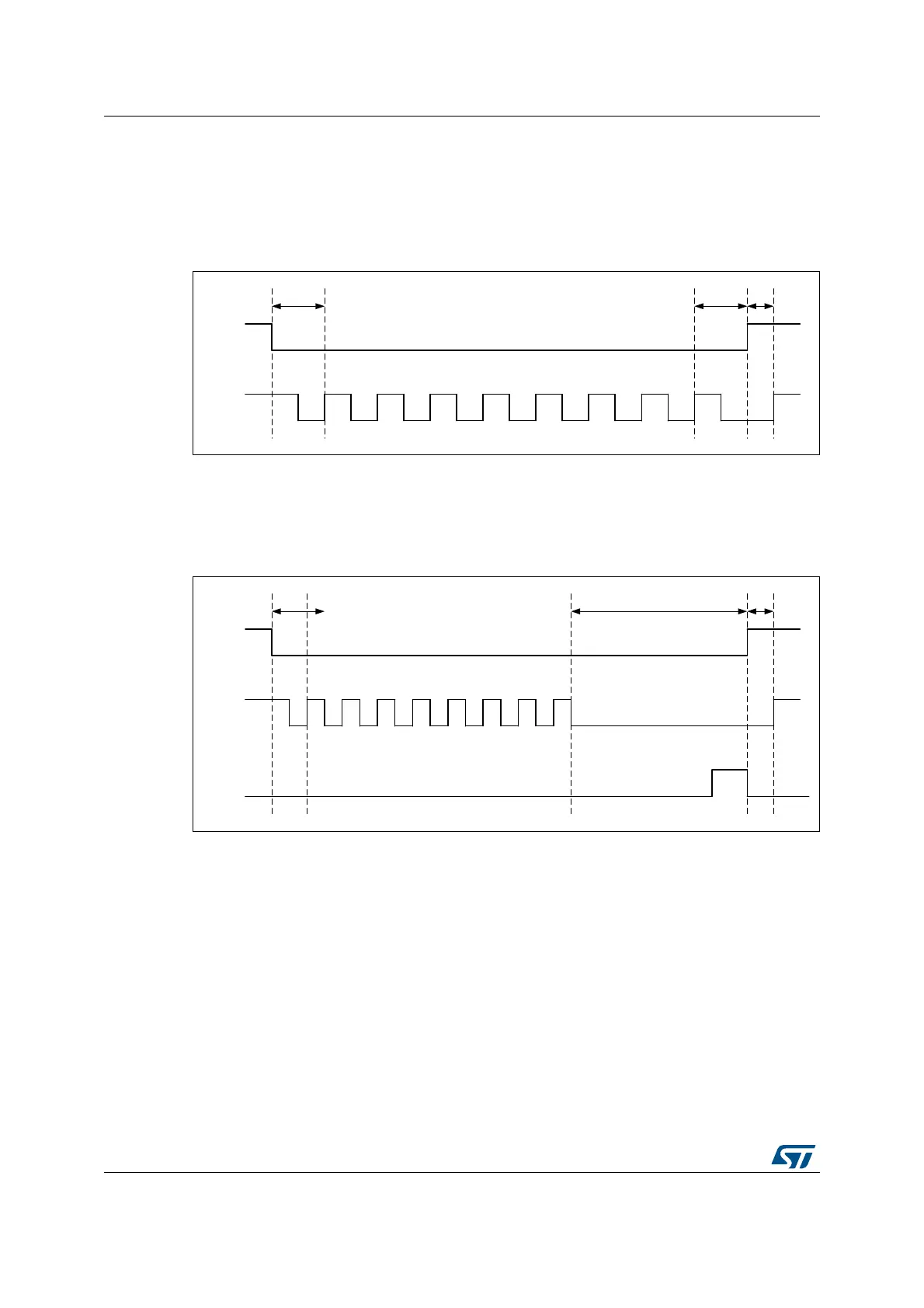
When CKMODE = 1 (“mode3”) and DDRM = 1 (DDR mode), nCS falls one CLK cycle
before an operation first rising CLK edge, and nCS rises one CLK cycle after the operation
final active rising CLK edge, as shown in Figure 80. Because DDR operations must finish
with a falling edge, CLK is low when nCS rises, and CLK rises back up one half of a CLK
cycle afterwards.
Figure 80. nCS when CKMODE = 1 in DDR mode (T = CLK period)
When the FIFO stays full in a read operation or if the FIFO stays empty in a write operation,
the operation stalls and CLK stays low until firmware services the FIFO. If an abort occurs
when an operation is stalled, nCS rises just after the abort is requested and then CLK rises
one half of a CLK cycle later, as shown in Figure 81.
Figure 81. nCS when CKMODE = 1 with an abort (T = CLK period)
When not in dual-flash mode (DFM = 0) and FSEL = 0 (default value), only FLASH 1 is
accessed and thus BK2_nCS stays high, if FSEL = 1, only FLASH 2 is accessed and
BK1_nCS stays high. In dual-flash mode, BK2_nCS behaves exactly the same as
BK1_nCS. Thus, if there is a FLASH 2 and if the application is dual-flash mode only, then
BK1_nCS signal can be used for FLASH 2 as well, and the pin devoted to BK2_nCS can be
used for other functions.
MS35322V1
nCS
SCLK
Clock stalledT T/2
Abort

 Loading...
Loading...